7. Microbial Biochemistry
7.3 Lipids
Learning Objectives
Describe the chemical composition of lipids
- Describe the unique characteristics and diverse structures of lipids
- Compare and contrast triacylglycerides (triglycerides) and phospholipids.
- Describe how phospholipids are used to construct biological membranes.
Although they are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, lipid molecules may also contain oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, and phosphorous. Lipids serve numerous and diverse purposes in the structure and functions of organisms. They can be a source of nutrients, a storage form for carbon, energy-storage molecules, or structural components of membranes and hormones. Lipids comprise a broad class of many chemically distinct compounds, the most common of which are discussed in this section.
Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerides
The fatty acids are lipids that contain long-chain hydrocarbons terminated with a carboxylic acid functional group. Because the long hydrocarbon chain, fatty acids are hydrophobic (“water fearing”) or non-polar. Fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains that contain only single bonds are called saturated fatty acids because they have the greatest number of hydrogen atoms possible and are, therefore, “saturated” with hydrogen. Fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains containing at least one double bond are called unsaturated fatty acids because they have fewer hydrogen atoms. Saturated fatty acids have a straight, flexible carbon backbone, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have “kinks” in their carbon skeleton because each double bond causes a rigid bend of the carbon skeleton. These differences in saturated versus unsaturated fatty acid structure result in different properties for the corresponding lipids in which the fatty acids are incorporated. For example, lipids containing saturated fatty acids are solids at room temperature, whereas lipids containing unsaturated fatty acids are liquids.
A triacylglycerol, or triglyceride, is formed when three fatty acids are chemically linked to a glycerol molecule (Figure 7.11). Triglycerides are the primary components of adipose tissue (body fat), and are major constituents of sebum (skin oils). They play an important metabolic role, serving as efficient energy-storage molecules that can provide more than double the caloric content of both carbohydrates and proteins.
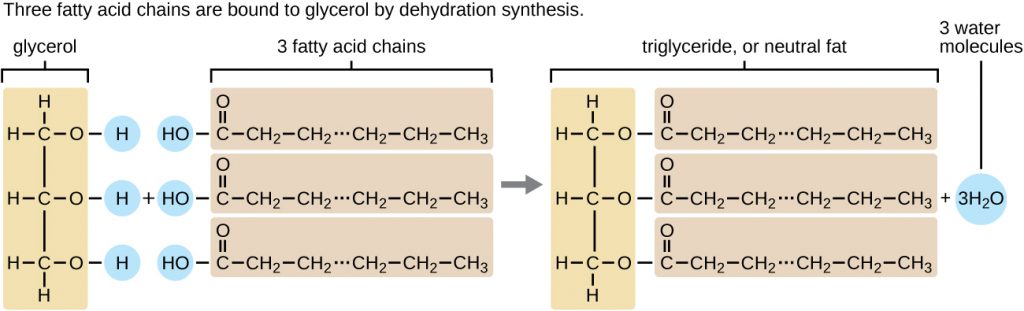
- Explain why fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains that contain only single bonds are called saturated fatty acids.
Phospholipids and Biological Membranes
Triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds: glycerol and fatty acids. In contrast, complex lipids contain at least one additional component, for example, a phosphate group (phospholipids) or a carbohydrate moiety (glycolipids). Figure 7.12 depicts a typical phospholipid composed of two fatty acids linked to glycerol (a diglyceride). The two fatty acid carbon chains may be both saturated, both unsaturated, or one of each. Instead of another fatty acid molecule (as for triglycerides), the third binding position on the glycerol molecule is occupied by a modified phosphate group.
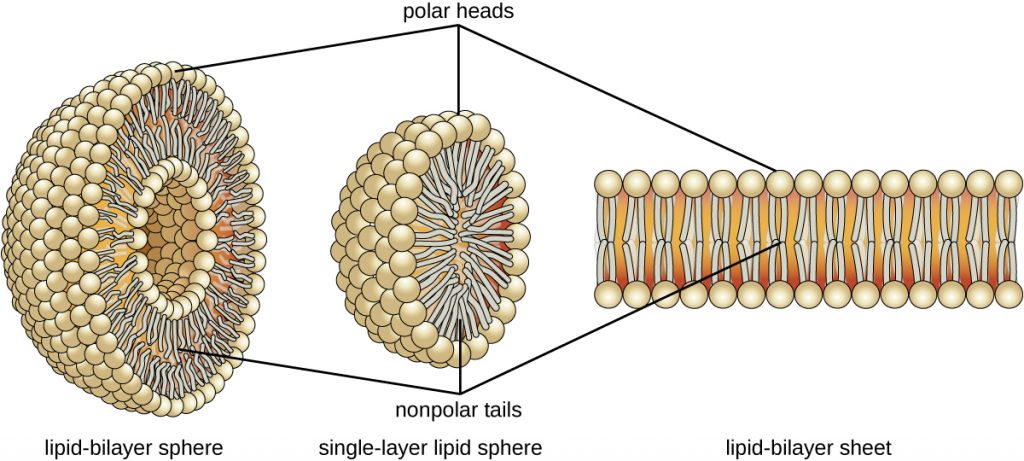
The molecular structure of lipids results in unique behaviour in aqueous environments. Figure 7.11 depicts the structure of a triglyceride. Because all three substituents on the glycerol backbone are long hydrocarbon chains, these compounds are non-polar and not significantly attracted to polar water molecules—they are hydrophobic. Conversely, phospholipids such as the one shown in Figure 7.12 have a negatively charged phosphate group. Because the phosphate is charged, it is capable of strong attraction to water molecules and thus is hydrophilic, or “water loving.” The hydrophilic portion of the phospholipid is often referred to as a polar “head,” and the long hydrocarbon chains as non-polar “tails.” A molecule presenting a hydrophobic portion and a hydrophilic moiety is said to be amphipathic. Notice the “R” designation within the hydrophilic head depicted in Figure 7.12, indicating that a polar head group can be more complex than a simple phosphate moiety. Glycolipids are examples in which carbohydrates are bonded to the lipids’ head groups.
The amphipathic nature of phospholipids enables them to form uniquely functional structures in aqueous environments. As mentioned, the polar heads of these molecules are strongly attracted to water molecules, and the non-polar tails are not. Because of their considerable lengths, these tails are, in fact, strongly attracted to one another. As a result, energetically stable, large-scale assemblies of phospholipid molecules are formed in which the hydrophobic tails congregate within enclosed regions, shielded from contact with water by the polar heads (Figure 7.13). The simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior of phospholipid tails and an outer surface of polar head groups. Larger and more complex structures are created from lipid-bilayer sheets, or unit membranes, which are large, two-dimensional assemblies of phospholipids congregated tail to tail. The cell membranes of nearly all organisms are made from lipid-bilayer sheets, as are the membranes of many intracellular components. These sheets may also form lipid-bilayer spheres that are the structural basis of vesicles and liposomes, sub-cellular components that play a role in numerous physiological functions.
- How is the amphipathic nature of phospholipids significant?
Isoprenoids and Sterols
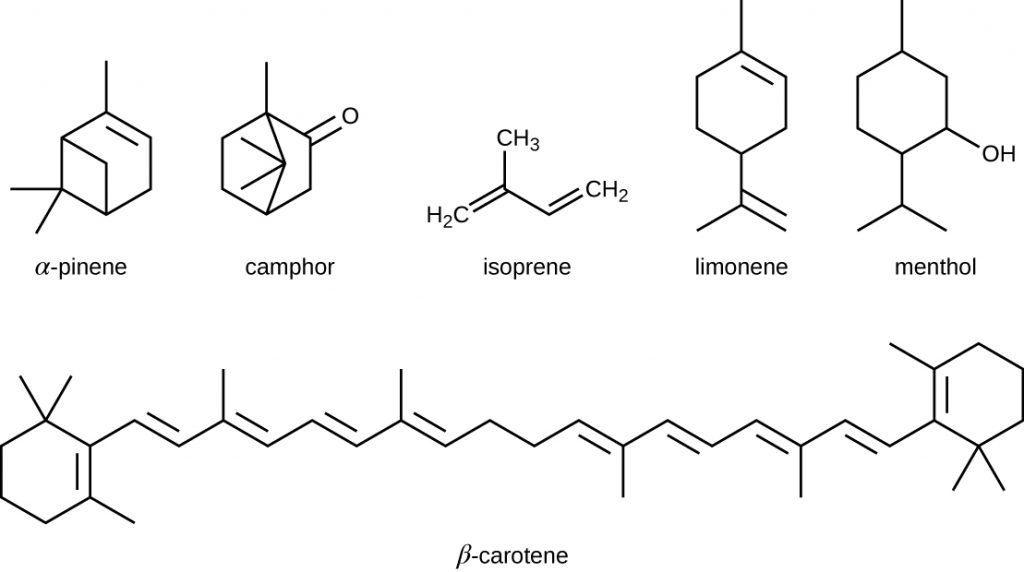
The isoprenoids are branched lipids, also referred to as terpenoids, that are formed by chemical modifications of the isoprene molecule (Figure 7.14). These lipids play a wide variety of physiological roles in plants and animals, with many technological uses as pharmaceuticals (capsaicin), pigments (e.g., orange beta carotene, xanthophylls), and fragrances (e.g., menthol, camphor, limonene [lemon fragrance], and pinene [pine fragrance]). Long-chain isoprenoids are also found in hydrophobic oils and waxes. Waxes are typically water resistant and hard at room temperature, but they soften when heated and liquefy if warmed adequately. In humans, the main wax production occurs within the sebaceous glands of hair follicles in the skin, resulting in a secreted material called sebum, which consists mainly of triacylglycerol, wax esters, and the hydrocarbon squalene. There are many bacteria in the microbiota on the skin that feed on these lipids. One of the most prominent bacteria that feed on lipids is Propionibacterium acnes, which uses the skin’s lipids to generate short-chain fatty acids and is involved in the production of acne.
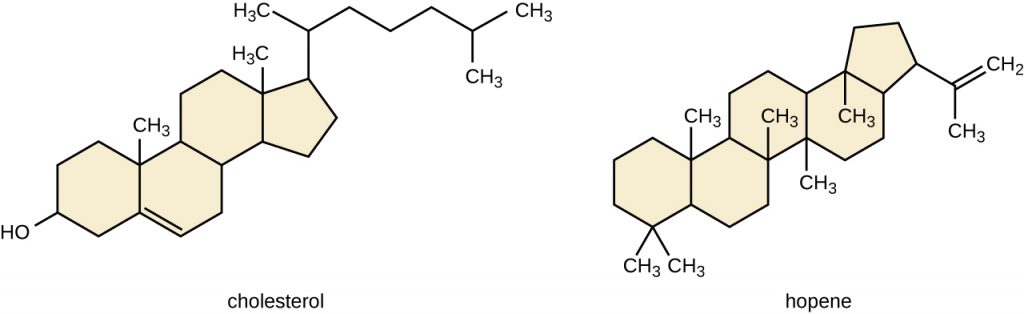
Another type of lipids are steroids, complex, ringed structures that are found in cell membranes; some function as hormones. The most common types of steroids are sterols, which are steroids containing an OH group. These are mainly hydrophobic molecules, but also have hydrophilic hydroxyl groups. The most common sterol found in animal tissues is cholesterol. Its structure consists of four rings with a double bond in one of the rings, and a hydroxyl group at the sterol-defining position. The function of cholesterol is to strengthen cell membranes in eukaryotes and in bacteria without cell walls, such as Mycoplasma. Prokaryotes generally do not produce cholesterol, although bacteria produce similar compounds called hopanoids, which are also multi-ringed structures that strengthen bacterial membranes (Figure 7.15). Fungi and some protozoa produce a similar compound called ergosterol, which strengthens the cell membranes of these organisms.
- How are isoprenoids used in technology?
CLINICAL FOCUS: Part 2
The moisturizing cream prescribed by Penny’s doctor was a topical corticosteroid cream containing hydrocortisone. Hydrocortisone is a synthetic form of cortisol, a corticosteroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands, from cholesterol. When applied directly to the skin, it can reduce inflammation and temporarily relieve minor skin irritations, itching, and rashes by reducing the secretion of histamine, a compound produced by cells of the immune system in response to the presence of pathogens or other foreign substances. Because histamine triggers the body’s inflammatory response, the ability of hydrocortisone to reduce the local production of histamine in the skin effectively suppresses the immune system and helps limit inflammation and accompanying symptoms such as pruritus (itching) and rashes.
- Does the corticosteroid cream treat the cause of Penny’s rash, or just the symptoms?
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
Key Takeaways
- Lipids are composed mainly of carbon and hydrogen, but they can also contain oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, and phosphorous. They provide nutrients for organisms, store carbon and energy, play structural roles in membranes, and function as hormones, pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and pigments.
- Fatty acids are long-chain hydrocarbons with a carboxylic acid functional group. Their relatively long non-polar hydrocarbon chains make them hydrophobic. Fatty acids with no double bonds are saturated; those with double bonds are unsaturated.
- Fatty acids chemically bond to glycerol to form structurally essential lipids such as triglycerides and phospholipids. Triglycerides comprise three fatty acids bonded to glycerol, yielding a hydrophobic molecule. Phospholipids contain both hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains and polar head groups, making them amphipathic and capable of forming uniquely functional large scale structures.
- Biological membranes are large-scale structures based on phospholipid bilayers that provide hydrophilic exterior and interior surfaces suitable for aqueous environments, separated by an intervening hydrophobic layer. These bilayers are the structural basis for cell membranes in most organisms, as well as subcellular components such as vesicles.
- Isoprenoids are lipids derived from isoprene molecules that have many physiological roles and a variety of commercial applications.
- A wax is a long-chain isoprenoid that is typically water resistant; an example of a wax-containing substance is sebum, produced by sebaceous glands in the skin. Steroids are lipids with complex, ringed structures that function as structural components of cell membranes and as hormones. Sterols are a subclass of steroids containing a hydroxyl group at a specific location on one of the molecule’s rings; one example is cholesterol.
- Bacteria produce hopanoids, structurally similar to cholesterol, to strengthen bacterial membranes. Fungi and protozoa produce a strengthening agent called ergosterol.
Multiple Choice
True/False
Fill in the Blank
Short Answer
- Describe the structure of a typical phospholipid. Are these molecules polar or non-polar?
Critical Thinking
- Microorganisms can thrive under many different conditions, including high-temperature environments such as hot springs. To function properly, cell membranes have to be in a fluid state. How do you expect the fatty acid content (saturated versus unsaturated) of bacteria living in high-temperature environments might compare with that of bacteria living in more moderate temperatures?
Media Attributions
- OSC_Microbio_07_03_trygly
- OSC_Microbio_07_03_micelle
- OSC_Microbio_07_03_isoprene
- OSC_Microbio_07_03_sterols
- microbiology sign © Nick Youngson


