Appendix I | Ionization Constants of Weak Bases
|
Ionization Constants of Weak Bases |
|||
|
Base |
Formula |
Kb at 25°C |
Lewis Structure1 |
|
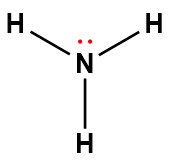
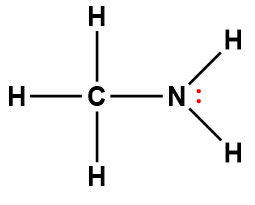
ammonia |
NH3 |
1.8 × 10-5 |
|
|
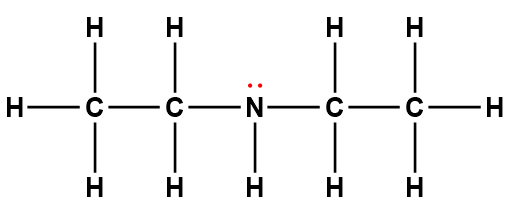
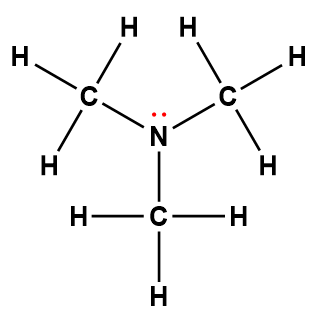
diethylamine |
(C2H5)2NH |
6.9 × 10-4 |
|
|
dimethylamine |
(CH3)2NH |
5.4 × 10-4 |
|
|
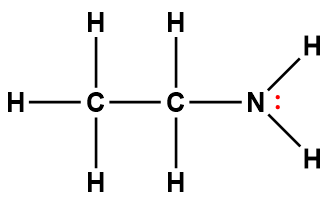
ethylamine |
C2H5NH2 |
4.5 × 10-4 |
|
|
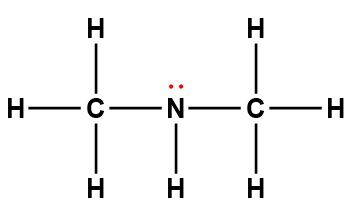
methylamine |
CH3NH2 |
4.6 × 10-4 |
|
|
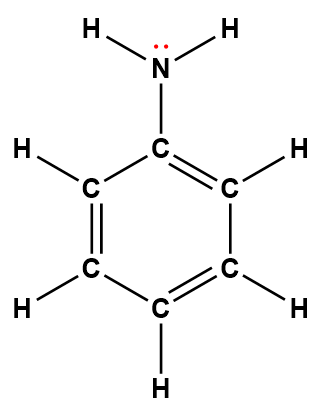
phenylamine (aniline) |
C6H5NH2 |
7.4 × 10-10 |
|
|
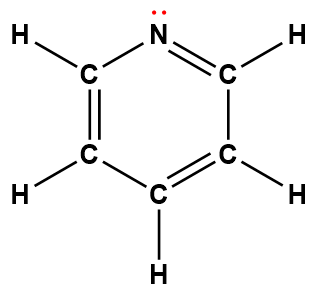
pyridine |
C5H5N |
1.7 × 10-9 |
|
|
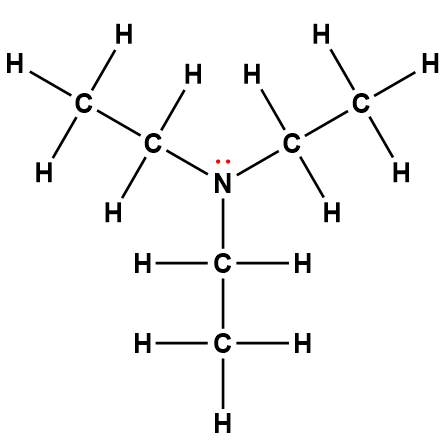
triethylamine |
(C2H5)3N |
5.6 × 10-4 |
|
|
trimethylamine |
(CH3)3N |
6.3 × 10-5 |
|
1Electrons indicated in red participate in accepting a proton from an acid in an acid-base reaction.
REFERENCES
1. “Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases” in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100th Edition (Internet Version 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.
2. “Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases” in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100th Edition (Internet Version 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.