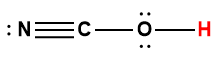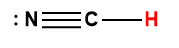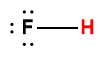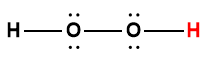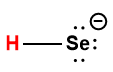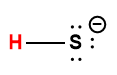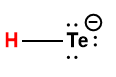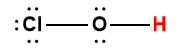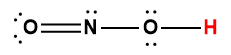Appendix H | Ionization Constants of Weak Acids
|
Ionization Constants of Weak Acids |
|||
|
Acid |
Formula |
Ka at 25°C |
Lewis Structure1 |
|
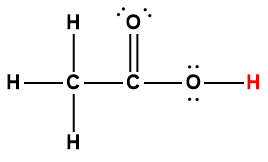
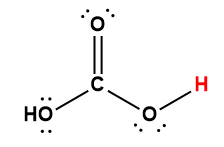
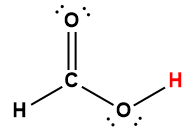
acetic |
CH3COOH |
1.75 × 10-5 |
|
|
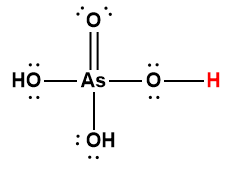
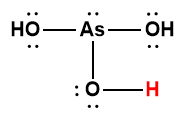
arsenic |
H3AsO4 |
5.5 × 10-3 |
|
|
|
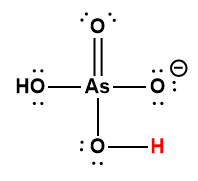
H2AsO4– |
1.7 × 10-7 |
|
|
|
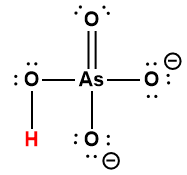
HAsO42- |
5.1 × 10-12 |
|
|
arsenous |
H3AsO3 |
5.1 × 10-10 |
|
|
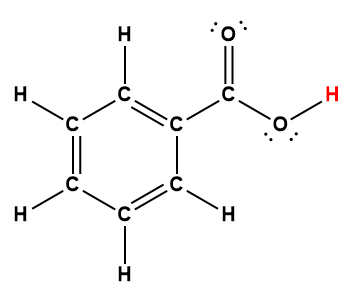
benzoic |
C6H5COOH |
6.25 × 10-5 |
|
|
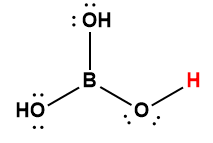
boric |
H3BO3 |
5.4 × 10-10 |
|
|
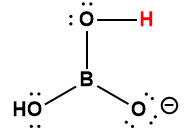
|
H2BO3– |
1 × 10-14 * |
|
|
carbonic |
H2CO3 |
4.5 × 10-7 |
|
|
|
HCO3– |
4.7 × 10-11 |
|
|
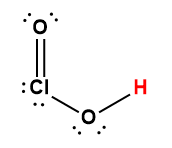
chlorous |
HClO2 |
1.1 × 10-2 |
|
|
cyanic |
HOCN |
3.5 × 10-4 |
|
|
formic |
HCOOH |
1.8 × 10-4 |
|
|
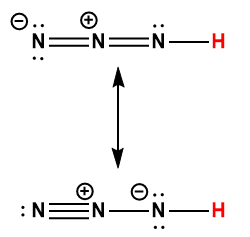
hydrazoic |
HN3 |
2 × 10-5 |
|
|
hydrocyanic |
HCN |
6.2 × 10-10 |
|
|
hydrofluoric |
HF |
6.3 × 10-4 |
|
|
hydrogen peroxide |
H2O2 |
2.4 × 10-12 |
|
|
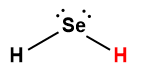
hydrogen selenide |
H2Se |
1.3 × 10-4 |
|
|
|
HSe– |
1.0 × 10-11 |
|
|
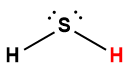
hydrogen sulfide |
H2S |
8.9 × 10-8 |
|
|
|
HS– |
1 × 10-19 |
|
|
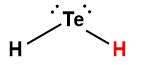
hydrogen telluride |
H2Te |
2 × 10-3 |
|
|
|
HTe– |
1 × 10-11 |
|
|
hypobromous |
HOBr |
2.8 × 10-9 |
|
|
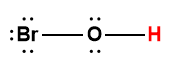
hypochlorous |
HOCl |
4.0 × 10-8 |
|
|
nitrous |
HNO2 |
5.6 × 10-4 |
|
|
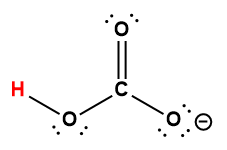
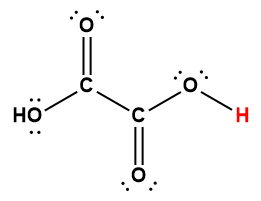
oxalic |
H2C2O4 |
5.6 × 10-2 |
|
|
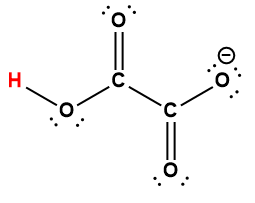
|
HC2O4– |
1.5 × 10-4 |
|
|
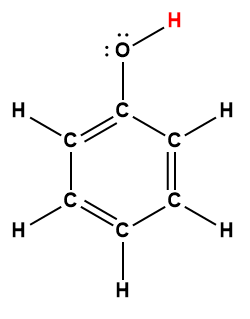
phenol |
C5H5OH |
1.0 × 10-10 |
|
|
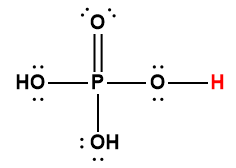
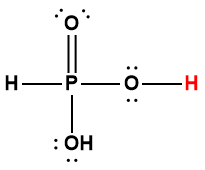
phosphoric |
H3PO4 |
6.9 × 10-3 |
|
|
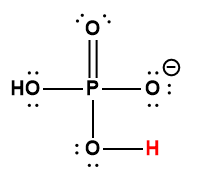
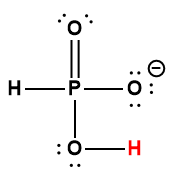
|
H2PO4– |
6.2× 10-8 |
|
|
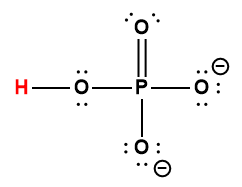
|
HPO42- |
4.8 × 10-13 |
|
|
phosphorous |
H3PO3 |
5 × 10-2 |
|
|
|
H2PO3– |
2.0 × 10-7 |
|
|
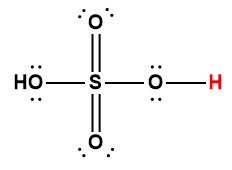
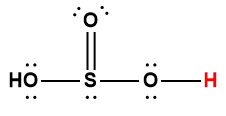
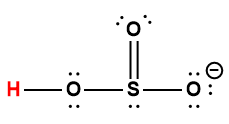
sulfuric |
H2SO4 |
strong acid |
|
|
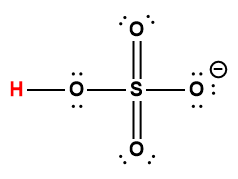
|
HSO4– |
1.0 × 10-2 |
|
|
sulfurous |
H2SO3 |
1.4 × 10-2 |
|
|
|
HSO3– |
6 × 10-8 |
|
1 Hydrogen atom indicated in red represents the donated proton in an acid-base reaction.
* Represents the lower limit value.
REFERENCES
1. “Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases” in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100th Edition (Internet Version 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.
2. “Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases” in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100th Edition (Internet Version 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.