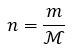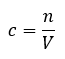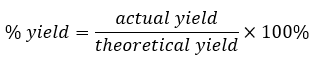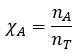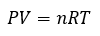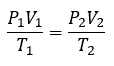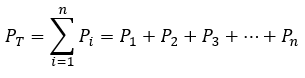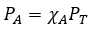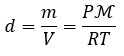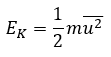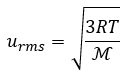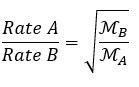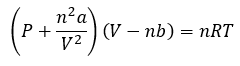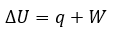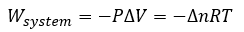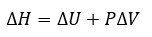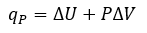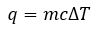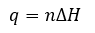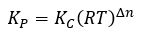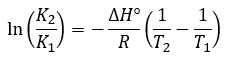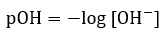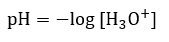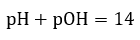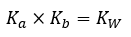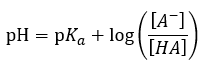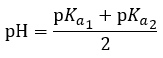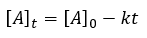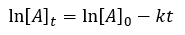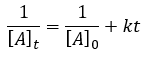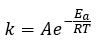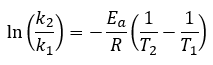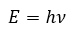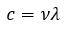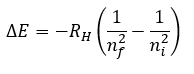Appendix E | Formulas & Fundamental Physical Constants
Key Formulas
General
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gases
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermochemistry
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
|
Acid/Base Equilibria
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chemical Kinetics
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Atomic Structure
|
|
|
|
Fundamental Physical Constants
|
Name and Symbol |
Value |
|
atomic mass unit (amu) |
1.6605390 × 10-27 kg |
|
Avogadro’s number (NA) |
6.0221408 × 1023 mol-1 |
|
Boltzmann’s constant (kB) |
1.380648 × 10-23 J K-1 |
|
charge-to-mass ratio for electron (e/me) |
1.75882002 × 1011 C kg-1 |
|
electron charge (e) |
1.60217662 × 10-19 C |
|
electron rest mass (me) |
9.1093836 × 10-31 kg |
|
Faraday’s constant (F) |
9.6485333 × 104 C mol-1 |
|
gas constant (R) |
8.314460 J mol-1 K-1 |
|
|
8.20573 × 10-2 L atm mol-1 K-1 |
|
|
8.314460 m3 Pa mol-1 K-1 |
|
|
8.314460 L kPa mol-1 K-1 |
|
|
8.314460 × 10-2 bar L mol-1 K-1 |
|
molar volume of an ideal gas, 1 atm, 273.15 K |
22.41396 L mol-1 |
|
molar volume of an ideal gas, 1 bar, 273.15 K |
22.71095 L mol-1 |
|
neutron rest mass (mn) |
1.6749275 × 10-27 kg |
|
Planck’s constant (h) |
6.6260700 × 10-34 J s |
|
proton rest mass (mp) |
1.6726219 × 10-27 kg |
|
Rydberg constant (RH) |
1.0973731568 × 107 m-1 |
|
|
2.1798723 × 10-18 J |
|
speed of light (in vacuum) (c) |
2.99792458 × 108 m s-1 |
Table E.1 Fundamental Physical Constants and their Values
REFERENCE
1. “CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2018” in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100th Edition (Internet Version 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.