1.5 Challenges of Global Marketing
A global company is generally referred to as a multinational corporation (MNC). An MNC is a company that operates in two or more countries, leveraging the global environment to approach varying markets in attaining revenue generation. These international operations are pursued as a result of the strategic potential provided by technological developments, making new markets a more convenient and profitable pursuit both in sourcing production and pursuing growth.
International operations are therefore a direct result of either achieving higher levels of revenue or a lower cost structure within the operations or value-chain. MNC operations often attain economies of scale, through mass producing in external markets at substantially cheaper costs, or economies of scope, through horizontal expansion into new geographic markets. If successful, these both result in positive effects on the income statement (either larger revenues or stronger margins), but contain the innate risk in developing these new opportunities.
Opportunities
As gross domestic product (GDP) growth migrates from mature economies, such as the US and EU member states, to developing economies, such as China and India, it becomes highly relevant to capture growth in higher-growth markets. It is a particularly strong visual representation of the advantages a global corporation stands to capture, where the darker green areas represent where the highest GDP growth potential resides. High growth in the external environment is a strong opportunity for most incumbents in the market.
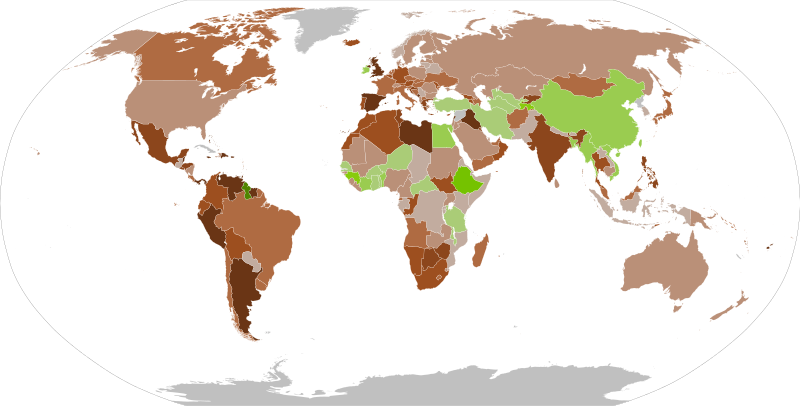
 Fig 1.5 GDP Growth Rate: This map highlights (via dark green) where the strongest growth opportunities currently are as of 2021. “IMF World Economic Outlook January 2021 Real GDP growth rate” by Brobt, CC BY-SA 4.0
Fig 1.5 GDP Growth Rate: This map highlights (via dark green) where the strongest growth opportunities currently are as of 2021. “IMF World Economic Outlook January 2021 Real GDP growth rate” by Brobt, CC BY-SA 4.0Challenges
However, despite the general opportunities a global market provides, there are significant challenges MNCs face in penetrating these markets. These challenges can loosely be defined through four factors:
- Public Relations: Public image and branding are critical components of most businesses. Building this public relations potential in a new geographic region is an enormous challenge, both in effectively localizing the message and in the capital expenditures necessary to create momentum.
- Ethics: Arguably the most substantial of the challenges faced by MNCs, ethics have historically played a dramatic role in the success or failure of global players. For example, Nike had its brand image hugely damaged through utilizing ‘sweat shops’ and low-wage workers in developing countries. Maintaining the highest ethical standards while operating in developing countries is an important consideration for all MNCs.
- Organizational Structure: Another significant hurdle is the ability to efficiently and effectively incorporate new regions within the value chain and corporate structure. International expansion requires enormous capital investments in many cases, along with the development of a specific strategic business unit (SBU) in order to manage these accounts and operations. Finding a way to capture value despite this fixed organizational investment is an important initiative for global corporations.
- Leadership: The final factor worth noting is attaining effective leaders with the appropriate knowledge base to approach a given geographic market. There are differences in strategies and approaches in every geographic location worldwide, and attracting talented managers with high intercultural competence is a critical step in developing an efficient global strategy.
Combining these four challenges for global corporations with the inherent opportunities presented by a global economy, companies are encouraged to chase the opportunities while carefully controlling the risks to capture the optimal amount of value. By effectively maintaining ethics and a strong public image, companies should create strategic business units with strong international leadership in order to capture value in a constantly expanding global market.
Globalization
Opportunities
Those in favour of globalization theorize that a wider array of products, services, technologies, medicines, and knowledge will become available and that these developments will have the potential to reach significantly larger customer bases. This means larger volumes of sales and exchange, larger growth rates in GDP, and more empowerment of individuals and political systems through acquiring additional resources and capital. These benefits of globalization are viewed as utilitarian, providing the best possible benefits for the largest number of people.
Challenges
Along with arguments supporting the benefits of a more globally-connected economy, there are criticisms that question the profits that are captured. Opponents argue that the expansion of global trade creates unfair exchanges between larger and smaller economies, arguing that developed economies capture significantly more value because of financial leverage. Other commonly raised concerns include damage to the environment, decreased food safety, unethical labour practices in sweatshops, increased consumerism, and the weakening of traditional cultural values.
Core Principles of International Marketing – Chapter 1.6 by Babu John Mariadoss is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

