8.4 Profits and Losses in Perfect Competition
The answer depends on the relationship between price and average total cost, which is the average profit or profit margin.
If the market price is higher than the firm’s average cost of production for that quantity produced, then the profit margin is positive and the firm will earn profits. Conversely, if the market price is lower than the average cost of production, the profit margin is negative and the firm will suffer losses. You might think that, in this situation, the firm may want to shut down immediately. Remember, however, that the firm has already paid for fixed costs, such as equipment, so it may continue to produce for a while and incur a loss.
In perspective
Fig 8.8 illustrates the three possible scenarios:
(A) where price intersects marginal cost at a level above the average cost curve,
(B) where price intersects marginal cost at a level equal to the average cost curve, and,
(C) where price intersects marginal cost at a level below the average cost curve.
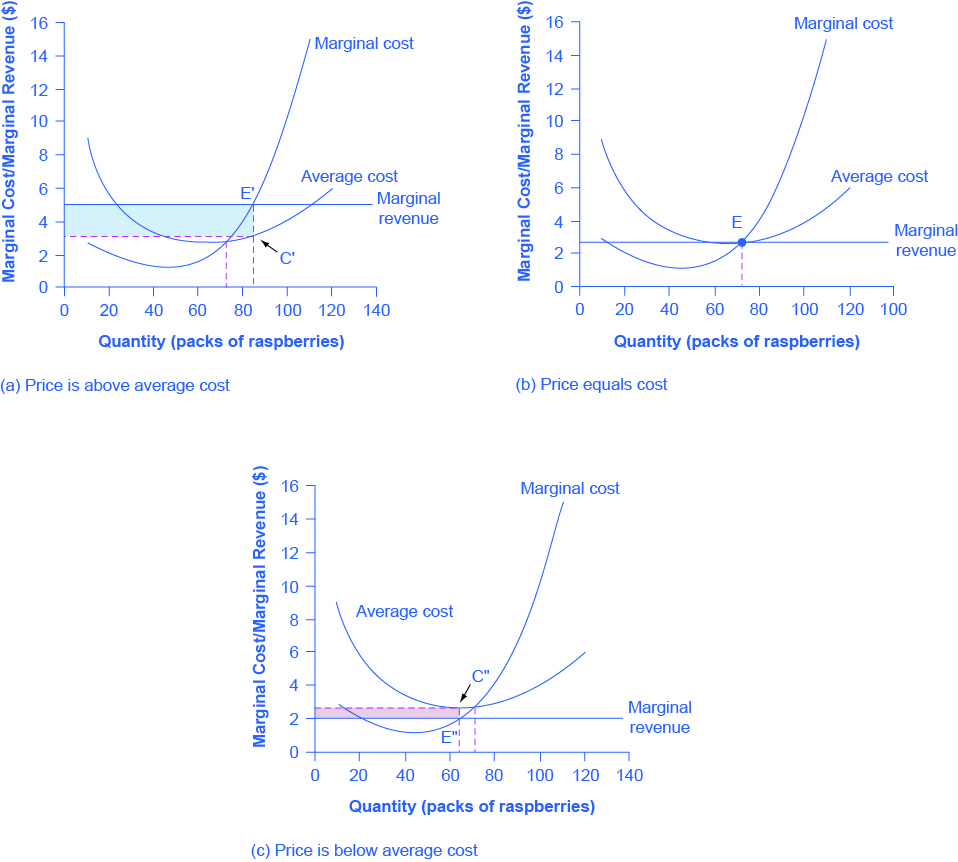
In Fig 8.8 A,
Economic Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost = (5 × 85) − (3.50 × 85) = $127.50
(POSITIVE ECONOMIC PROFIT)
In Fig 8.8 B,
Economic Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost = (2.75 × 75) − (2.75 × 75) = $0
(ZERO ECONOMIC PROFIT)
In Fig 8.8 C,
Economic Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost = (2 × 65) − (2.73 × 65) = − $47.45
(NEGATIVE ECONOMIC PROFIT OR ECONOMIC LOSS)
| If.... | Then... |
|---|---|
| Price > ATC | Firm earns an economic profit |
| Price = ATC | Firm earns zero economic profit |
| Price < ATC | Firm earns a loss |
Fig 8.9
Attribution
“8.2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions” in Principles of Economics 2e by OpenStax is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

