12.3. Managerial Decision Making
Decision-making is the action or process of thinking through possible options and selecting one. It is important to recognize that managers are continually making decisions, and that the quality of their decision-making has an impact—sometimes quite significant—on the effectiveness of the organization and its stakeholders. Stakeholders are all the individuals or groups that are affected by an organization (such as customers, employees, shareholders, etc.).
Members of the top management team regularly make decisions that affect the future of the organization and all its stakeholders, such as deciding whether to pursue a new technology or product line. A good decision can enable the organization to thrive and survive long-term, while a poor decision can lead a business into bankruptcy. Managers at lower levels of the organization generally have a smaller impact on the organization’s survival, but can still have a tremendous impact on their department and its workers. Poor decision-making by lower-level managers is unlikely to drive the entire firm out of existence, but it can lead to many adverse outcomes. Therefore, increasing effectiveness in decision making is critical, and using a model can help.
The Decision-Making Process
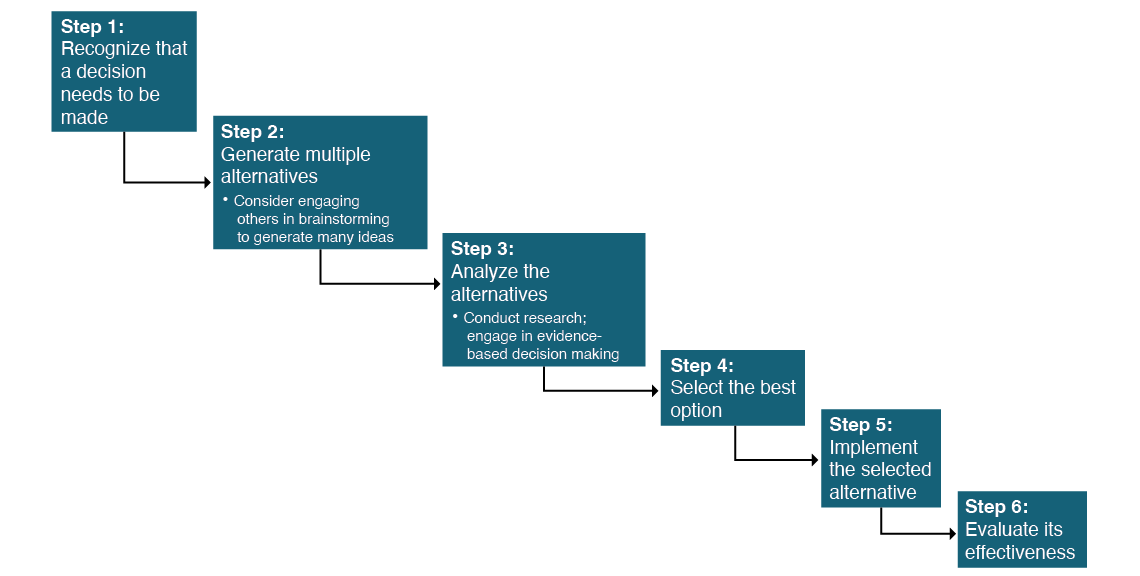
Decision makers should use a systematic process for making decisions. The decision-making process can be broken down into a series of six steps, as follows:
- Recognize that a decision needs to be made.
- Generate multiple alternatives.
- Analyze the alternatives.
- Select an alternative.
- Implement the selected alternative.
- Evaluate its effectiveness.
While these steps may seem straightforward, individuals often skip steps or spend too little time on some steps. In fact, sometimes people will refuse to acknowledge a problem (Step 1) because they aren’t sure how to address it.
“2.1 Overview of Managerial Decision-Making” from Principles of Management by Open Stax is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License

