Chapter 25 – Review
25.1 Carboxylic Acids – Structure and Naming
- Give IUPAC names for the following substances:
-
(credit: Organic Chemistry (OpenStax), CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Check answer[1]
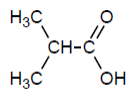 Check answer[2]
Check answer[2]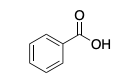 Check answer[3]
Check answer[3]-
(credit: Organic Chemistry (OpenStax) CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Check answer[4]
-
(credit: Organic Chemistry (OpenStax), CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Check answer[5]
-
(credit: Organic Chemistry (OpenStax), CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) Check answer[6]
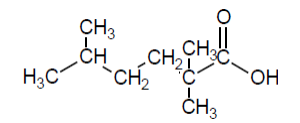 Check answer[7]
Check answer[7]
-
- Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
25.2 Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
- Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that have long hydrocarbon chains attached to a carboxylate group. How does a saturated fatty acid differ from an unsaturated fatty acid? How are they similar? Check answer[13]
- What carboxylic acid is responsible for the pain of an ant sting? Check answer[14]
- What carboxylic acid is found in vinegar? Check answer[15]
25.3 Formation and Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
- Write the balance chemical equation for the dissociation of propanoic acid in water. Check answer[16]
- Write the balanced equations for each of the following reactions;
- ethanol reacts with propionic acid
- benzoic acid, C6H5CO2H, is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide
25.4 Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids – Ionization and Neutralization
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the neutralization of propanoic acid with sodium hydroxide. Check answer[17]
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of each of the following carboxylic acids with NaOH:
25.5 Esters – Structure, Properties and Naming
- Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester formed when each of the following reacts with methyl alcohol:
- Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following:
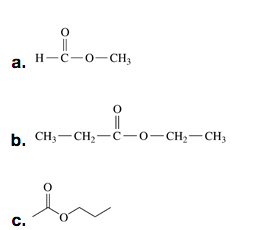
Check answer[22]
25.6 Reactions of Esters
- How do acidic hydrolysis and basic hydrolysis of an ester differ in terms of products obtained? Check answer[23] And the extent of reaction? Check answer[24]
- An ester that has the smell of pineapple can be synthesized from butanoic acid and methanol. Write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of this ester. Check answer[25]
- Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of ethyl butyrate (CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3) and name the products. Check answer [26]
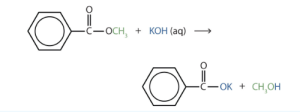
- Write an equation for the hydrolysis of methyl benzoate in a potassium hydroxide solution. Check answer[27]
Links to Enhanced Learning
Create your own organic nomenclature quiz to identify, name and draw carboxylic acids and esters using Organic Nomenclature [New tab]. You can customize the types of questions you receive and get instant feedback. Khan Academy [New tab] reviews Carboxylic Acids [New tab]
Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, this page (including images in solutions) is adapted by Caryn Fahey from:
- “Naming Carboxylic Acids Derivatives” In Organic Chemistry by John McMurray, CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Access for free at Organic Chemistry (OpenStax)
- “18.3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters” In General Chemistry 1 & 2 by Rice University, a derivative of Chemistry (Open Stax) by Paul Flowers, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley & William R. Robinson and is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at Chemistry (OpenStax)
- Images that are not marked otherwise are adapted from course materials by Caryn Fahey and JR van Haarlem
- Images in solutions are from the original source, except:
- 25.6 Question 3, 4: Intro Chem: GOB (V. 1.0)., CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
- 4-Methylpentanoyl chloride ↵
- 2-methylpropanoic acid ↵
- benzoic acid ↵
- Isopropyl 2-methylpropanoate ↵
- Benzoic anhydride ↵
- Isopropyl cyclopentanecarboxylate ↵
- 2,2,5-trimethylhexanoic acid ↵
-
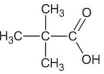 ↵
↵ -
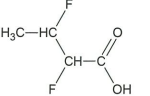 ↵
↵ -
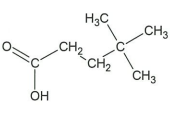 ↵
↵ - C6H5CO2C6H5 ↵
- (CH3)2CHCH2CH(CH3)COCl ↵
- Since they are both carboxylic acids, they each contain the –COOH functional group and its characteristics. The difference is the hydrocarbon chain in a saturated fatty acid contains no double or triple bonds, whereas the hydrocarbon chain in an unsaturated fatty acid contains one or more multiple bonds. ↵
- formic acid ↵
- acetic acid ↵
- The dissociation of propanoic acid produces a carboxylate ion and a hydronium ion. ↵
- A chemical equation for the neutralization of a carboxylic acid includes the reactants, a carboxylic acid and a base, and the products, a carboxylate salt and water. ↵
- HCOOH + NaOH = HCOONa +H2O ↵
- C3H5ClO2 + NaOH = C3H4ClO2 + Na+ + H2O ↵
- CH3COOH + CH3OH = C3H6O2 ↵
- CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH + CH3OH = C6H12O2 ↵
- a. Acetic acid or ethanoic acid (IUPAC), b. ethyl propanoate, c. propyl ethanoate ↵
- acidic hydrolysis: carboxylic acid + alcohol; basic hydrolysis: carboxylate salt + alcohol ↵
- basic hydrolysis: completion; acidic hydrolysis: incomplete reaction ↵
- The ester formed is methyl butanoate. It has a fruity pineapple smell. Reaction: CH3CH2CH2COOH + CH3OH=CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 ↵
- The products are butyric acid (butanoic acid) and ethanol.
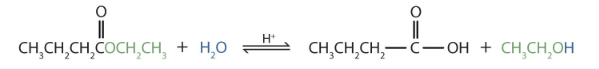 ↵
↵ - In basic hydrolysis, the molecule of the base splits the ester linkage. The acid portion of the ester ends up as the salt of the acid (in this case, the potassium salt). The alcohol portion of the ester ends up as the free alcohol.
 ↵
↵

