Chapter 15
Solutions
Exercise 15.1
| Item | Taxable Temporary Difference |
Deductible Temporary Different |
Permanent Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A property owner collects rent in advance. The amounts are taxed when they are received. | X | ||
| Depreciation claimed for tax purposes exceeds depreciation charged for accounting purposes. | X | ||
| Dividends received from an investment in another company are reported as income, but are not taxable. | X | ||
| A provision for future warranty costs is recorded but is not deductible for tax purposes until the expenditure is actually incurred. | X | ||
| Membership dues at a golf club are reported as a promotion expense but are not deductible for tax purposes. | X | ||
| Construction revenue is reported using the percentage of completion method but is not taxed until the project is finished. | X | ||
| The present value of the costs for the future site remediation of an oil-drilling property has been capitalized as part of the asset’s carrying value. This will increase the amount of depreciation claimed over the life of the asset. These costs are not deductible for tax purposes until they are actually incurred. | X | ||
| A revaluation surplus (accumulated other comprehensive income) is reported for assets accounted for under the revaluation model. The gains will not be taxed until the respective assets are sold. | X | ||
| Included in current assets is a prepaid expense that is fully deductible for tax purposes when paid. | X | ||
| A penalty is paid for the late filing of the company’s income tax return. This penalty is not deductible for tax purposes. | X |
Exercise 15.2
| Amount | ||
|---|---|---|
| Accounting profit | $350,000 | |
| Permanent difference: | ||
|
Life insurance not taxable |
(100,000) | |
| Temporary difference: | ||
|
Depreciation not deductible |
20,000 | |
| Taxable profit | 270,000 | |
| Tax rate | 20% | |
| Current tax payable | $54,000 |
| Tax expense comprised of: | ||
|
Current tax expense |
$54,000 | |
|
Deferred tax income ( |
(4,000) | |
|
Total tax expense |
$50,000 |
Exercise 15.3
- Current Tax:
Amount Accounting profit $3,500,000 Permanent differences: None
Temporary differences: Construction not yet taxable
(900,000) Capital allowance > depreciation
(1,100,000) Taxable profit 1,500,000 Tax rate 30% Current tax payable $450,000 Temporary difference re: depreciation calculated as follows:
Cost of asset $6,800,000 Accumulated depreciation 1,200,000 Carrying value 5,600,000 Less tax base 4,500,000 Excess capital allowance $1,100,000 Deferred Tax Liability:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Construction revenue 900,000 0 (900,000) 30% (270,000) PPE 5,600,000 4,500,000 (1,100,000) 30% (330,000) Total (600,000) 
-
Profit before tax $3,500,000 Income taxes Current expense
(450,000) Deferred expense
(600,000) (1,050,000) Net profit for the year $2,450,000
Exercise 15.4
- Current Tax:
Amount Accounting profit $3,700,000 Permanent differences: None
Temporary differences: Construction now taxable
900,000 Capital allowance < depreciation
400,000 Taxable profit 5,000,000 Tax rate 30% Current tax payable $1,500,000 Temporary difference re: depreciation calculated as follows:
Cost of asset $6,800,000 Accumulated depreciation 2,600,000 Carrying value 4,200,000 Less tax base 3,500,000 Excess capital allowance $700,000 Since last year’s excess was $1,100,000, $400,000 of the temporary difference reversed during the year.
Deferred Tax Liability:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Const. rev. 0 0 0 30% 0 PPE 4,200,000 3,500,000 (700,000) 30% (210,000) Total (210,000) Opening bal. (600,000) Adjustment 390,000 
-
Profit before tax $3,700,000 Income taxes Current expense
(1,500,000) Deferred income
390,000 (1,110,000) Net profit for the year $2,590,000
Exercise 15.5
- Opening deferred tax liability balance of $17,500 implies an opening temporary difference of (17,500 ÷ 25%) = $70,000. If the carrying amount at 31 December 2021 was $320,000, then the tax base must have been (320,000 – 70,000) = $250,000. At 31 December 2022, the carrying amount will be (320,000 – 50,000) = $270,000. At 31 December 2022, the tax base will be (250,000 – 58,000) = $192,000Current Tax:
Amount Accounting profit $416,000 Permanent differences: Non-deductible entertainment
21,000 Temporary differences: Warranty not deductible in 2022
56,000 Capital allowance > depreciation
(8,000) Taxable profit 485,000 Tax rate 25% Current tax payable $121,250 Deferred Tax Liability:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Warranty (56,000) 0 56,000 25% 14,000 PPE 270,000 192,000 (78,000) 25% (19,500) Total (5,500) Opening bal. (17,500) Adjustment 12,000 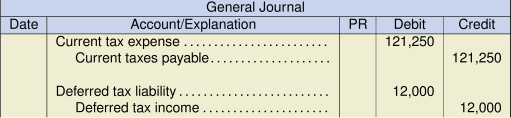
-
Profit before tax $416,000 Income taxes Current expense
(121,250) Deferred income
12,000 (109,250) Net profit for the year $306,750 -
Current Liabilities Income taxes payable
$121,250 Non-Current Liabilities Deferred income taxes
5,500
Exercise 15.6
- Current Tax:
2021 2022 2023 Accounting profit 110,000 242,000 261,000 Permanent differences: Dividend
(10,000) (10,000) (10,000) Temporary differences: (plug to balance)
(15,000) (36,000) 34,000 Taxable profit 85,000 196,000 285,000 Tax rate 20% 23% 23% Current tax payable/exp. 17,000 45,080 65,550 Deferred Tax Liability – 2021:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 15,000 0 (15,000) 20% (3,000) Opening bal. 0 Adjustment (3,000) Deferred Tax Liability – 2022:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 51,000 0 (51,000) 23% (11,730) Opening bal. (3,000) Adjustment (8,730) Deferred Tax Liability – 2023:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 17,000 0 (17,000) 23% (3,910) Opening bal. (11,730) Adjustment (7,820) - Summary:
Income Statement2021 2022 2023 Current tax expense 17,000 45,080 65,550 Deferred tax expense (income) 3,000 8,730 (7,820) Balance Sheet
2021 2022 2023 Deferred tax liability 3,000 11,730 3,910 -
Profit before tax $242,000 Income taxes Current
45,080 Deferred resulting from temporary differences
8,280 Deferred resulting from tax rate change
450 53,810 Net profit for the year $188,190 Note: The deferred tax resulting from the rate change is calculated as the opening temporary difference from 2021 multiplied by the rate differential: $15,000 × (23% – 20%) = $450. The deferred tax resulting from temporary differences is calculated as the current year temporary differences multiplied by the current rate: $36,000 × 23% = $8,280. Deferred tax adjustments resulting from rate changes must be disclosed separately from deferred tax adjustments resulting from changes in temporary differences.
Exercise 15.7
- Current Tax:
2021 2022 2023 Accounting profit 110,000 242,000 261,000 Permanent differences: Dividend
(10,000) (10,000) (10,000) Temporary differences: (plug to balance)
(15,000) (36,000) 34,000 Taxable profit 85,000 196,000 285,000 Tax rate 20% 23% 23% Current tax payable/exp. 17,000 45,080 65,550 Deferred Tax Liability – 2021:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 15,000 0 (15,000) 23% (3,450) Opening bal. 0 Adjustment (3,450) NOTE: Deferred tax is recorded at the rate expected to be in effect. This is substantively enacted rate at the end of 2021.
Deferred Tax Liability – 2022:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 51,000 0 (51,000) 23% (11,730) Opening bal. (3,450) Adjustment (8,280) Deferred Tax Liability – 2023:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 17,000 0 (17,000) 23% (3,910) Opening bal. (11,730) Adjustment 7,820 - Summary:
2021 2022 2023 Current tax expense 17,000 45,080 65,550 Deferred tax expense (income) 3,450 8,280 (7,820) Deferred tax liability 3,450 11,730 3,910 -
Profit before tax $242,000 Income taxes Current
45,080 Deferred
8,280 53,360 Net profit for the year $188,640 Note: The deferred tax resulting from the rate change does not need to be reported as it was already accounted for in 2021.
Exercise 15.8
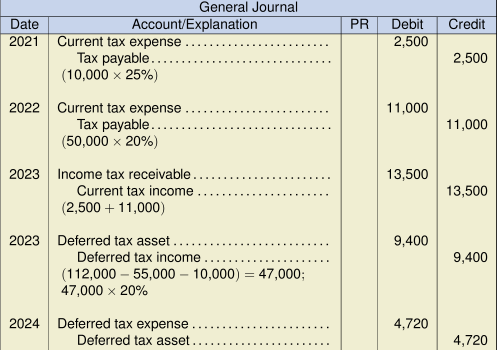
(47,000 – 21,000) = 26,000 ending balance of carry forward after applying loss to reduce current taxable income to 0
Ending deferred tax = 26,000 × 18% = 4,680
Adjustment to deferred tax asset = 9,400 – 4,680 = 4,720. There is no adjustment for current taxes in 2024 because taxable income has been reduced to 0 by the carryforward.
No j/e in 2023 for the benefit of the loss carry forward, as the asset is not recognized. However, disclosure will be made of the unrecorded carry forward amount (47,000). No j/e in 2024, as current tax will be 0 and no deferred tax asset will be established. However, disclosure is required of the current tax expense components:Current tax expense 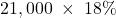
$3,780 Less benefit of loss carried forward (3,780) Current tax expense $0 As well, disclosure of the remaining, unrecorded loss carried forward (26,000) would continue.
Exercise 15.9
- Current Tax:
Amount Accounting profit $750,000 Permanent differences: Non-deductible fines
12,000 Non-taxable dividends
(7,500) Temporary differences: Previously taxed revenue now earned
(95,000) New subscriptions taxed but not earned
68,000 Capital allowance < depreciation
13,000 Taxable profit 740,500 Tax rate 30% Current tax payable $222,150 Deferred Tax:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Unearned revenue (220,000) 0 220,000 30% 66,000 PPE 298,000 192,000 (106,000) 30% (31,800) Total 34,200 Opening bal. 38,400 Adjustment (4,200) Unearned revenue =
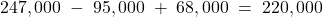
Carrying amount PPE =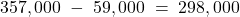
Tax base PPE =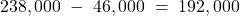

-
Profit before tax $750,000 Income taxes Current expense
(222,150) Deferred expense
(4,200) (226,350) Net profit for the year $523,650 -
2022 2021 Current assets Income taxes receivable
– 16,250 Non-current assets Deferred income taxes
34,200 38,400 Current liabilities Income taxes payable
222,150 –
Exercise 15.10
- Deferred Tax Liability – 2021:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 180,000 165,000 (15,000) 25% (3,750) Opening bal. 0 Adjustment (3,750) Deferred Tax Liability – 2022:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 160,000 135,000 (25,000) 30% (7,500) Opening bal. (3,750) Adjustment (3,750) Deferred Tax Liability – 2023:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 140,000 135,000 (5,000) 35% (1,750) Opening bal. (7,500) Adjustment 5,750 Deferred Tax Liability/Asset – 2024:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 120,000 135,000 15,000 35% 5,250 Opening bal. (1,750) Adjustment 7,000 Deferred Tax Asset – 2025:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Temp Diff 100,000 110,000 10,000 30% 3,000 Opening bal. 5,250 Adjustment (2,250) NOTE: The carrying amount/tax base are determined by taking the original cost of $200,000 and deducting the accumulated depreciation/accumulated capital allowances at the end of each year.
- Current taxes
2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 Accounting profit (loss) reported 150,000 60,000 (440,000) (80,000) 350,000 Temporary difference: Depreciation expense
20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 Capital allowance claimed for
tax purposes
(35,000) (30,000) 0 0 (25,000) Taxable profit (loss) 135,000 50,000 (420,000) (60,000) 345,000 Enacted tax rate 25% 30% 35% 35% 30% Tax payable (refund) 33,750 15,000 (48,750)* 0** 15,000*** * In 2023, a tax refund is generated as follows:
Tax loss applied to 2021 taxable profit 135,000 Rate 25% Refund 33,750 Tax loss applied to 2022 taxable profit 50,000 Rate 30% Refund 15,000 Total refund and tax income for the year $48,750 ** In 2024, the additional loss cannot be carried back, as there are no further taxable profits to apply it against. Therefore, no tax refund is generated.
*** In 2025, the current tax payable is determined as follows:
Taxable profit 345,000 Less loss carry forward applied: 2023 tax loss
(420,000) Applied to 2021
135,000 Applied to 2022
50,000 2024 loss
(60,000) Total loss available in 2025
(295,000) Taxable profit after loss carry forward applied 50,000 Tax rate 30% Tax payable 15,000 -
2023 2024 Opening balance of loss 0 (235,000) Current tax loss/profit (420,000) (60,000) Carried back to 2021 and 2022 185,000 – Balance to carry forward (235,000) (295,000) Probability of use 80% 10% Expected benefit (188,000) 0 Tax rate 35% 35% Deferred tax asset 65,800 0 Opening balance 0 65,800 Adjustment required 65,800 (65,800) In 2024, management’s estimate of its ability to utilize the tax losses has dropped to 10%, which means it is no longer probable that the asset can be realized. At this point, the asset should be derecognized.
In 2025, the balance of the loss ($295,000) can be fully used against current taxable profit ($345,000). In 2025, the company will record current tax income of $295,000 × 30% = $88,500. This will offset the current tax expense of $345,000 × 30% = $103,500, leaving a net current tax expense of $15,000. Although there is no deferred tax adjustment as the asset was previously derecognized, disclosure of the two different components of current tax expense will be required.
-
2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 Current tax expense (income) 33,750 15,000 (48,750) 0 15,000 (from part b)
Deferred tax expense (income) – PPE 3,750 3,750 (5,750) (7,000) 2,250 (from part a)
Deferred tax (income) expense – loss 0 0 (65,800) 65,800 0 (from part c)
Total tax expense (income) 37,500 18,750 (120,300) 58,800 17,250
Exercise 15.11
- Current Tax:
Amount Accounting profit $150,000 Permanent differences: None
Temporary differences: Unearned rent taxed in current year
96,000 Construction revenue not taxable
(90,000) Capital allowance > depreciation
(4,000) Taxable income 152,000 Tax rate 30% Current tax payable $45,600 Future Tax:
Item Carrying Amount Tax Base Temp. Diff. Rate Deferred Tax Unearned rent revenue (96,000) 0 96,000 30% 28,800 Construction revenue 90,000 0 (90,000) 30% (27,000) PPE 108,000 119,000 11,000 30% 3,300 Total 5,100 Opening bal. 4,500 Adjustment 600 NOTE: Opening balance =
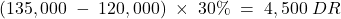
Summary:
Current tax expense $(45,600) Future tax benefit 600 Total tax expense $(45,000) - Balance sheet presentation
Non-current assets Future income taxes
$17,700 Current liabilities Income taxes payable
45,600 Future income taxes
12,600 NOTE:
Non-current future tax asset =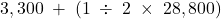
Current future tax liability =
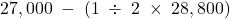
One-half of the future tax related to unearned revenue is classified as current and one-half as non-current because this is way in which the underlying unearned revenue would be classified. The future tax related to construction revenue is classified as current because the underlying construction in process account would be classified this way. The future tax related to the PPE is classified as non-current because PPE would be classified as non-current.
- Income Statement Presentation:
Income tax expense $(45,600) Balance Sheet Presentation:
Current liabilities Income tax payable
$45,600 No future tax amounts are recorded.
Exercise 15.12
1. Deferred tax asset or liability
|
Balance Sheet |
Tax Base |
Accounting Base |
Difference |
Tax % |
DTA (DTL) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCC | -$10,500 | $- | -$10,500 | 20% | -$2,100 | DTL (since negative) |
2. Taxable income
| Accounting income | $103,600 | ||
| Permanent difference: | |||
| CEO Life insurance | 6,820 | add back since NOT deductible for tax purposes | |
| Temporary difference | |||
| CCA > Depreciation | -10,500 | from above | |
| Taxable income | 99,920 | ||
| Tax rate | 20% | ||
| Income tax expense | $19,984 | ||
| Note: CCA = Capital Cost Allowance | |||
3. Journal entries
| Current tax expense | 19,984 | ||
| Income tax payable | 19,984 | ||
| to record current taxes based on taxable income | |||
| Deferred tax expense | 2,100 | ||
| Deferred tax Liability | 2,100 | ||
| to record deferred taxes based on temporary difference | |||
4. Partial income statement
| Income before taxes | $103,600 | ||
| Income tax | |||
| Current | 19,984 | ||
| Deferred | 2,100 | 22,084 | |
| Net income | $81,516 | ||
Exercise 15.13
1. Deferred tax asset or liability
|
Balance Sheet |
Tax Base |
Accounting Base |
Difference |
Tax % |
DTA (DTL) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warranty | $- | -$75,000 | $75,000 | 30% | $22,500 | DTA (positive) |
| UCC | -$124,900 | $- | -$124,900 | 30% | -$37,470 | DTL (negative) |
| -$14,970 | DTL (net) |
2. Taxable income
| Accounting income | $347,800 | ||
| Permanent difference: | |||
| CEO Life insurance | 14,550 | add back since NOT deductible for tax purposes | |
| Fines and penalties | 10,250 | ||
| Temporary difference | |||
| Warranties | 75,000 | ||
| CCA > Depreciation | -124,900 | ||
| Taxable income | 322,700 | ||
| Tax rate | 30% | ||
| Income tax expense | $96,810 | ||
| Note: CCA = Capital Cost Allowance | |||
3. Journal entries
| Current tax expense | 96,810 | ||
| Income tax payable | 96,810 | ||
| to record current taxes based on taxable income | |||
| Deferred tax expense | 14,970 | ||
| Deferred tax Liability | 14,970 | ||
| to record deferred taxes based on temporary difference | |||
4. Partial income statement
| Income before taxes | $347,800 | ||
| Income tax | |||
| Current | 96,810 | ||
| Deferred | 14,970 | 111,780 | |
| Net income | $236,020 | ||
Exercise 15.14
| Y3 | Income Tax Expense | 31,575 | |||
| Income Tax Payable | 31,575 | ||||
| ($126,300 × 25%) | |||||
| Y4 | Income Tax Expense | 24,650 | |||
| Income Tax Payable | 24,650 | ||||
| ($98,600 × 25%) | |||||
| Y5 | Income Tax Expense | 11,780 | |||
| Income Tax Payable | 11,780 | ||||
| (58,900 × 20%) | |||||
| Y6 | Income Tax Receivable | 25,400 | |||
| Current Income tax Expense | 25,400 | ||||
| apply Y6 loss to request refund from Y3 ($101,600 × 25%) | |||||
| Y7 | Income Tax Receivable | 42,605 | |||
| Income tax benefit | 42,605 | ||||
| remaining income from Y3 | 24,700 | × 25% | 6,175 | ||
| request refund from Y4 | 98,600 | × 25% | 24,650 | ||
| request refund from Y5 | 58,900 | × 20% | 11,780 | ||
| loss used | 182,200 | 42,605 (refund of prior taxes) |
|||
| available loss | 198,500 | ||||
| to carryforward | 16,300 | × 20% | 3,260 | ||
| Y7 | Deferred tax asset | 3,260 | |||
| Deferred tax expense | 3260 | ||||
| to record carryforward amount to apply (see above) | |||||
| Y8 | Income Tax Expense | 14,640 | |||
| Income Tax Payable | 14,640 | ||||
| ($89,500 × 20%) - ($16,300 × 20%) | |||||
| Deferred tax expense | 3,260 | ||||
| Deferred tax asset | 3,260 | ||||
| Y9 | Income Tax Expense | 41,280 | |||
| Income Tax Payable | 41,280 | ||||
| ($206,400 × 20%) | |||||

