25.6 Reactions of Esters
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify and describe the substances from which most esters are prepared.
- Describe the typical reaction that takes place with esters.
- Identify the products of an acidic hydrolysis of an ester.
- Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester.
Preparation of Esters
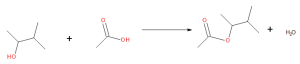
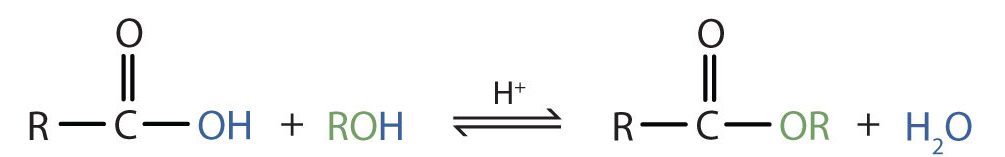
Some esters can be prepared by esterification, a reaction in which a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, heated in the presence of a mineral acid catalyst, form an ester and water (Figure 25.6a.).
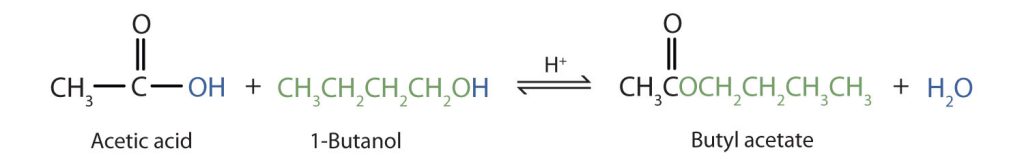
The reaction is reversible. As a specific example of an esterification reaction, butyl acetate can be made from acetic acid and 1-butanol (Figure 25.6b.).
Exercise 25.6a
What is the major product when the following reaction occurs?
Check Your Answer:[1]
Source: Exercise 25.6a by Samantha Sullivan Sauer, drawn using Biovia Draw, CC BY-NC 4.0
The video below outlines the basic structure of esters as well as examining how they are formed. Watch GCSE Chemistry – Esters #59 On YouTube (2 mins)
Video Source: GCSE Chemistry. (2020, March 26). GCSE Chemistry – Esters #59 (youtube.com) [Video]. YouTube.
Reactions of Esters
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (OR′) group of an ester is replaced by another group. One such reaction is hydrolysis, literally “splitting with water.” The hydrolysis of esters is catalyzed by either an acid or a base.
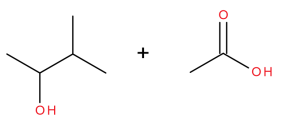
Acidic hydrolysis is simply the reverse of esterification. The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid catalyst (Figure 25.6c.). Like esterification, the reaction is reversible and does not go to completion.
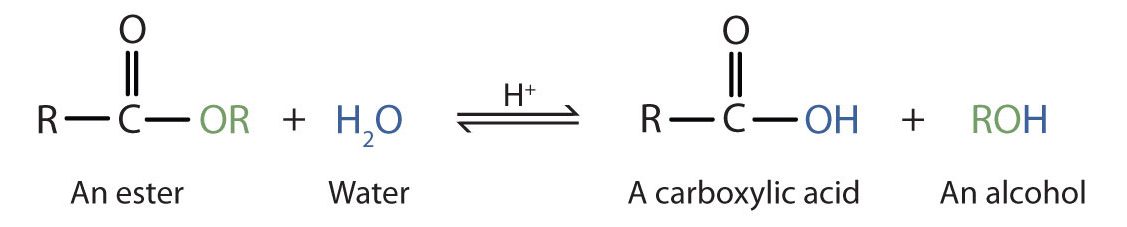
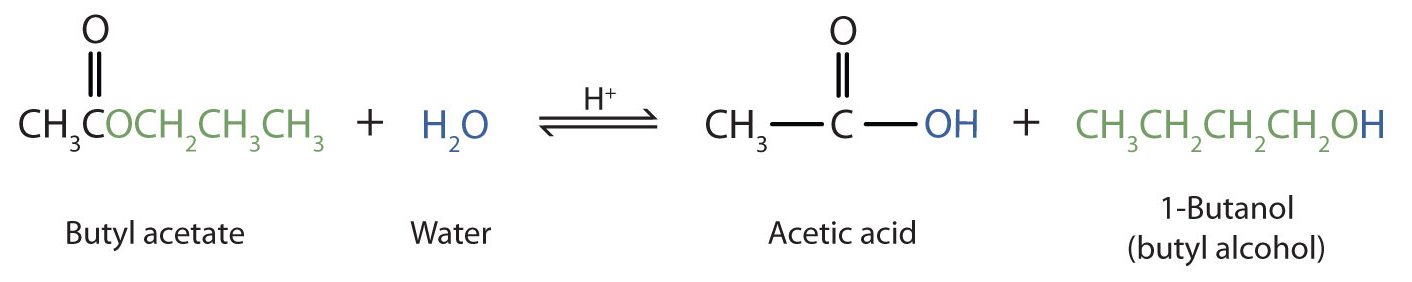
As a specific example, butyl acetate and water react to form acetic acid and 1-butanol (Figure 25.6d.). The reaction is reversible and does not go to completion.
Links to Enhanced Learning
For more detailed hydrolysis reactions involving esters click on the video link below.
Example 25.6a
Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of ethyl butyrate (CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3) and name the products.
Solution
Remember that in acidic hydrolysis, water (HOH) splits the ester bond. The H of HOH joins to the oxygen atom in the OR part of the original ester, and the OH of HOH joins to the carbonyl carbon atom. The products are butyric acid (butanoic acid) and ethanol.
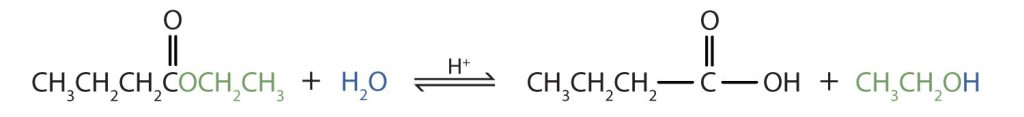
Exercise 25.6b
Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of methyl butanoate and name the products.
Check Your Answer[2]
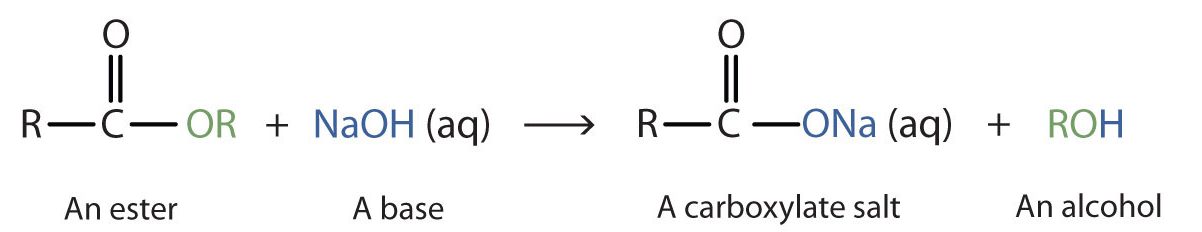
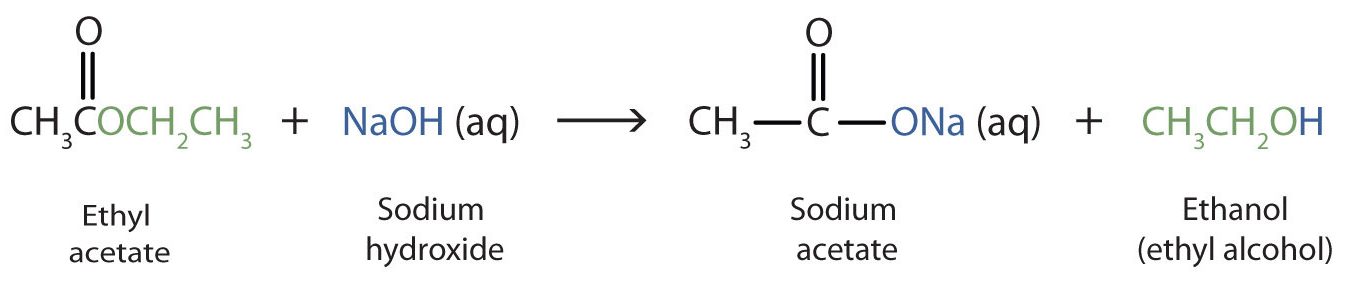
When a base (such as sodium hydroxide [NaOH] or potassium hydroxide [KOH]) is used to hydrolyze an ester, the products are a carboxylate salt and an alcohol (Figure 25.6f.). Because soaps are prepared by the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils, alkaline hydrolysis of esters is called saponification (Latin sapon, meaning “soap,” and facere, meaning “to make”). In a saponification reaction, the base is a reactant, not simply a catalyst. The reaction goes to completion:
As a specific example, ethyl acetate and NaOH react to form sodium acetate and ethanol (Figure 25.6g.).
Example 25.6b
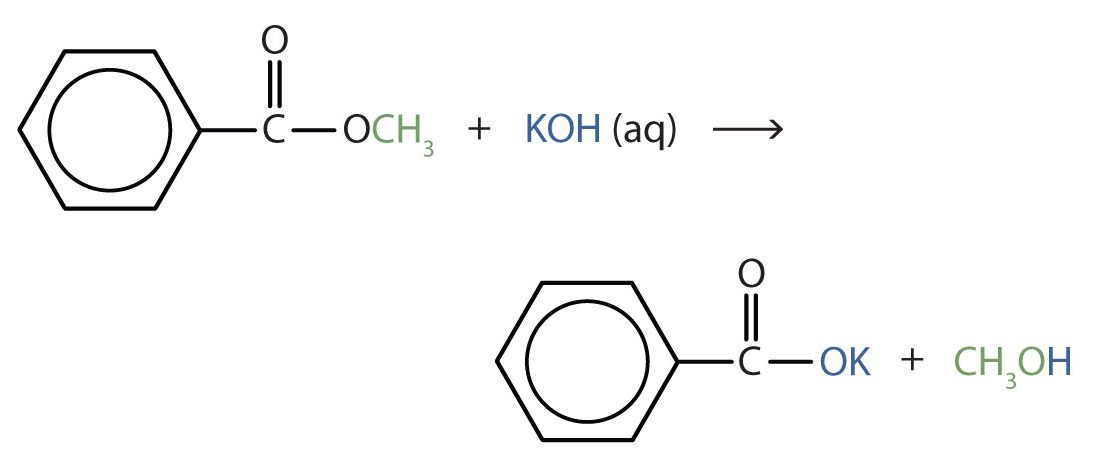
Write an equation for the hydrolysis of methyl benzoate in a potassium hydroxide solution.
Solution
In basic hydrolysis, the molecule of the base splits the ester linkage. The acid portion of the ester ends up as the salt of the acid (in this case, the potassium salt). The alcohol portion of the ester ends up as the free alcohol.
Exercise 25.6c
Write the equation for the hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate in a sodium hydroxide solution.
Check Your Answer[3]
Spotlight on Everyday Chemistry: Soap and Stains

Household soaps such as, hand soap, bar soap, dish soap and shampoo are among some of the common personal items we use on a daily basis. The modern processes for creating these hygiene products, include the use of methyl esters as a key ingredient. Methyl esters are fatty acids which have important physical and chemical properties such as excellent solubility and lubricity. They are also sustainable and biodegradable which make them great components of cleaning products. These esters are derived from natural products such as vegetable oil or animal fats which are heated with a base (such as sodium hydroxide), hydrolyzed to form a salt of the carboxylic acid and eventually used in soap production (Cremer North America, 2022). For more information about soap production and the variety of hygiene products we produce and use everyday, visit Compound Interest: Soaps versus body wash – in C&EN [New tab].
Soy methyl esters commonly found in eco-friendly stain removers can be combined with natural essential oils to effectively clean fabrics and are commonly used in natural or eco-friendly laundry products. For more information on stain removal see Compound Interest: The Chemistry of Stain Removal [New tab].
Not all laundry soaps are created equal and laundry pods tend to be far more concentrated in chemical components than regular liquid detergents. Higher concentrations of alcohols and esters within these cleaning solutions caused them to be highly alkaline which can lead to chemical burns if ingested. For more information on laundry pods and the dangers of ingestion see, Compound Interest: The chemistry behind why you shouldn’t eat laundry pods [New tab].
Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, this page is adapted by Caryn Fahey from
- “15.7: Preparation of Esters” & “15.8: Hydrolysis of Esters” In Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (Ball et al.) by David W. Ball, John W. Hill, and Rhonda J. Scott via LibreTexts, CC BY-NC-SA 4.0./ A LibreTexts version of Introduction to Chemistry: GOB (v. 1.0), CC BY-NC 3.0.
References cited in-text
Cremer North America. (2022, July 6). How methyl esters play a key role in making soap.
The process of combining an organic acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water.
hydrolysis of esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols in a basic solution.