Core mechanics and gameplay
Eamon Slevin
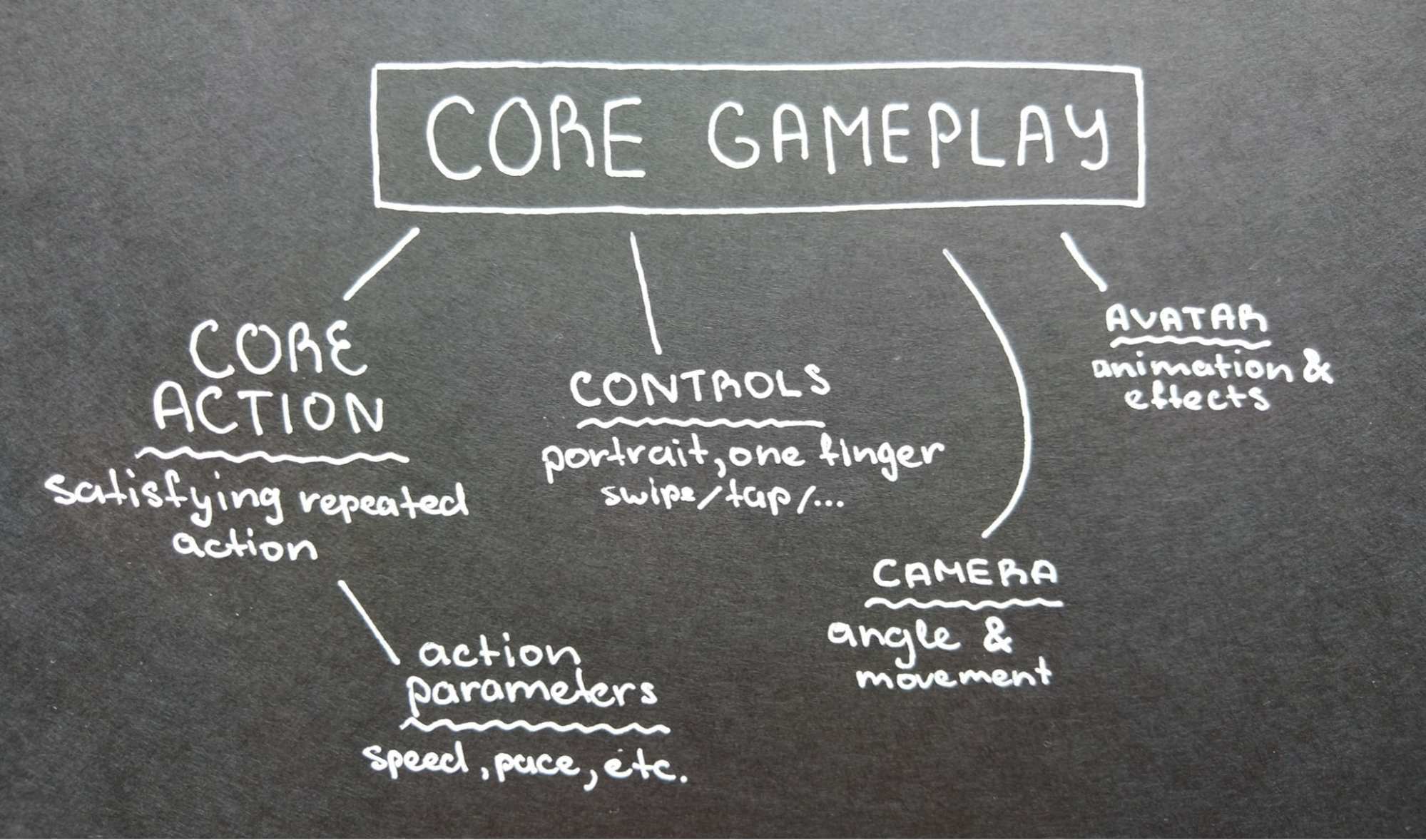
The Core Mechanics and Gameplay of games is the centre stone of what a game is. It is the aspect of the game that engages the player and breaks the game into its own media group of interactive entertainment. The differentiation between a movie and a game is that a movie is told to you through acting and screenplay, while a game is a playable story. The mechanics and gameplay are what creates this interaction within the game, which can be used in many ways to achieve different results and emotions. Studies have shown how proper designing and implementation of core mechanics and gameplay, create promise and improvement towards education within the virtual world. Positives of improvements within the development of core mechanics and gameplay can be seen, but this raises the debate of negatives that have arisen as well over the years. Such negatives include the damaging effects online social interactions can have on people and also the addiction mechanics dynamic. The exploration of educational, comparison, evolutional and addiction mechanics is researched to show its involvement within the core mechanics and gameplay of games.
Educational Aspects of Core Mechanics and Gameplay
The theme of education within gaming is a topic that is tackled all the time, the studies such as (Oberdörfer and Latoschik 2019), which have been researched, show that it can be very effective if the mechanics and gameplay are developed in correlation. Education and gaming are very different and are considered to be on the opposite side to one another when it comes to perspectives on enjoyment and learning, but through research and study, it has been shown that gaming can have great impacts on people’s motivation and learning ability. One way this topic was tackled, was through the mediums of 3D games and virtual reality games. It is said that both can have great impacts on the subjects learning abilities, if the gameplay is designed correctly, furthermore the idea and implementation of virtual reality is said to heighten players motivation and engagement, causing greater learning “In this way, the user study confirms that using VR technology can be beneficial for the overall learning quality of a serious game. This result is supported by the behaviour of the participants. Except for the vr-Group, all other conditions showed some dropouts. The VR-Group, however, even reported having experienced a strong intrinsic motivation to attend every session, thus confirming the measured high learning quality.”(Oberdörfer and Latoschik 2019). The ideas and research taken from these papers could really help to further develop the use of gaming in an educational setting. The ideas expressed within these research papers can show that if developed correctly, games can lead to further and greater learning ability. With the pace of technological growth, virtual reality could play a big part within the educational sector in years to come.
Comparison of Different Core Mechanics and Gameplay
The comparison between games and their core mechanics is a topic that can range from the massively multiplayer online game (MMOs)and their vast community engagement to a single-player game where a player has to tackle the game’s challenges on their own. The core mechanics and gameplay of games differ all the time, evoking unique emotions from the player, from game to game. The comparison made within one of these studies, (Miller, et al., 2019) was how the addition of social aspects can affect a player and their moment to moment gameplay. This was tackled within a 2D platformer game, in which players played the game on their own but also other players played within groups. It was fascinating to see the research proving that players perform differently depending on the addition of social aspects. Players within the single-player game simply didn’t perform as well, as the multiplayer group but then again, the single-player group didn’t suffer from peer pressure and group leader scenarios. “However, an increased presence, flow, and immersion were noticed in scenarios that focused on social groups and dynamics. In particular, competitive, cooperative, or non-interactive (but with shared risk/reward gameplay moments) group cohesion was observed in these scenarios.” (Miller et al., 2019) The idea that real-world scenarios such as peer pressure can develop within the digital world, shows the capacity that the mechanics and gameplay of a game can achieve, bringing real-world dynamics into a digital space.
Evolution of Core Mechanics and Gameplay
Game Evolution is something that is visible to anyone, whether that be someone who plays games or someone who doesn’t. You don’t need to be a person who plays video games, to see the evolution and development of games throughout the past fifty years. One thing that has come a long way that isn’t the graphics of games, is the core mechanics and gameplay of games. A comparison that can be made is the mechanics of the first “Super Mario Bros”, to a newer “Skyrim”. These games are years apart but show the development that has come throughout the years. When looking at the “Super Mario Bros” game, we see that the mechanics range from the player being able to run, jump and collect power-ups These were very innovative for its time, but then we look to the 2011 game “Skyrim”. This game was highly acclaimed and still continues to be played to this day.
One of the things that catapulted the game to success was its innovative gameplay and freedom for the player to do as they chose. The player started the game and gets endless customization for them to choose from, for the look of their character. The player could be whoever they wanted to be and could do whatever they chose. This shows the innovation and development that has been achieved, from a simple Mario game, with simplistic mechanics, to a complex Skyrim world. ”As new technologies emerged, however, players were given more opportunities to meaningfully shape the narrative as developers became more ambitious with storytelling in video games. Coupled with greater degrees of transformation (i.e., identification with an avatar), video games have become an ideal platform for individuals seeking interactive fantasy in a virtual world.” (Kuoet et. al. 2017). Players looking for games with innovative core mechanics and creative gameplay. Gaming has near surpassed the stage of mind-blowing visuals, the attraction for the new players is within the mechanics and core gameplay.
Addiction Mechanics within Core Mechanics and Gameplay
Gaming has always been placed within the bracket of ethical or unethical discussion, due to violence and other issues, but one thing that has been proven to be a huge problem within society is the addiction mechanics of gaming. The idea of violence within gaming has never been proven to be problematic but addiction mechanics has shown and endorsed the development of gambling addiction within the youth. Addiction mechanics have been developed and implemented within games over the years because they have been proven to draw back the player to play some more. There are several ways this has been implemented which have caused many different debates about the idea of gambling within games, being endorsed to children and the overall youth that play these games. “Experience has shown that gamers tend to be more engaged towards achieving a particular goal when they have the sense that they are gradually moving towards it (Lewis-Evans, 2013). Such behaviour is in line with the behaviourist theory of goal-gradient, which predicts that subjects expend more effort as they approach a reward (Kivetz et al.2006).” (Alexiou and Schippers 2018). This is a problem for game developers that have taken the decision to add reward mechanisms and mechanics that players grind towards. These can be manipulated in ways that force the player to spend hours and hours playing to receive that reward they are working towards. This is something that has to be moderated as game developers continue to implement these predatory mechanics for monetary gain.
The loot box mechanic continues to pop up in the gaming news as countries try to debate with these gaming industries about how these can be considered gambling rather than gameplay. This situation has been developing for years and continues to push towards the idea that they’re gambling. Due to monetary gain, they have not been removed from games yet, showing how these industries do not care about the idea of “addiction mechanics” and gaming endorsement. Overall, this idea of addiction mechanics is present within nearly every game developed in the modern-day with the purpose of monetary gain, but in certain situations, these mechanics can be considered unethical and dangerous to the youth they are exposed to.
Conclusion
A game designer has to craft the core mechanics and gameplay of a game in such a way that is ethical but also engaging for the players. This is a challenge that very few get right, as the difference between trying to engage the player and the over implementation of addiction mechanics is a very slim margin. The core mechanics and gameplay of games are what makes the game playable. These can be designed and implemented in many different ways to achieve varied results, from educational aspects to unethical gambling endorsement mechanics. The player has seen the growth of core mechanics and gameplay, from small simplistic games at the start of the gaming industry, to gigantic open world games that are released yearly. Players know what attracts them to a game, and it is clear that it’s within the core mechanics and gameplay that brings them back to play more and more. Game developers are in a power position that should be regulated, so that their games are designed in ethical ways that engage the player, but are not driven by damaging addiction and gambling mechanics.
Check your understanding
- What’s the difference between mechanics and gameplay?
- Name one addiction mechanic?
- Name one social scenario that developed due to multiplayer mechanics?
- Name two things that were heightened within social groups and dynamics?
- Virtual reality mechanics heightens players what?
- Which core mechanics showed greater learning opportunities? 3D or VR mechanics?
Bibliography
Alexiou, A. & Schippers, M.C. (2018) Digital Game Elements, User Experience and Learning: A Conceptual Framework. Education & Information Technologies. 23 (6), pp. 2545.
Kuo, A., Hiler, J.L. & Lutz, R.J. (2017) From Super Mario to Skyrim: A Framework for the Evolution of Video Game Consumption. Journal of Consumer Behaviour. 16 (2), pp. 101-120.
Miller, M., Paige, N., Clair, G. & Eckhardt, C. (2019) An Analysis of Peer Presence Social Group Dynamics to Enhance Player Engagement in Multiplayer Games. 2019 IEEE Conference on Games (CoG), Games (CoG), 2019 IEEE Conference On. pp. 1-8.
Oberdörfer, S. & Latoschik, M.E. (2019) Knowledge Encoding in Game Mechanics: Transfer-Oriented Knowledge Learning in Desktop-3D and VR. International Journal of Computer Games Technology. pp. 1.
Author

Eamon Slevin is a second-year Creative Digital Media student, studying in TUD Blanchardstown. Eamon is an amateur photographer, graphic designer, web designer and movie maker, using his time in college to build a portfolio to be ready to head out to the workforce. He is enjoying his time in TUD Blanchardstown, as it gives him the opportunity to learn and explore different mediums of media, that he hasn’t before. Eamon is a part-time barman that enjoys having a weekend off to head out with his friends. He is really into keeping fit, going out for runs to clear his head and also always up for playing new and interesting games on the PlayStation. One of Eamons favourite things to do is to watch the newest Netflix movie, whether it be great or unwatchable.

