4.1 What is Language?
 Reminder from Chapter One – Communication is the process of understanding and sharing meaning (Pearson & Nelson, 2000).
Reminder from Chapter One – Communication is the process of understanding and sharing meaning (Pearson & Nelson, 2000).How do you communicate? What do you think? We use language as a system to create and exchange meaning with one another, and the types of words we use influence both our perceptions and others’ interpretations of our meanings. What kinds of words would you use to describe your thoughts and feelings, your preferences in music, cars, food, or other things that matter to you?
Watch the following 10-minute video featuring psychologist Steven Pinker describing the intricacies of language.
Video: RSA ANIMATE: Language as a Window into Human Nature by RSA Animate [10:53] transcript available
In this chapter, you will learn more about the importance of delivering your message in words. You will explore how the characteristics of language interact in ways that can both improve and diminish effective business communication. You will examine how language plays a significant role in how you perceive and interact with the world, and how culture, language, education, gender, race, and ethnicity all influence this dynamic process. You will look at ways to avoid miscommunication and focus on constructive ways to get your message delivered to your receiver with the meaning you intended.
People are raised in different cultures, with different values, beliefs, customs, and different languages to express those cultural attributes. Even people who speak the same language, like speakers of English in London, New Delhi, or Calgary, speak and interact using their own words that are community-defined, self-defined, and have room for interpretation. This variation in our use of language is a creative way to form relationships and communities, but can also lead to miscommunication.
Words themselves, then, actually hold no meaning. It takes at least two people to use them, to give them life and purpose. Words change meaning over time. The dictionary entry for the meaning of a word changes because we change, and multiple meanings can lead to miscommunication.

Languages are living exchange systems of meaning and are bound by context. If you are assigned to a team that coordinates with suppliers from Shanghai, China, and a sales staff in London, Ontario you may encounter terms from both groups that influence your team.
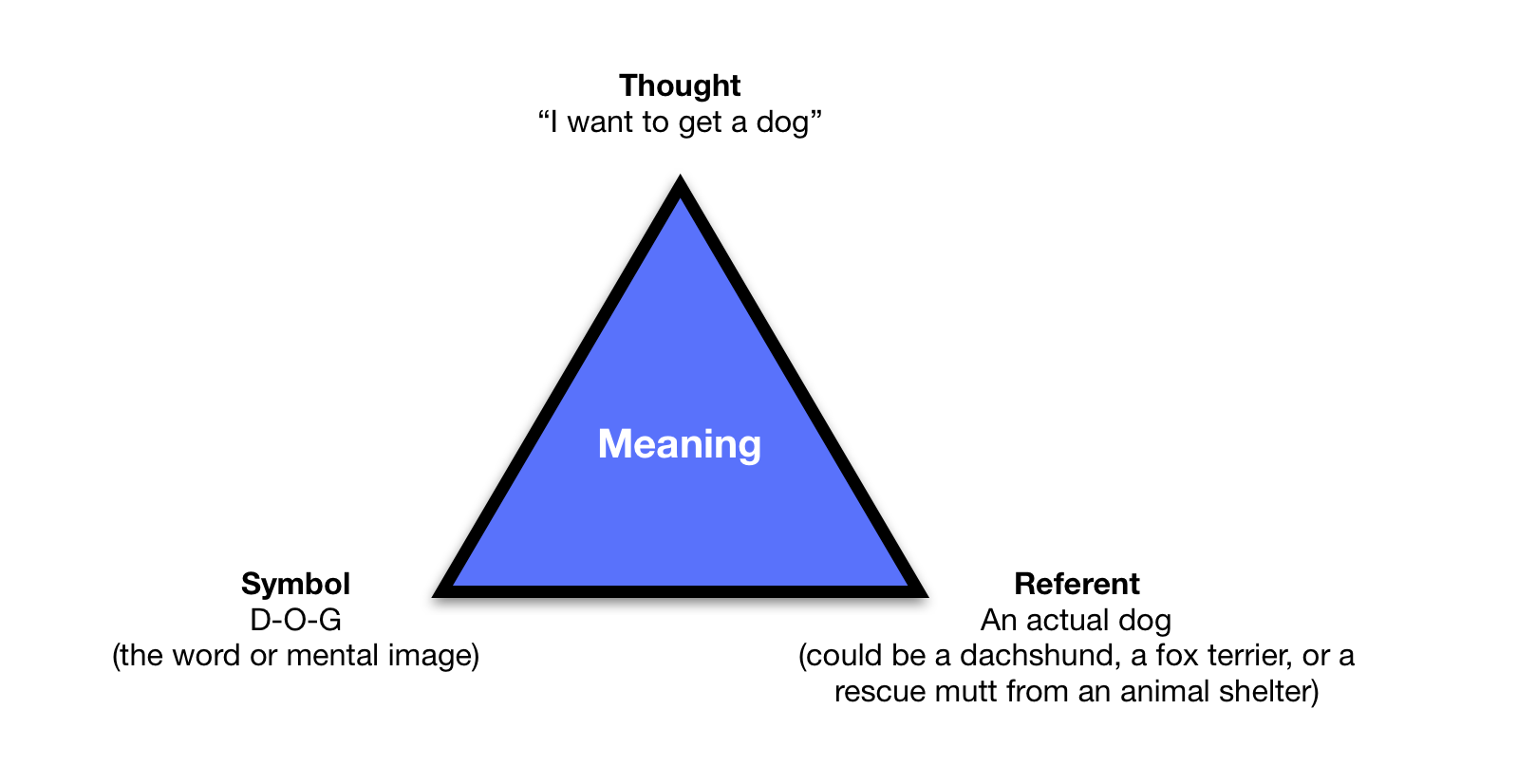
Triangle of Meaning
The triangle of meaning is a model of communication that indicates the relationship among a thought, symbol, and referent and highlights the indirect relationship between the symbol and referent (Ogden & Richards, 1932). As represented in Figure 4.1 below, the thought is the concept or idea a person references. The symbol is the word that represents the thought, and the referent is the object or idea to which the symbol refers. This model is useful for you as a communicator because when you are aware of the indirect relationship between symbols and referents, you are aware of how common misunderstandings occur, as the following example illustrates:
Triangle of Meaning Example
Jasper and Abby have been thinking about getting a new dog. So each of them is having a similar thought. They are each using the same symbol, the word dog, to communicate their thought. Their referents, however, are different. Jasper is thinking about a small dog like a dachshund, and Abby is thinking about an Australian shepherd. Since the word dog doesn’t refer to one specific object in our reality, it is possible for them to have the same thought, and use the same symbol, but end up in an awkward moment when they get to the shelter and fall in love with their respective referents only to find out the other person didn’t have the same thing in mind. Abby could ask questions for clarification, like “Sounds like you’re saying that a smaller dog might be better. Is that right?” Getting to a place of shared understanding can be difficult, even when we define our symbols and describe our referents.
“9. Introduction” from Communication for Business Professionals by eCampusOntario is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
“10. What is Language?” from Communication for Business Professionals by eCampusOntario is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

