Human Resources Strategic Projects-Teacher/Student Resources
12.4. Employee Selection Strategy
Scope
Create a selection strategy to select the right candidate most suitable for vacant positions within an organization through interviewing and evaluating their qualities and work experience. The candidates will be required to meet specific job requirements. The candidates’ credentials and talents will match to organizational needs. The selection of the right candidate will be an asset to the organization, in turn helping the organization reach its goals and mission.
Key Stakeholders
The Line Manager, the Recruiter and the Candidate will probably be the main participants. Senior management, directors, senior team members, HR, important client or customer connections, or anybody else who must be considered, are examples of second-tier stakeholders.
- Recruitment and Selection – Sources, Recruiters, Recruiting Coordinators and Recruiting Managers
- Hiring Team – Hiring Manager/Team Managers and Interviewers
- Management – Directors or VPs, Budget Allocation Team (sometimes when the compensation goes overboard) and Human Resource Business Partners
- Compensation and Benefits
- Vendors – Background Verification
Business Case
Only when effective matching can selection be done, and an organization will receive high performance from its workforce. The selection process involves choosing the appropriate personnel for the right jobs, which significantly impacts the organization and workforce. This also affects the economy and competitiveness in the dynamic environment(Roshani, n.d.).
Organization
- Selection of suitable candidates results in lower absenteeism and labour turnover rates.
- Good selection process can increase the organization’s productivity. Effective hiring boosts organizational effectiveness and overall worker performance.
- People who are unfit and unqualified can be eliminated.
- By identifying qualified applicants, effective selection minimizes the loss of time, effort, and resources.
- Making the right choices is essential for developing a qualified workforce.
Employees
- Increases employee motivation, helps build trust with the company and boosts employee morale.
- Helps achieve goals/targets, contributing to overall team building and increased performance.
- Enhances culture of healthy competition amongst peers.
- Builds a culture of learning and growth.
- Gives more opportunities for career growth and progression.
Management
- A wise choice of executives may strengthen the company’s managerial structure.
- Helps build management capability and strengthens succession planning.
- Reduces rehire time, efforts, and costs.
- Employee testing, interviews and background checks help eliminate the chances of a “wrong hire.”
Project Description
The process of selection is the second step in the staffing process. It involves choosing the candidates who best meet the qualifications and aptitude for the job. The main objective of this process is to match individual characteristics such as ability, experience, and so on with the job’s requirements. The wrong selection also leads to absenteeism and retrenchment.
Outcome
The project’s goal is to put policies and processes in place to hire the best candidate for the job without having to do it repeatedly. This also means aligning the selection process to the needs of the organization.
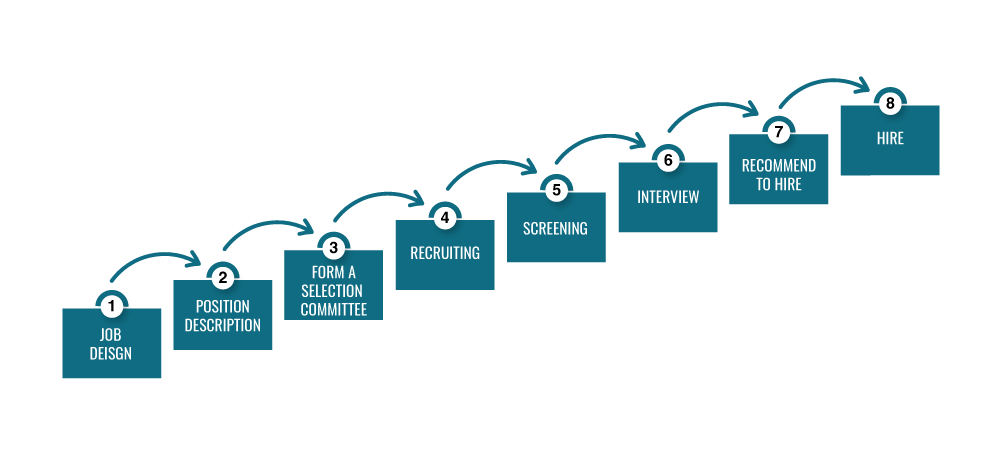
The eight steps to an effective selection process include:
- Job Design
- Job Description
- Create Selection Team
- Recruitment
- Screen applicants
- Complete interviews
- Make recommendations to hire
- Hire applicant
Resources
- People Involved: recruitment and selection team, management, payroll/compensation department, vendors (if applicable)
- Tools required: Human Resources Information System, interview room (physical or virtual), testing/assessment tools, sourcing media (ie LinkedIn, Indeed, etc.)
- Resources required: salary information, job description, testing/assessment questionnaires, background/legal checks, external analysis (competition)
Deliverables
- Benchmarks
- Standard job posting form, contents
- ATS (Applicant Tracking System)
- Structured interview manual
- Assessment & Selection criteria
- The weighting system for the assessment
- Project performance report
Action Plan
- Classify the selection benchmarks – Design a selection benchmark or criteria with the hiring manager, such as Education requirements, KSAO Requirements, relevant Labour Market trends, target applicant pool, and selection method.
- Create a standard selection process & timeline – This can be done by planning a timeframe on the steps needed for the selection. This should be discussed with the hiring team to set expectations.
- Standard job posting form, contents – Job posting guides provide information and guidance to job seekers. A job board can offer application guidelines, requirements, qualifications, etc. Job sites post their job advertisements online, including the latest job openings and postings. The guides also help potential job seekers decide what jobs interest them and which may be more suitable.
- Choose the proper ATS (Applicant Tracking System) – After analyzing and reviewing areas that need to increase efficiency throughout the current recruitment process, the project team will examine which ATS solutions can help improve the recruitment process.
- Standard screening criteria – Candidate screening is a process to find the best candidates who have applied. This screening helps the recruiter shortlist or screen candidates. Recruiters might test for basic knowledge or any other capability related to the job.
- Structured interview manual – Update job analysis and description data of each job and define the necessary competencies with high performers based on these data. Then, a grading scale is established, and a standardized interview guide is produced.
- Structured interview questions – A structured interview is where they ask a very set of questions. Candidates would be aware of the type of questions they would be asked. You will be informed beforehand of a set of formulas.
- Conduct preliminary interview – The candidate’s abilities, academic competencies, and interests are assessed during the preliminary interview. Interviews can be conducted over the phone or via video conferencing.
- Extensive interview procedure – Design a standardized interview process and precise method for in-depth interviews, and train interviewers about the output to apply to actual interviews.
- Conduct is written and physical tests for shortlisting candidates – Written tests are used in the selection process, such as aptitude, intelligence, reasoning, personality, and others. The purpose of these tests is to evaluate a potential applicant objectively. We should not be biased in any way in this assessment.
- Assessment & Selection criteria – This summarizes the tasks that you will perform in your role. The results create a combined picture story of the behavioural profile. HR and the manager discuss the strengths and weaknesses of this profile in detail. Once satisfied, they approve and sign the shape, utilized as the foundation for hiring or succession planning.
- The weighting system for the assessment – Agree with the stakeholders on which evaluation items to give more importance and score during the interview of candidates for employment and create an evaluation table based on the consensus result.
- Project performance report – Review the effectiveness of new recruitment strategies based on specific quantitative outcomes (e.g., the actual number of applicants versus the number of recruits) and prepare a communication report for evaluating project performance at the management level.
Class of 2022 Contributions: Mariefer Atienza, Keziah Butal, Taeguk Seok,

