Annexe I | Constantes d’ionisation des bases faibles
|
Base |
Formule |
Kb à 25 °C |
Structure de Lewis1 |
|
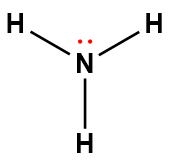
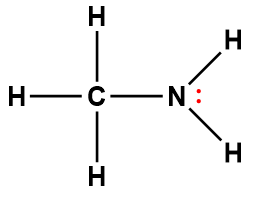
ammoniaque |
NH3 |
1,8 × 10-5 |
|
|
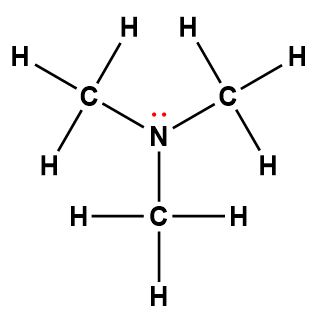
diéthylamine |
(C2H5)2NH |
6,9 × 10-4 |
|
|
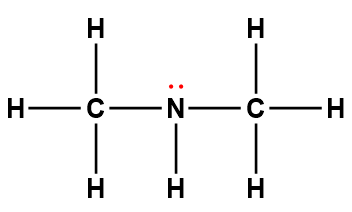
diméthylamine |
(CH3)2NH |
5,4 × 10-4 |
|
|
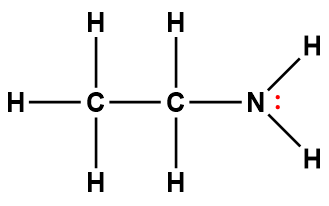
éthylamine |
C2H5NH2 |
4,5 × 10-4 |
|
|
méthylamine |
CH3NH2 |
4,6 × 10-4 |
|
|
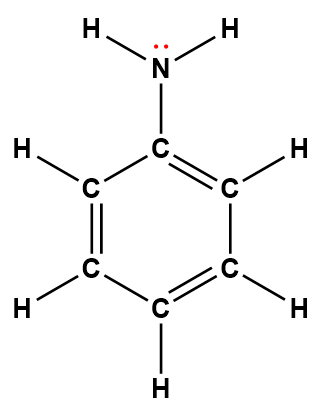
phénylamine (aniline) |
C6H5NH2 |
7,4 × 10-10 |
|
|
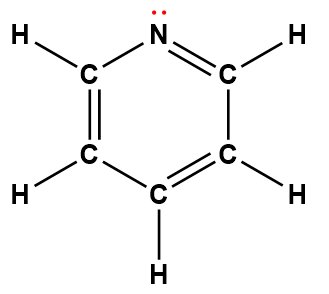
pyridine |
C5H5N |
1,7 × 10-9 |
|
|
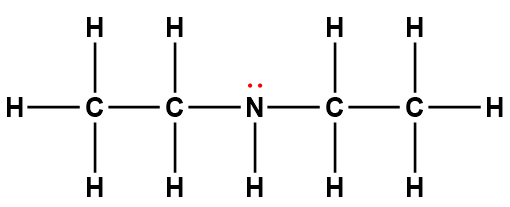
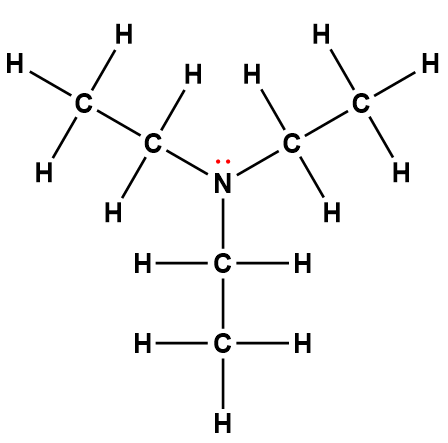
triéthylamine |
(C2H5)3N |
5,6 × 10-4 |
|
|
triméthylamine |
(CH3)3N |
6,3 × 10-5 |
|
1 Les électrons indiqués en rouge participent à l’acceptation d’un proton provenant d’un acide dans une réaction acide-base.
RÉFÉRENCES
1) « Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases » in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100e édition (version Internet 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.
2) « Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases » in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 100e édition (version Internet 2019), John R. Rumble, ed., CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL.