9.6 – Government Policies to Reduce Income Inequality
Learning Objectives
- Explain the arguments for and against government intervention in a market economy
- Identify beneficial ways to reduce the economic inequality in a society
- Show the tradeoff between incentives and income equality
No society should expect or desire complete equality of income at a given point in time, for a number of reasons. First, most workers receive relatively low earnings in their first few jobs, higher earnings as they reach middle age, and then lower earnings after retirement. Thus, a society with people of varying ages will have a certain amount of income inequality. Second, people’s preferences and desires differ. Some are willing to work long hours to have income for large houses, fast cars and computers, luxury vacations, and the ability to support children and grandchildren.
These factors all imply that a snapshot of inequality in a given year does not provide an accurate picture of how people’s incomes rise and fall over time. Even if we expect some degree of economic inequality at any point in time, how much inequality should there be? There is also the difference between income and wealth, as the following Clear It Up feature explains.
Clear It Up
How do you measure wealth versus income inequality?
Income is a flow of money received, often measured on a monthly or an annual basis. Wealth is the sum of the value of all assets, including money in bank accounts, financial investments, a pension fund, and the value of a home. In calculating wealth, one must subtract all debts, such as debt owed on a home mortgage and on credit cards. A retired person, for example, may have relatively little income in a given year, other than a pension or Social Security. However, if that person has saved and invested over time, the person’s accumulated wealth can be quite substantial.
In the United States, the wealth distribution is more unequal than the income distribution, because differences in income can accumulate over time to make even larger differences in wealth. However, we can measure the degree of inequality in the wealth distribution with the same tools we use to measure the inequality in the income distribution, like quintile measurements. Once every three years the Federal Reserve Bank publishes the Survey of Consumer Finance which reports a collection of data on wealth.
Even if they cannot answer the question of how much inequality is too much, economists can still play an important role in spelling out policy options and tradeoffs. If a society decides to reduce the level of economic inequality, it has three main sets of tools: redistribution from those with high incomes to those with low incomes; trying to assure that a ladder of opportunity is widely available; and a tax on inheritance.
Redistribution
Redistribution means taking income from those with higher incomes and providing income to those with lower incomes. Earlier in this chapter, we considered some of the key government policies that provide support for the poor: the welfare program TANF, the earned income tax credit, SNAP, and Medicaid. If a reduction in inequality is desired, these programs could receive additional funding.
The federal income tax, which is a progressive tax system designed in such a way that the rich pay a higher percent in income taxes than the poor funds the programs. Data from household income tax returns in 2009 shows that the top 1% of households had an average income of $1,219,700 per year in pre-tax income and paid an average federal tax rate of 28.9%. The effective income tax, which is total taxes paid divided by total income (all sources of income such as wages, profits, interest, rental income, and government transfers such as veterans’ benefits), was much lower. The effective tax paid by that top 1% of householders paid was 20.4%, while the bottom two quintiles actually paid negative effective income taxes, because of provisions like the earned income tax credit. News stories occasionally report on a high-income person who has managed to pay very little in taxes, but while such individual cases exist, according to the Congressional Budget Office, the typical pattern is that people with higher incomes pay a higher average share of their income in federal income taxes.
Of course, the fact that some degree of redistribution occurs now through the federal income tax and government antipoverty programs does not settle the questions of how much redistribution is appropriate, and whether more redistribution should occur.
The Ladder of Opportunity
Economic inequality is perhaps most troubling when it is not the result of effort or talent, but instead is determined by the circumstances under which a child grows up. One child attends a well-run grade school and high school and heads on to college, while parents help out by supporting education and other interests, paying for college, a first car, and a first house, and offering work connections that lead to internships and jobs. Another child attends a poorly run grade school, barely makes it through a low-quality high school, does not go to college, and lacks family and peer support. These two children may be similar in their underlying talents and in the effort they put forth, but their economic outcomes are likely to be quite different.
Public policy can attempt to build a ladder of opportunities so that, even though all children will never come from identical families and attend identical schools, each child has a reasonable opportunity to attain an economic niche in society based on their interests, desires, talents, and efforts. Table 9.6a shows some of those initiatives.
| Children | College Level | Adults |
|---|---|---|
| • Improved day care | • Widespread loans and grants for those in financial need | • Opportunities for retraining and acquiring new skills |
| • Enrichment programs for preschoolers | • Public support for a range of institutions from two-year community colleges to large research universities | • Prohibiting discrimination in job markets and housing on the basis of race, gender, age, and disability |
| • Improved public schools | – | – |
| • After school and community activities | – | – |
| • Internships and apprenticeships | – | – |
Inheritance Taxes
There is always a debate about inheritance taxes. It goes like this: Why should people who have worked hard all their lives and saved up a substantial nest egg not be able to give their money and possessions to their children and grandchildren? In particular, it would seem un-American if children were unable to inherit a family business or a family home. Alternatively, many Americans are far more comfortable with inequality resulting from high-income people who earned their money by starting innovative new companies than they are with inequality resulting from high-income people who have inherited money from rich parents.
The United States does have an estate tax that is, a tax imposed on the value of an inheritance—which suggests a willingness to limit how much wealth one can pass on as an inheritance. However, according to the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, in 2015 the estate tax applied only to those leaving inheritances of more than $5.43 million and thus applies to only a tiny percentage of those with high levels of wealth.
The Tradeoff between Incentives and Income Equality
Government policies to reduce poverty or to encourage economic equality, if carried to extremes, can injure incentives for economic output. The poverty trap, for example, defines a situation where guaranteeing a certain level of income can eliminate or reduce the incentive to work. An extremely high degree of redistribution, with very high taxes on the rich, would be likely to discourage work and entrepreneurship. Thus, it is common to draw the tradeoff between economic output and equality, as Figure 9.6a (a) shows. In this formulation, if society wishes a high level of economic output, like point A, it must also accept a high degree of inequality. Conversely, if society wants a high level of equality, like point B, it must accept a lower level of economic output because of reduced incentives for production.
This view of the tradeoff between economic output and equality may be too pessimistic, and Figure 9.6a (b) presents an alternate vision. Here, the tradeoff between economic output and equality first slopes up, in the vicinity of choice C, suggesting that certain programs might increase both output and economic equality. For example, the policy of providing free public education has an element of redistribution, since the value of the public schooling received by children of low-income families is clearly higher than what low-income families pay in taxes. A well-educated population, however, is also an enormously powerful factor in providing the skilled workers of tomorrow and helping the economy to grow and expand. In this case, equality and economic growth may complement each other.
Moreover, policies to diminish inequality and soften the hardship of poverty may sustain political support for a market economy. After all, if society does not make some effort toward reducing inequality and poverty, the alternative might be that people would rebel against market forces. Citizens might seek economic security by demanding that their legislators pass laws forbidding employers from ever laying off workers or reducing wages, or laws that would impose price floors and price ceilings and shut off international trade. From this viewpoint, policies to reduce inequality may help economic output by building social support for allowing markets to operate.
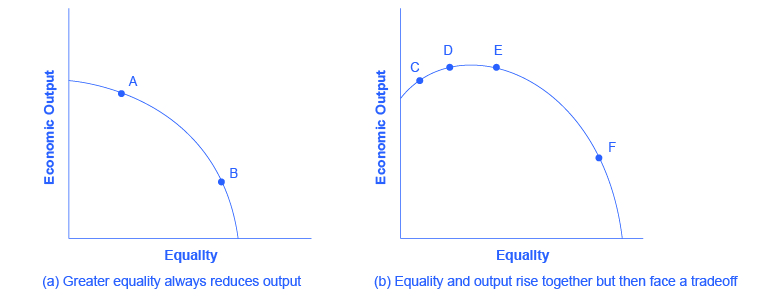
The tradeoff in Figure 9.6a (b) then flattens out in the area between points D and E, which reflects the pattern that a number of countries that provide similar levels of income to their citizens—the United States, Canada, European Union nations, Japan, and Australia—have different levels of inequality. The pattern suggests that countries in this range could choose a greater or a lesser degree of inequality without much impact on economic output. Only if these countries push for a much higher level of equality, like at point F, will they experience the diminished incentives that lead to lower levels of economic output. In this view, while a danger always exists that an agenda to reduce poverty or inequality can be poorly designed or pushed too far, it is also possible to discover and design policies that improve equality and do not injure incentives for economic output by very much—or even improve such incentives.
Bring It Home
Occupy Wall Street
The Occupy movement took on a life of its own over the last few months of 2011, bringing to light issues that many people faced on the lower end of the income distribution. The contents of this chapter indicate that there is a significant amount of income inequality in the United States. The question is: What should be done about it?
The 2008-2009 Great Recession caused unemployment to rise and incomes to fall. Many people attribute the recession to mismanagement of the financial system by bankers and financial managers—those in the 1% of the income distribution—but those in lower quintiles bore the greater burden of the recession through unemployment. This seemed to present the picture of inequality in a different light: the group that seemed responsible for the recession was not the group that seemed to bear the burden of the decline in output. A burden shared can bring a society closer together. A burden pushed off onto others can polarize it.
On one level, the problem with trying to reduce income inequality comes down to whether you still believe in the American Dream. If you believe that one day you will have your American Dream—a large income, large house, happy family, or whatever else you would like to have in life—then you do not necessarily want to prevent anyone else from living out their dream. You certainly would not want to run the risk that someone would want to take part of your dream away from you. Thus, there is some reluctance to engage in a redistributive policy to reduce inequality.
However, when those for whom the likelihood of living the American Dream is very small are considered, there are sound arguments in favor of trying to create greater balance. As the text indicated, a little more income equality, gained through long-term programs like increased education and job training, can increase overall economic output. Then everyone is made better off, and the 1% will not seem like such a small group any more.
Key Concepts and Summary
Policies that can affect the level of economic inequality include redistribution between rich and poor, making it easier for people to climb the ladder of opportunity; and estate taxes, which are taxes on inheritances. Pushing too aggressively for economic equality can run the risk of decreasing economic incentives. However, a moderate push for economic equality can increase economic output, both through methods like improved education and by building a base of political support for market forces.
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is adapted from “Government Policies to Reduce Income Inequality” and “Key Concepts and Summary” In Principles of Economics 2e by Steven A. Greenlaw & David Shapiro, licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Adaptations include addition of chapter ley concepts and summary.
Access for free at Principles of Microeconomics 2e
Original Source Chapter References
Ebeling, Ashlea. 2014. “IRS Announces 2015 Estate And Gift Tax Limits.” Forbes. Accessed March 16, 2015. http://www.forbes.com/sites/ashleaebeling/2014/10/30/irs-announces-2015-estate-and-gift-tax-limits/.
Federal Register: The Daily Journal of the United States Government. “State Median Income Estimates for a Four-Person Household: Notice of the Federal Fiscal Year (FFY) 2013 State Median Income Estimates for Use Under the Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP).” Last modified March 15, 2012. https://www.federalregister.gov/articles/2012/03/15/2012-6220/state-median-income-estimates-for-a-four-person-household-notice-of-the-federal-fiscal-year-ffy-2013#t-1.
Luhby, Tami. 2014. “Income is on the rise . . . finally!” Accessed April 10, 2015. http://money.cnn.com/2014/08/20/news/economy/median-income/.
Meyer, Ali. 2015. “56,023,000: Record Number of Women Not in Labor Force.” CNSNews.com. Accessed March 16, 2015. http://cnsnews.com/news/article/ali-meyer/56023000-record-number-women-not-labor-force.
Orshansky, Mollie. “Children of the Poor.” Social Security Bulletin. 26 no. 7 (1963): 3–13. http://www.ssa.gov/policy/docs/ssb/v26n7/v26n7p3.pdf.
The World Bank. “Data: Poverty Headcount Ratio at $1.25 a Day (PPP) (% of Population).” http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.DDAY.
U.S. Department of Commerce: United States Census Bureau. “American FactFinder.” http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/nav/jsf/pages/index.xhtml.
U.S. Department of Commerce: United States Census Bureau. “Current Population Survey (CPS): CPS Table Creator.” http://www.census.gov/cps/data/cpstablecreator.html.
U.S. Department of Commerce: United States Census Bureau. “Income: Table F-6. Regions—Families (All Races) by Median and Mean Income.” http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/income/data/historical/families/.
U.S. Department of Commerce: United States Census Bureau. “Poverty: Poverty Thresholds.” Last modified 2012. http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/poverty/data/threshld/.
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015. “2015 Poverty Guidelines.” Accessed April 10, 2015. http://www.medicaid.gov/medicaid-chip-program-information/by-topics/eligibility/downloads/2015-federal-poverty-level-charts.pdf.
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015. “Information on Poverty and Income Statistics: A Summary of 2014 Current Population Survey Data.” Accessed April 13, 2015. http://aspe.hhs.gov/hsp/14/povertyandincomeest/ib_poverty2014.pdf.
Congressional Budget Office. 2015. “The Effects of Potential Cuts in SNAP Spending on Households With Different Amounts of Income.” Accessed April 13, 2015. https://www.cbo.gov/publication/49978.
Falk, Gene. Congressional Research Service. “The Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) Block Grant: Responses to Frequently Asked Questions.” Last modified October 17, 2013. http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/RL32760.pdf.
Library of Congress. “Congressional Research Service.” http://www.loc.gov/crsinfo/about/.
Office of Management and Budget. “Fiscal Year 2013 Historical Tables: Budget of the U.S. Government.” http://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2013/assets/hist.pdf.
Tax Policy Center: Urban Institute and Brookings Institution. “The Tax Policy Briefing Book: Taxation and the Family: What is the Earned Income Tax Credit?” http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/briefing-book/key-elements/family/eitc.cfm.
Frank, Robert H., and Philip J. Cook. The Winner-Take-All Society. New York: Martin Kessler Books at The Free Press, 1995.
Institute of Education Sciences: National Center for Education Statistics. “Fast Facts: Degrees Conferred by Sex and Race.” http://nces.ed.gov/fastfacts/display.asp?id=72.
Nhan, Doris. “Census: More in U.S. Report Nontraditional Households.” National Journal. Last modified May 1, 2012. http://www.nationaljournal.com/thenextamerica/demographics/census-more-in-u-s-report-nontraditional-households-20120430.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: BLS Reports. “Report 1040: Women in the Labor Force: A Databook.” Last modified March 26, 2013. http://www.bls.gov/cps/wlf-databook-2012.pdf.
U.S. Department of Commerce: United States Census Bureau. “Income: Table H-2. Share of Aggregate Income Received by Each Fifth and Top 5 Percent of Households.” http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/income/data/historical/household/.
United States Census Bureau. 2014. “2013 Highlights.” Accessed April 13, 2015. http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/poverty/about/overview/.
United States Census Bureau. 2014. “Historical Income Tables: Households: Table H-2 Share of Aggregate Income Received by Each Fifth and Top 5% of Income. All Races.” Accessed April 13, 2015. http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/income/data/historical/household/.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. “Research Resources: Survey of Consumer Finances.” Last modified December 13, 2013. http://www.federalreserve.gov/econresdata/scf/scfindex.htm.
Congressional Budget Office. “The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009.” Last modified July 10, 2012. http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43373.
Huang, Chye-Ching, and Nathaniel Frentz. “Myths and Realities About the Estate Tax.” Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. Last modified August 29, 2013. http://www.cbpp.org/files/estatetaxmyths.pdf.
Media Attributions
- Figure © Steven A. Greenlaw & David Shapiro (OpenStax) is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
A flow of money received, often measured on a monthly or an annual basis
The sum of the value of all assets, including money in bank accounts, financial investments, a pension fund, and the value of a home
Taking income from those with higher incomes and providing income to those with lower incomes
A tax system in which the rich pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes, rather than a higher absolute amount
Percentage of total taxes paid divided by total income
Dividing a group into fifths, a method economists often use to look at distribution of income
A tax imposed on the value of an inheritance

