10.3 How a Monopolistic Competitor Chooses Price and Quantity
Monopolistic Competition
To explore monopolistic competition, let’s consider Rogers, one of the Cellular companies in the market. Rogers faces a downward sloping demand curve and has ATC and MC curves similar to the ones we have seen before.
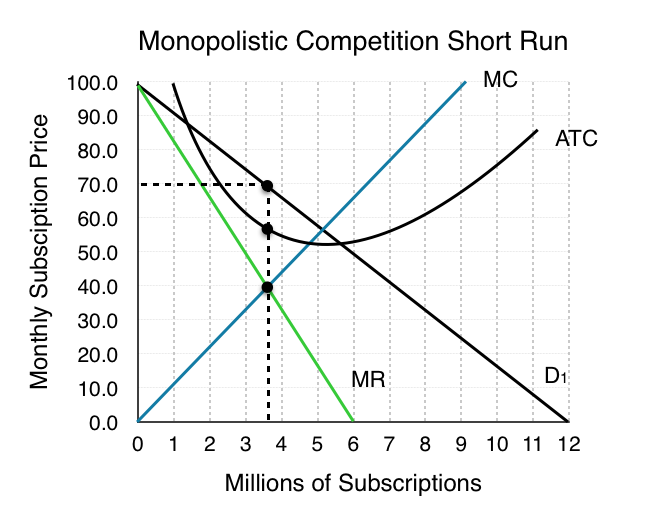
The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Since they face a downward sloping demand curve, the same considerations about how elasticity affects revenue are relevant, and the firm will maximize profits where MR = MC when P > MR. Rogers determines its profit-maximizing level of output. This will occur where MR = MC. MR and MC intersect when Rogers has 3.6 million subscribers.
Rogers decides what price to charge. When the firm has determined its profit-maximizing quantity of output, it will behave like a monopoly and charge the maximum it can at the quantity. On the graph, this process can be shown as a vertical line reaching up through the profit-maximizing quantity until it hits the firm’s perceived demand curve. For Rogers, this occurs at a price of $70/month.
Although the process by which a monopolistic competitor makes decisions about quantity and price is similar to the way in which a monopolist makes such decisions, two differences are worth remembering.
- First, although both a monopolist and a monopolistic competitor face downward-sloping demand curves, the monopolist’s demand curve is the market demand curve, while the perceived demand curve for a monopolistic competitor is based on the extent of its product differentiation and how many competitors it faces.
- Second, a monopolist is surrounded by barriers to entry, but a monopolistic competitor who earns profits must expect the entry of firms with similar, but differentiated, products.
Attribution
“8.4 Monopolistic Competition” in Principles of Microeconomics by Dr. Emma Hutchinson, University of Victoria is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

