Chapter 17
Solutions
Exercise 17.1
a. Lessee analysis (ASPE):
- Does ownership title pass? No, title remains with the lessor.
- Is there a BPO or a bargain renewal option? Yes
- Is the lease term 75% or more of the asset’s estimated economic or useful life? No
6 years/10 years = 60%, which does not meet the 75% threshold
- Does the present value of the minimum lease payments exceed 90% of the leased asset’s fair value? Yes, as calculated below.Present value of minimum lease payments: PV = (25,100 PMT/AD, 7 I/Y, 6 N, 3,000 FV) = $130,014 (rounded) ASPE interest rate used must be the lower of the two rates, since both are known. The present value compared to the fair value of $130,000 exceeds the 90% numeric threshold. Note that the leased asset and obligation cannot exceed fair value, so $130,000 will be the amount used as the valuation in the journal entries below.
Any one of the criteria met will result in a classification of a capital lease. In this case, the lease agreement has met two criteria: a bargain purchase option, and a present value of the minimum lease payments that exceeds 90% of the fair value of the asset.
Lessor Analysis (ASPE)
The lease agreement meets the capitalization criteria for the lessee above. Additionally, there are no uncertainties regarding the collectability of the lease payments and the costs yet to be incurred by the lessor (both must be met). This would, therefore, be classified as a capital lease for the lessor. The initial amount of net investment (fair value) of $130,000 exceeds the lessor’s cost of $90,000, making the lease a sales-type lease to the lessor.
b. Gross investment (lease receivable) for the lessor:The minimum lease payments regarding this lease are:
| Calculation: | = | $150,600 | |
| BPO | + | 3,000 | |
| Gross investment at inception | $153,600 |
Net investment for the lessor:
The $130,000 fair value in this case (or the present value if it does not exceed the fair value).
c.
| Lessee and Lessor Lease Amortization Schedule |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Annual Lease Payment Plus BPO | Interest @ 7% | Reduction of Lease Obligation | Balance Lease Obligation |
| Jul 1, 2021 | $25,100 | $130,000 | ||
| Jul 1, 2021 | 25,100 | $25,100 | 104,900 | |
| Jul 1, 2022 | 25,100 | $7,343 | 17,757 | 87,143 |
| Jul 1, 2023 | 25,100 | 6,100 | 19,000 | 68,143 |
| Jul 1, 2024 | 25,100 | 4,770 | 20,330 | 47,813 |
| Jul 1, 2025 | 25,100 | 3,347 | 21,753 | 26,060 |
| Jul 1, 2026 | 25,100 | 1,824 | 23,276 | 2,784 |
| Jun 30, 2027 | 3,000 | 216* | 2,784 | 0 |
| $153,600 | $23,600 | $130,000 | ||
* Note: The lease valuation is limited to its fair value of $130,000 instead of the present value of $130,014. The difference ($14) is insignificant, thus a new interest rate is not required for the amortization schedule above. Had the present value been significantly higher than the fair value, a new effective interest rate would be required and calculated using the following methodology.
I/Y = (+/- 130,000 PV, 25,100 PMT/AD, 6 N, 3,000 FV) = 7.004876% or 7%
As can be seen, the 7% rate for the lessor has not significantly changed, so 7% will be the rate used in the amortization schedule above.
d. Lessee journal entries:
 Year-end adjusting entries:
Year-end adjusting entries:
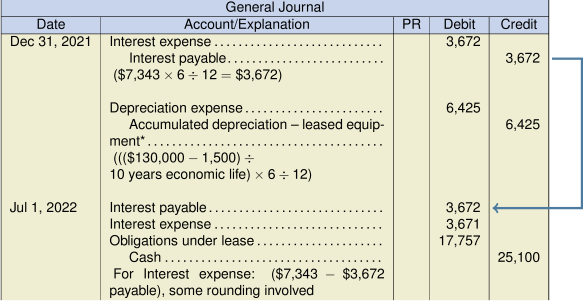 * Note: Because there is a bargain purchase option, the leased asset is depreciated over its economic life rather than over the lease term. This is because the BPO, much less than the market price at that time, will be exercised by the lessee and the asset will be used beyond the lease term.
* Note: Because there is a bargain purchase option, the leased asset is depreciated over its economic life rather than over the lease term. This is because the BPO, much less than the market price at that time, will be exercised by the lessee and the asset will be used beyond the lease term.

e. Lessor entries
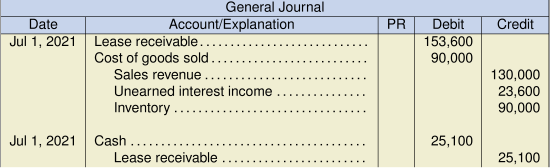 Year-end adjusting entry:
Year-end adjusting entry:
 2022 payment:
2022 payment:
 Year-end adjusting entry:
Year-end adjusting entry:
 Note: The lessor could record six months of interest income in July, and six months of interest income on December 31 to match the lessee interest entries. However, the minimum reporting requirement would be to recognize interest income each reporting date (December 31). If the lessor also had interim reporting every six months within the fiscal year, interest income would be accrued every six months to ensure that both the interim and year-end financial statements were complete.
Note: The lessor could record six months of interest income in July, and six months of interest income on December 31 to match the lessee interest entries. However, the minimum reporting requirement would be to recognize interest income each reporting date (December 31). If the lessor also had interim reporting every six months within the fiscal year, interest income would be accrued every six months to ensure that both the interim and year-end financial statements were complete.
f. For the lessee: Rather than using quantitative factors, such as the 75% and the 90% hurdles, the IFRS (IAS 17) criteria use qualitative factors to establish whether the risks and rewards of ownership have transferred to the lessee, which supports the classification as a capitalized lease:
- There is reasonable assurance that the lessee will obtain ownership of the leased property by the end of the lease term. If there is a bargain purchase option in the lease, it is assumed that the lessee will exercise it and obtain ownership of the asset (same as with ASPE).
- The lease term is long enough that the lessee will receive substantially all of the economic benefits that are expected to be derived from using the leased property over its life (equivalent to the 75% numeric threshold for ASPE).
- The lease allows the lessor to recover substantially all of its investment in the leased property and to earn a return on the investment. Evidence of this is provided if the present value of the minimum lease payments is close to the fair value of the leased asset (equivalent to the 90% numeric threshold for ASPE).
- The leased assets are so specialized that, without major modification, they are of use only to the lessee (IFRS (IAS 17) only).
If the lease is deemed as a lease subject to capitalization, the accounting treatment of the lease by the lessee would be the same as ASPE, although it would be referred to as a finance lease, rather than a capital, direct financing lease.
The treatment of the lease by the lessor would be the same as the lessee above, using qualitative criteria rather than numeric thresholds used for ASPE. (The criteria will not include the two-revenue recognition-based tests for uncertainty regarding collectability of lease payments and estimated un-reimbursable costs for the lessor.) The lease would be referred to as a finance lease, manufacturer or dealer rather than a sales-type lease.
g. If the lease agreement included an unguaranteed residual, the leased asset would be physically returned to the lessor at the end of the lease term. The depreciation charge would, therefore, be over the lease term and not the asset’s economic life, which is the case when a bargain purchase is involved. As well, the depreciation calculation would not include a residual value.
Exericse 17.2
- Lessee analysis (IFRS, IAS 17)
- Does ownership title pass? No, title remains with the lessor.
- Is there a BPO or a bargain renewal option? No
- Is the lease term covering the majority of the asset’s estimated economic or useful life? Consider that the lease term is eight years and the economic life is ten years, so this constitutes a major part of the economic life of the asset. Yes, capitalize leased asset.
- The leased asset is a specialized piece of landscaping machinery, so it will only benefit the lessee without major modifications. Yes, capitalize leased asset.
- Does the present value of the minimum lease payments allow the lessor to recover substantially all of the leased asset’s fair value as well as realizing a return on the investment? Consider that the present value of the minimum lease payments shown below is nearly equal to the fair value of $270,000, so it appears that the lessor will be reimbursed for all of the leased investment, including a return on investment. Yes, capitalize leased asset. Present value calculation:
Yearly payment $46,754 Less: Executory costs 2,000 Minimum annual lease payment $44,754 Present value of minimum lease payments:
PV = (44,754 PMT/AD, 9 I/Y, 8 N, 0 FV) = $269,999 (which is virtually 100% of the fair value of $270,000)
Under IFRS (IAS 17), the lessee will classify this lease as a finance lease since the lease term covers substantially all of the asset’s useful life, the present value of the minimum lease payments allows the lessor to recover almost all of the leased asset’s fair value (as well as realizing a return on the investment), and the machinery is highly specialized. Three of the criteria considered were met so it is reasonable to assume that the lessee will capitalize the lease.
The treatment of the lease by the lessor would be the same as the lessee above, using the qualitative criteria rather than numeric thresholds used for ASPE. Except the lessor classification criteria will not include the two-revenue recognition-based tests for uncertainty regarding collectability of lease payments and estimated un-reimbursable costs for the lessor. Again, since three criteria were met, it is reasonable to assume that the lease would be classified as a finance lease.
- IFRS (IAS 17) states that the rate implicit in the lease is to be used wherever it is reasonably determinable. Using the fair value of $270,000, the implicit rate can be calculated: I/Y = (+/- 270,000 PV, 44,754 PMT/AD, 8 N) = 9% (rounded) which is the same rate as the lessee’s
Mercy Ltd.
Lease Amortization Schedule
(Lessee)
Date Annual Lease Payment Excluding Executory Costs) Interest @ 9% Reduction of Lease Obligation Balance Lease Obligation $270,000 Jan 1, 2021 $44,754 $44,754 225,246 Jan 1, 2022 44,754 $20,272 24,482 200,764 Jan 1, 2023 44,754 18,069 26,685 174,079 Jan 1, 2024 44,754 15,667 29,087 144,992 Jan 1, 2025 44,754 13,049 31,705 113,287 Jan 1, 2026 44,754 10,196 34,558 78,729 Jan 1, 2027 44,754 7,086 37,668 41,061 Jan 1, 2028 44,754 3,693* 41,061 0 $358,032 $88,032 $270,000 * rounded 
| Mercy Ltd. Statement of Financial Position December 31, 2022 |
||
|---|---|---|
| Non-current assets | ||
|
Equipment under lease |
$270,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation |
(67,500) | |
| 202,500 | ||
| Current liabilities | ||
|
Interest payable |
18,069 | |
|
Current portion of long-term lease obligation* |
26,685 | |
| Non-current liabilities | ||
|
Long-term lease obligation () |
$174,079 | |
* The principal portion of the lease payment over the next 12 months after the reporting date of December 31, 2022. Refer to the amortization schedule above.
Required disclosure in the notes:
The following is a schedule of future minimum lease payments under the finance lease, expiring December 31, 2028, together with the balance of the obligation under finance lease.
| Year ending December 31 | ||
| 2023 | $46,754 | |
| 2024 | 46,754 | |
| 2025 | 46,754 | |
| 2026 | 46,754 | |
| 2027 | 46,754 | |
| 2028 | 46,754 | |
| 280,524 | ||
| Less amount representing executory costs | 12,000 | |
| Total minimum lease payments | 268,524 | |
| Less amount representing interest at 9%* | 67,760 | |
| Balance of the obligation, December 31, 2022 | $200,764 | |
* ![]()
Note: Additional disclosures would also be required about material lease arrangements, including contingent rents, sub-lease payments, and lease-imposed restrictions. These do not apply in this case.
Exercise 17.3
Lessee Analysis (IFRS, IAS 17)
- Does the ownership title pass? No, title remains with the lessor.
- Is there a BPO or a bargain renewal option? No
- Does the lease term cover the majority of the asset’s estimated economic or useful life? Consider that the lease term is eight years, and the economic life is twelve years, the lease covers a major part of the economic life of the asset. Yes, capitalize leased asset.
- As the leased asset is a specialized piece of landscaping machinery, it will only benefit the lessee without major modifications. Yes, capitalize leased asset.
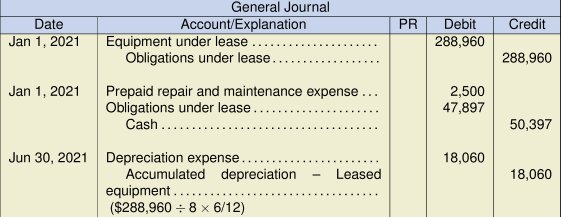
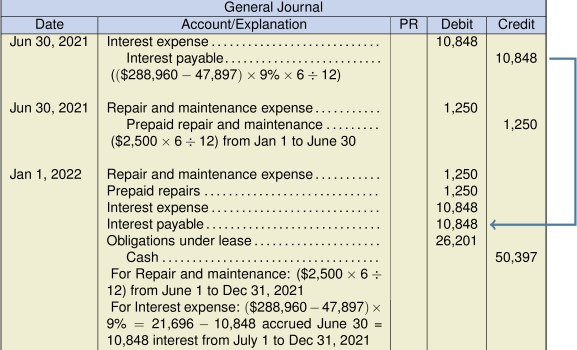
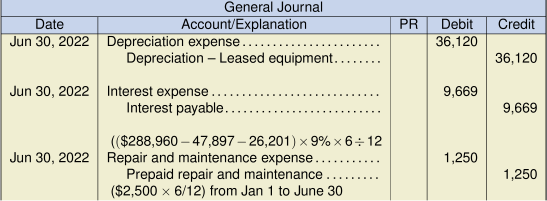
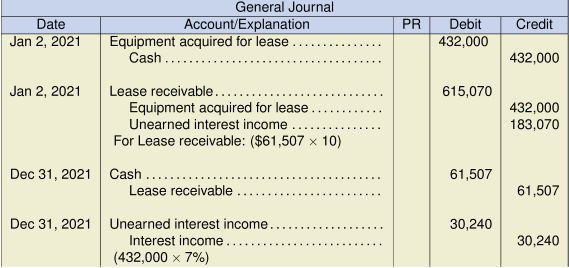
- Does the present value of the minimum lease payments allow the lessor to recover substantially all of the leased asset’s fair value, as well as realizing a return on the investment? Consider that the present value of the minimum lease payments is $288,960, compared to the fair value of $300,000, making the minimum lease payments nearly equal to the fair value at that date. As such, the lessor will recover substantially all of the leased asset’s fair value, as well as a return of 9% on the investment. Yes, as calculated below. Present value calculation:
Yearly payment $50,397 Less: Executory costs 2,500 Minimum annual lease payment $47,897 Present value of minimum lease payments:
PV = (47,897 PMT/AD, 9 I/Y, 8 N, 0 FV) = 288,960 (which is substantially most of the fair value of $300,000)Consider the following criteria: The lease term covers substantially all of the asset’s useful life, the present value of the minimum lease payments recovers substantially most of the leased asset’s fair value (as well as realizing a return on the investment), and the machinery is highly specialized for the lessee. As these three factors have been met, it is reasonable to assume that the lease will be classified as a finance lease for the lessee under IFRS (IAS 17).
Exercise 17.4
- This is a finance lease to Oberton Ltd. The IFRS (IAS 17) criteria use qualitative factors to establish whether the risks and rewards of ownership are transferred to the lessee, and supports classification as a finance lease:
- There is reasonable assurance that the lessee will obtain ownership of the leased property by the end of the lease term. If there is a bargain purchase option in the lease, it is assumed that the lessee will exercise it and obtain ownership of the asset. No
- The lease term is long enough that the lessee will receive substantially all of the economic benefits that are expected to be derived from using the leased property over its life (as evidenced by a four-year lease compared to a six-year estimated economic life). Yes, this represents a major part of the economic life of the asset.
- The lease allows the lessor to recover substantially all of its investment in the leased property and to earn a return on the investment. Evidence of this is provided if the present value of the minimum lease payments is close to the fair value of the leased asset. Yes PV = (4,313 PMT/AD excl. executory costs, 8 I/Y, 4 N, 3,500 guaranteed residual) = 18,000Compared to a fair value of $18,000 = 100% recovery of investment + an 8% return on investment.
- The leased assets are so specialized that, without major modification and/or significant cost to the lessor, they are of use only to the lessee. No
The standard also states that these indicators are not always conclusive. The decision has to be made on the substance of each specific transaction. If the lessee determines that the risks and benefits of ownership have not been transferred to it, the lease is classified as an operating lease. In this case, two factors have been met so it would be reasonable to classify this lease as a finance lease for the lessee.
For Black Ltd. (the lessor) under IFRS (IAS 17), the lease would receive the same treatment as for the lessee using the qualitative factors. Black Ltd. reasonably meets the factors, and is not a manufacturer or dealer, and so this is a finance lease.
- Calculation of annual rental payment: PMT = +/- 18,000 PV, 8 I/Y, 4 N, 3,500 FV =
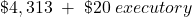 = $4,333 lease payment, including executory costs of $20.This confirms that the interest rate used to calculate the lease payment was 8% per annum.
= $4,333 lease payment, including executory costs of $20.This confirms that the interest rate used to calculate the lease payment was 8% per annum. -
Lease Amortization Schedule Date Lease Payment Excluding Lease Executive Costs) Interest @ 8% Reduction of Lease Obligation Balance Lease Obligation $18,000 Jan. 1, 2021 $4,313 $4,313 13,687 Jan. 1, 2022 4,313 $1,095 3,218 10,469 Jan. 1, 2023 4,313 838 3,475 6,994 Jan. 1, 2024 4,313 560 3,753 3,241 Jan. 1, 2025 3,500 259 3,241 0 $20,752 $2,752 $18,000 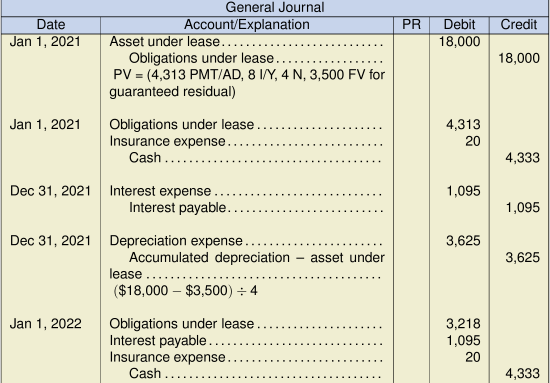
-
Oberton Ltd.
Statement of Income
For the Year Ended December 31, 2021Non-current assets Property, plant, and equipment Vehicles under lease
$18,000 Less accumulated depreciation
3,625 14,375 Current liabilities Interest payable
1,095 Obligations under lease (Note 1)
3,218 Non-current liabilities Obligations under lease (Note 1)
$10,469 Note 1: The following is a schedule of future minimum payments under finance lease expiring January 1, 2025, together with the present balance of the obligation under the lease.
Year ending December 31, 2021 2022 $4,333 2023 4,333 2024 4,333 2025 3,500 16,499 Amount representing executory costs (60) Amount representing interest (2,752) Balance of obligation December 31, 2021 $13,687 Oberton Ltd.
Statement of Income
For the Year Ended December 31, 2021Administrative expense Depreciation expense
$3,625 Insurance expense
20 Other expenses Interest expense
1,095 * from lease amortization schedule part (c)

- Entries for Black Ltd.:

-
Black Ltd. Income
Statement For the Year Ended
December 31, 2021Revenue Interest income (leases)*
$1,095 * from lease amortization schedule part (c)
Note: The insurance recovery of $20 per year would offset the original insurance expense incurred by Black Ltd.
Exercise 17.5
a. Lessor Analysis (ASPE)The lease is a capital lease for the following reasons: the lease term exceeds 75% of the asset’s estimated economic life (10 ÷ 12 years = 83%), the collectability of payments is reasonably assured, and there are no further costs to be incurred. Furthermore, it is a sales-type lease because Helmac Ltd. will realize a gross profit of $199,122 ($283,774 – $84,652) in addition to the financing charge of $75,878 to be amortized over the lease term using the effective interest method.
b.
* ![]()
Note: The unguaranteed residual value is included in the lessor’s gross investment even though the lessee does not guarantee it. From the lessor’s perspective, it anticipates receiving $25,000 from a third party at the end of the lease term and it does not matter who they receive it from.
** The residual value is unguaranteed, so its present value must be removed from the sale price to the lessee.Present value of the minimum lease payments = (35,000 PMT/AD, 5 I/Y, 10 N, 25,000 FV) = $299,122 Sales price ![]() OR remove the $25,000 residual value from the present value calculation above. PV = (35,000 PMT/AD, 5 I/Y, 10 N) = $283,774
OR remove the $25,000 residual value from the present value calculation above. PV = (35,000 PMT/AD, 5 I/Y, 10 N) = $283,774
*** The unearned interest income of $75,878 is calculated as the lease receivable (gross investment) less the present value of the minimum lease payments (![]() ).
).

c. Assuming the $25,000 residual value was guaranteed by the lessee, this would change the initial entry for the sale as follows:
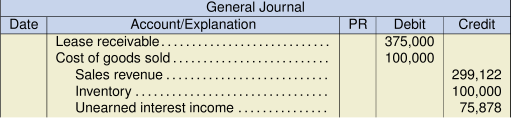
The sales revenue and cost of goods sold would not need to be reduced by the present value of the estimated residual value ($15,348) calculated in part (b). The sales revenue would, therefore, be the amount equaling the present value of the minimum lease payments.
d. Lease payment PMT/AD = (299,122 PV, 5 I/Y, 12 N, 40,000 FV) = $29,748 (rounded)
Exercise 17.6
a. Lessee Analysis (ASPE)
- Does ownership title pass? Yes, legal title passes to the lessee at the end of the lease term.
- Is there a BPO or a bargain renewal option? N/A, title passes, so BPO is not relevant.
- Is the lease term 75% or more of the asset’s estimated economic or useful life? Yes
10 years/10 years = 100% which meets the 75% threshold
- Does the present value of the minimum lease payments exceed 90% of the leased asset’s fair value? Yes, as calculated below. Present value of minimum lease payments:PV = (61,507 PMT/A, 7 I/Y, 10 N, 0 FV) = $432,000 (rounded)The ASPE interest rate used must be the lower of the two, since both are known.The present value is equal to the fair value of $432,000, so it exceeds the 90% numeric threshold.Any one of the criteria met will result in a classification of a capital lease for the lessee. In this case, the lease agreement has met three criteria: legal title passes to the lessee, a lease term that exceeds 75% of the estimated economic life of the leased asset, and a present value of the minimum lease payments that exceeds 90% of the fair value of the asset.
Lessor Analysis (ASPE)
The lease agreement meets the capitalization criteria for the lessee above. In addition, there are no uncertainties regarding the collectability of the lease payments or the costs yet to be incurred by the lessor (both must be met). This would, therefore, be classified as a capital lease for the lessor. Additionally, as the lessor is a financing company this lease would be classified as a direct-financing lease by the lessor.
b. Kimble Ltd. (lessee) entries
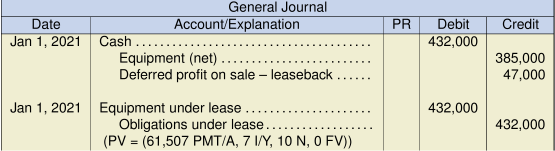
Note: The present value calculation in this case will involve the annual payment (PMT) of an ordinary annuity (paid at the end of each year) for 10 periods at 7%. The interest rate under ASPE is to be the lower of the two rates, if both are known.Earlier leasing questions involved the annual payment of an annuity due at the beginning of each year over the lease term.
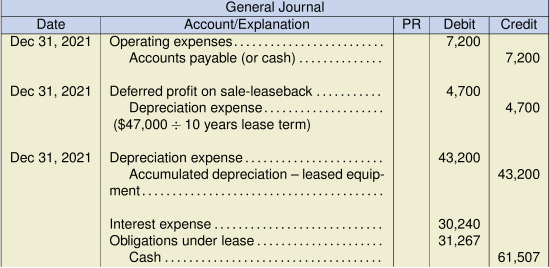
Note: Under ASPE, Kimble Ltd. is to use the lower of the two rates. The deferred profit on the sale-leaseback is to be amortized on the same basis that the asset is being depreciated, which, in this case, is ten years.
Exercise 17.7
1. Present value and amortization schedule
| PV | $359,495 | Notes |
| Rate | 12% | |
| Nper | 10 | |
| Pmt | -56,808 | |
| FV | 0 | since residual value is not guaranteed, do not include |
| Type | 1 | type 1 always for leases (payment at beginning of period) |
|
Date |
Cash |
Interest |
Amortization |
Carrying Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/Y2 | $359,495 | |||
| 1/1/Y2 | 56,808 | - | 56,808 | 302,687 |
| 12/31/Y2 | 56,808 | 36,322 | 20,486 | 282,202 |
| 12/31/Y3 | 56,808 | 33,864 | 22,944 | 259,258 |
| 12/31/Y4 | 56,808 | 31,111 | 25,697 | 233,561 |
| 12/31/Y5 | 56,808 | 28,027 | 28,781 | 204,780 |
| 12/31/Y6 | 56,808 | 24,574 | 32,234 | 172,546 |
| 12/31/Y7 | 56,808 | 20,705 | 36,103 | 136,443 |
| 12/31/Y8 | 56,808 | 16,373 | 40,435 | 96,008 |
| 12/31/Y9 | 56,808 | 11,521 | 45,287 | 50,721 |
| 12/31/Y10 | 56,808 | 6,087 | 50,721 | 0 |
2. Type of lease
This is a capital lease.
- does not qualify for the short term exemption: length of term is 10 years.
- does not qualify for the low dollar exemption: present value of the lease is a significant portion of the fair value.
3. Journal entries for Hamilton
| 1/1/Y2 | Right-of-use asset | 359,495 | ||
| Lease Liability | 359,495 | |||
| setup leased asset and record liability | ||||
| 1/1/Y2 | Lease Liability | 56,808 | ||
| Cash | 56,808 | |||
| record first payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y2 | Depreciation Expense | 35,950 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 35,950 | |||
| (359,495 / 10 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y2 | Interest Expense | 36,322 | ||
| Interest Payable | 36,322 | |||
| to accrue for interest on lease (could use Lease Liability) | ||||
| 1/1/Y3 | Interest Payable | 36,322 | ||
| Lease Liability | 20,486 | |||
| Cash | 56,808 | |||
| record lease payment (if lease liability is used @12/31/Y2, only lease liability would be debited) | ||||
| 12/31/Y3 | Depreciation Expense | 35,950 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 35,950 | |||
| (359,495 / 10 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y3 | Interest Expense | 33,864 | ||
| Interest Payable | 33,864 | |||
| to accrue for interest on lease | ||||
4. Note Presentation
Note ##. The following is a schedule of future lease payments under a contract-based lease liability expiring December 31, Y10.
| Year Ending December 31 | |
| Y4 | $56,808 |
| Y5 | 56,808 |
| Y6 | 56,808 |
| Y7 | 56,808 |
| Y8 | 56,808 |
| Y9 and beyond | 113,616 |
| Total lease payments | 397,656 |
| Less: Interest @12% | 138,398 |
| Balance of lease liability | $259,258 |
Exercise 17.8
1. Type of lease
This is a capital lease because it does not qualify for the short term exemption and it does not qualify for the low-dollar value exemption.
For the lessor (Kitchener), this is a sales type lease because the collectability of the lease payments is reasonably predictable and there are no uncertainties surround unreimburseable costs.
2. Present value and amortization schedule
| PV | $117,451 |
| Rate | 10% |
| Nper | 6 |
| Pmt | -24,516 |
| FV | 0 |
| Type | 1 |
|
Date |
Cash |
Interest |
Amortization |
Carrying |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/Y4 | 117,451 | |||
| 1/1/Y4 | 24,516 | - | 24,516 | 92,935 |
| 12/31/Y4 | 24,516 | 9,293 | 15,223 | 77,712 |
| 12/31/Y5 | 24,516 | 7,771 | 16,745 | 60,968 |
| 12/31/Y6 | 24,516 | 6,097 | 18,419 | 42,548 |
| 12/31/Y7 | 24,516 | 4,255 | 20,261 | 22,287 |
| 12/31/Y8 | 24,516 | 2,229 | 22,287 | 0 |
| 147,096 | 29,645 | 117,451 |
3. Journal Entries
Waterloo (lessee)
| 1/1/Y4 | Right-of-Use Asset | 117,451 | ||
| Lease Liability | 117,451 | |||
| to set up leased asset and liability | ||||
| 1/1/Y4 | Lease Liability | 24,516 | ||
| Cash | 24,516 | |||
| to record first lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y4 | Depreciation Expense | 19,575 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 19,575 | |||
| ($117,451 / 6 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y4 | Interest Expense | 9,293 | ||
| Interest Payable | 9,293 | |||
| to record interest incurred in Y4 | ||||
| 1/1/Y5 | Interest Payable | 9,293 | ||
| Lease Liability | 15,223 | |||
| Cash | 24,516 | |||
| record lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Depreciation Expense | 19,575 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 19,575 | |||
| ($117,451 / 6 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Interest Expense | 7,771 | ||
| Interest Payable | 7,771 | |||
| to record interest incurred in Y5 | ||||
Kitchener (lessor)
| 1/1/Y4 | Lease Receivable | 147,096 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 86,325 | |||
| Sales Revenue | 117,451 | |||
| Inventory | 86,325 | |||
| Unearned Interest Revenue | 29,645 | |||
| to record lease receivable and sales revenue earned | ||||
| 1/1/Y4 | Cash | 24,516 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 24,516 | |||
| to record lease payment received | ||||
| 12/31/Y4 | Unearned Interest Revenue | 9,293 | ||
| Interest Revenue | 9,293 | |||
| to record interest revenue earned | ||||
| 1/1/Y5 | Cash | 24,516 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 24,516 | |||
| to record lease payment received | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Unearned Interest Revenue | 7,771 | ||
| Interest Revenue | 7,771 | |||
| to record interest revenue earned | ||||
Exercise 17.9
1. Type of lease
| Lease term | 5 | years = | 83.33% | Since 83% > 75% of lease term, it's a capital lease |
| Life of asset | 6 | years |
2. Present value and amortization schedule
| PV | $147,980 |
| Rate | 5% |
| Nper | 5 |
| Pmt | -32,552 |
| FV | 0 |
| Type | 1 |
|
Date |
Cash |
Interest |
Amortization |
Carrying Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/Y5 | 147,980 | |||
| 1/1/Y5 | 32,552 | - | 32,552 | 115,428 |
| 12/31/Y5 | 32,552 | 5,771 | 26,781 | 88,647 |
| 12/31/Y6 | 32,552 | 4,432 | 28,120 | 60,528 |
| 12/31/Y7 | 32,552 | 3,026 | 29,526 | 31,002 |
| 12/31/Y8 | 32,552 | 1,550 | 31,002 | 0 |
| 162,760 | 14,780 | 147,980 |
3. Journal entries
Paulus (lessee)
| 1/1/Y5 | Equipment under lease | 147,980 | ||
| Obligation under lease | 147,980 | |||
| to set up leased asset and obligation | ||||
| 1/1/Y5 | Obligation under lease | 32,552 | ||
| Cash | 32,552 | |||
| to record lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Depreciation Expense | 29,596 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 29,596 | |||
| ($147,980 / 5 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Interest Expense | 5,771 | ||
| Interest Payable | 5,771 | |||
| to account for interest incurred | ||||
| 1/1/Y6 | Interest Payable | 5,771 | ||
| Obligation under lease | 26,781 | |||
| Cash | 32,552 | |||
| to record lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y6 | Depreciation Expense | 29,596 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 29,596 | |||
| ($147,980 / 5 years) | ||||
| 12/31/Y6 | Interest Expense | 4,432 | ||
| Interest Payable | 4,432 | |||
| to account for interest incurred | ||||
Min (lessor)
| 1/1/Y5 | Lease Receivable | 162,760 | ||
| Equipment acquired for lessee | 147,980 | |||
| Unearned Interest Revenue | 14,780 | |||
| to setup lease receivable | ||||
| 1/1/Y5 | Cash | 32,552 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 32,552 | |||
| to record receipt of lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y5 | Unearned Interest Revenue | 5,771 | ||
| Interest Revenue | 5,771 | |||
| to record interest revenue earned | ||||
| 1/1/Y6 | Cash | 32,552 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 32,552 | |||
| to record receipt of lease payment | ||||
| 12/31/Y6 | Unearned Interest Revenue | 4,432 | ||
| Interest Revenue | 4,432 | |||
| to record interest revenue earned | ||||