Chapter 4.4: Polar Coordinates
Learning Objectives
In this section, you will:
- Plot points using polar coordinates.
- Convert from polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates.
- Convert from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates.
- Transform equations between polar and rectangular forms.
- Identify and graph polar equations by converting to rectangular equations.
Over 12 kilometers from port, a sailboat encounters rough weather and is blown off course by a 16-knot wind (see (Figure)). How can the sailor indicate his location to the Coast Guard? In this section, we will investigate a method of representing location that is different from a standard coordinate grid.

Plotting Points Using Polar Coordinates
When we think about plotting points in the plane, we usually think of rectangular coordinates ![]() in the Cartesian coordinate plane. However, there are other ways of writing a coordinate pair and other types of grid systems. In this section, we introduce to polar coordinates, which are points labeled
in the Cartesian coordinate plane. However, there are other ways of writing a coordinate pair and other types of grid systems. In this section, we introduce to polar coordinates, which are points labeled ![]() and plotted on a polar grid. The polar grid is represented as a series of concentric circles radiating out from the pole, or the origin of the coordinate plane.
and plotted on a polar grid. The polar grid is represented as a series of concentric circles radiating out from the pole, or the origin of the coordinate plane.
The polar grid is scaled as the unit circle with the positive x-axis now viewed as the polar axis and the origin as the pole. The first coordinate ![]() is the radius or length of the directed line segment from the pole. The angle
is the radius or length of the directed line segment from the pole. The angle ![]() measured in radians, indicates the direction of
measured in radians, indicates the direction of ![]() We move counterclockwise from the polar axis by an angle of
We move counterclockwise from the polar axis by an angle of ![]() and measure a directed line segment the length of
and measure a directed line segment the length of ![]() in the direction of
in the direction of ![]() Even though we measure
Even though we measure ![]() first and then
first and then ![]() the polar point is written with the r-coordinate first. For example, to plot the point
the polar point is written with the r-coordinate first. For example, to plot the point ![]() we would move
we would move ![]() units in the counterclockwise direction and then a length of 2 from the pole. This point is plotted on the grid in (Figure).
units in the counterclockwise direction and then a length of 2 from the pole. This point is plotted on the grid in (Figure).

Plotting a Point on the Polar Grid
Plot the point ![]() on the polar grid.
on the polar grid.
Show Solution
The angle ![]() is found by sweeping in a counterclockwise direction 90° from the polar axis. The point is located at a length of 3 units from the pole in the
is found by sweeping in a counterclockwise direction 90° from the polar axis. The point is located at a length of 3 units from the pole in the ![]() direction, as shown in (Figure).
direction, as shown in (Figure).

Try It
Plot the point ![]() in the polar grid.
in the polar grid.
Show Solution

Plotting a Point in the Polar Coordinate System with a Negative Component
Plot the point ![]() on the polar grid.
on the polar grid.
Show Solution
We know that ![]() is located in the first quadrant. However,
is located in the first quadrant. However, ![]() We can approach plotting a point with a negative
We can approach plotting a point with a negative ![]() in two ways:
in two ways:
- Plot the point
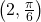 by moving
by moving 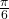 in the counterclockwise direction and extending a directed line segment 2 units into the first quadrant. Then retrace the directed line segment back through the pole, and continue 2 units into the third quadrant;
in the counterclockwise direction and extending a directed line segment 2 units into the first quadrant. Then retrace the directed line segment back through the pole, and continue 2 units into the third quadrant; - Move
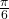 in the counterclockwise direction, and draw the directed line segment from the pole 2 units in the negative direction, into the third quadrant.
in the counterclockwise direction, and draw the directed line segment from the pole 2 units in the negative direction, into the third quadrant.
See (Figure)(a). Compare this to the graph of the polar coordinate ![]() shown in (Figure)(b).
shown in (Figure)(b).

Try It
Plot the points ![]() and
and ![]() on the same polar grid.
on the same polar grid.
Show Solution

Converting from Polar Coordinates to Rectangular Coordinates
When given a set of polar coordinates, we may need to convert them to rectangular coordinates. To do so, we can recall the relationships that exist among the variables ![]() and
and ![]()
Dropping a perpendicular from the point in the plane to the x-axis forms a right triangle, as illustrated in (Figure). An easy way to remember the equations above is to think of ![]() as the adjacent side over the hypotenuse and
as the adjacent side over the hypotenuse and ![]() as the opposite side over the hypotenuse.
as the opposite side over the hypotenuse.

Converting from Polar Coordinates to Rectangular Coordinates
To convert polar coordinates ![]() to rectangular coordinates
to rectangular coordinates ![]() let
let
How To
Given polar coordinates, convert to rectangular coordinates.
- Given the polar coordinate
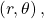 write
write 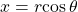 and
and 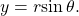
- Evaluate
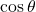 and
and 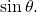
- Multiply
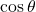 by
by  to find the x-coordinate of the rectangular form.
to find the x-coordinate of the rectangular form. - Multiply
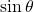 by
by  to find the y-coordinate of the rectangular form.
to find the y-coordinate of the rectangular form.
Writing Polar Coordinates as Rectangular Coordinates
Write the polar coordinates ![]() as rectangular coordinates.
as rectangular coordinates.
Show Solution
Use the equivalent relationships.
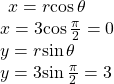
The rectangular coordinates are ![]() See (Figure).
See (Figure).

Writing Polar Coordinates as Rectangular Coordinates
Write the polar coordinates ![]() as rectangular coordinates.
as rectangular coordinates.
Show Solution
See (Figure). Writing the polar coordinates as rectangular, we have
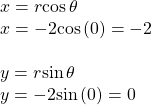
The rectangular coordinates are also ![]()

Try It
Write the polar coordinates ![]() as rectangular coordinates.
as rectangular coordinates.
Show Solution
![]()
Converting from Rectangular Coordinates to Polar Coordinates
To convert rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, we will use two other familiar relationships. With this conversion, however, we need to be aware that a set of rectangular coordinates will yield more than one polar point.
Converting from Rectangular Coordinates to Polar Coordinates
Converting from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates requires the use of one or more of the relationships illustrated in (Figure).
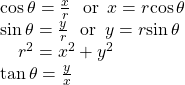

Writing Rectangular Coordinates as Polar Coordinates
Convert the rectangular coordinates ![]() to polar coordinates.
to polar coordinates.
Show Solution
We see that the original point ![]() is in the first quadrant. To find
is in the first quadrant. To find ![]() use the formula
use the formula ![]() This gives
This gives
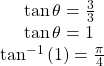
To find ![]() we substitute the values for
we substitute the values for ![]() and
and ![]() into the formula
into the formula ![]() We know that
We know that ![]() must be positive, as
must be positive, as ![]() is in the first quadrant. Thus
is in the first quadrant. Thus
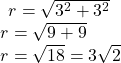
So, ![]() and
and ![]() giving us the polar point
giving us the polar point ![]() See (Figure).
See (Figure).

Analysis
There are other sets of polar coordinates that will be the same as our first solution. For example, the points ![]() and
and ![]() will coincide with the original solution of
will coincide with the original solution of ![]() The point
The point ![]() indicates a move further counterclockwise by
indicates a move further counterclockwise by ![]() which is directly opposite
which is directly opposite ![]() The radius is expressed as
The radius is expressed as ![]() However, the angle
However, the angle ![]() is located in the third quadrant and, as
is located in the third quadrant and, as ![]() is negative, we extend the directed line segment in the opposite direction, into the first quadrant. This is the same point as
is negative, we extend the directed line segment in the opposite direction, into the first quadrant. This is the same point as ![]() The point
The point ![]() is a move further clockwise by
is a move further clockwise by ![]() from
from ![]() The radius,
The radius, ![]() is the same.
is the same.
Transforming Equations between Polar and Rectangular Forms
We can now convert coordinates between polar and rectangular form. Converting equations can be more difficult, but it can be beneficial to be able to convert between the two forms. Since there are a number of polar equations that cannot be expressed clearly in Cartesian form, and vice versa, we can use the same procedures we used to convert points between the coordinate systems. We can then use a graphing calculator to graph either the rectangular form or the polar form of the equation.
How To
Given an equation in polar form, graph it using a graphing calculator.
- Change the MODE to POL, representing polar form.
- Press the Y= button to bring up a screen allowing the input of six equations:
- Enter the polar equation, set equal to
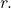
- Press GRAPH.
Writing a Cartesian Equation in Polar Form
Write the Cartesian equation ![]() in polar form.
in polar form.
Show Solution
The goal is to eliminate ![]() and
and ![]() from the equation and introduce
from the equation and introduce ![]() and
and ![]() Ideally, we would write the equation
Ideally, we would write the equation ![]() as a function of
as a function of ![]() To obtain the polar form, we will use the relationships between
To obtain the polar form, we will use the relationships between ![]() and
and ![]() Since
Since ![]() and
and ![]() we can substitute and solve for
we can substitute and solve for ![]()

Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() should generate the same graph. See (Figure).
should generate the same graph. See (Figure).

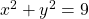 (b) Polar form
(b) Polar form 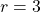
To graph a circle in rectangular form, we must first solve for ![]()
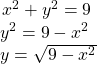
Note that this is two separate functions, since a circle fails the vertical line test. Therefore, we need to enter the positive and negative square roots into the calculator separately, as two equations in the form ![]() and
and ![]() Press GRAPH.
Press GRAPH.
Rewriting a Cartesian Equation as a Polar Equation
Rewrite the Cartesian equation ![]() as a polar equation.
as a polar equation.
Show Solution
This equation appears similar to the previous example, but it requires different steps to convert the equation.
We can still follow the same procedures we have already learned and make the following substitutions:
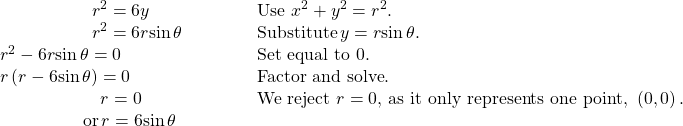
Therefore, the equations ![]() and
and ![]() should give us the same graph. See (Figure).
should give us the same graph. See (Figure).

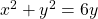 (b) polar form
(b) polar form 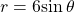
The Cartesian or rectangular equation is plotted on the rectangular grid, and the polar equation is plotted on the polar grid. Clearly, the graphs are identical.
Rewriting a Cartesian Equation in Polar Form
Rewrite the Cartesian equation ![]() as a polar equation.
as a polar equation.
Show Solution
We will use the relationships ![]() and
and ![]()
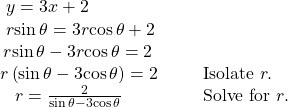
Try It
Rewrite the Cartesian equation ![]() in polar form.
in polar form.
Show Solution
![]()
Identify and Graph Polar Equations by Converting to Rectangular Equations
We have learned how to convert rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, and we have seen that the points are indeed the same. We have also transformed polar equations to rectangular equations and vice versa. Now we will demonstrate that their graphs, while drawn on different grids, are identical.
Graphing a Polar Equation by Converting to a Rectangular Equation
Covert the polar equation ![]() to a rectangular equation, and draw its corresponding graph.
to a rectangular equation, and draw its corresponding graph.
Show Solution
The conversion is
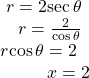
Notice that the equation ![]() drawn on the polar grid is clearly the same as the vertical line
drawn on the polar grid is clearly the same as the vertical line ![]() drawn on the rectangular grid (see (Figure)). Just as
drawn on the rectangular grid (see (Figure)). Just as ![]() is the standard form for a vertical line in rectangular form,
is the standard form for a vertical line in rectangular form, ![]() is the standard form for a vertical line in polar form.
is the standard form for a vertical line in polar form.

A similar discussion would demonstrate that the graph of the function ![]() will be the horizontal line
will be the horizontal line ![]() In fact,
In fact, ![]() is the standard form for a horizontal line in polar form, corresponding to the rectangular form
is the standard form for a horizontal line in polar form, corresponding to the rectangular form ![]()
Rewriting a Polar Equation in Cartesian Form
Rewrite the polar equation ![]() as a Cartesian equation.
as a Cartesian equation.
Show Solution
The goal is to eliminate ![]() and
and ![]() and introduce
and introduce ![]() and
and ![]() We clear the fraction, and then use substitution. In order to replace
We clear the fraction, and then use substitution. In order to replace ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() we must use the expression
we must use the expression ![]()

The Cartesian equation is ![]() However, to graph it, especially using a graphing calculator or computer program, we want to isolate
However, to graph it, especially using a graphing calculator or computer program, we want to isolate ![]()
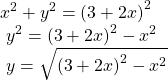
When our entire equation has been changed from ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() and
and ![]() we can stop, unless asked to solve for
we can stop, unless asked to solve for ![]() or simplify. See (Figure).
or simplify. See (Figure).

The “hour-glass” shape of the graph is called a hyperbola. Hyperbolas have many interesting geometric features and applications, which we will investigate further in Analytic Geometry.
Analysis
In this example, the right side of the equation can be expanded and the equation simplified further, as shown above. However, the equation cannot be written as a single function in Cartesian form. We may wish to write the rectangular equation in the hyperbola’s standard form. To do this, we can start with the initial equation.
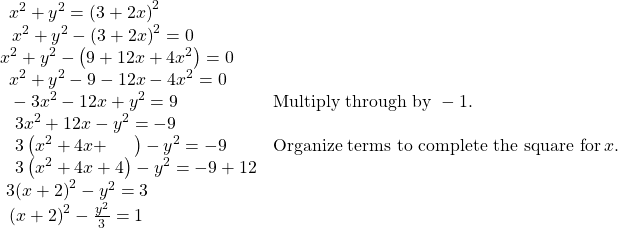
Try It
Rewrite the polar equation ![]() in Cartesian form.
in Cartesian form.
Show Solution
![]() or, in the standard form for a circle,
or, in the standard form for a circle, ![]()
Rewriting a Polar Equation in Cartesian Form
Rewrite the polar equation ![]() in Cartesian form.
in Cartesian form.
Show Solution
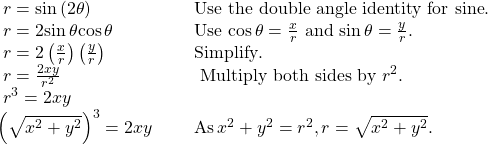
This equation can also be written as
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with polar coordinates.
Key Equations
| Conversion formulas | 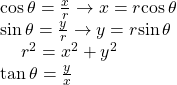 |
Key Concepts
- The polar grid is represented as a series of concentric circles radiating out from the pole, or origin.
- To plot a point in the form
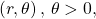 move in a counterclockwise direction from the polar axis by an angle of
move in a counterclockwise direction from the polar axis by an angle of 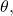 and then extend a directed line segment from the pole the length of
and then extend a directed line segment from the pole the length of  in the direction of
in the direction of 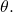 If
If 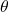 is negative, move in a clockwise direction, and extend a directed line segment the length of
is negative, move in a clockwise direction, and extend a directed line segment the length of  in the direction of
in the direction of 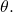 See (Figure).
See (Figure). - If
 is negative, extend the directed line segment in the opposite direction of
is negative, extend the directed line segment in the opposite direction of 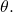 See (Figure).
See (Figure). - To convert from polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates, use the formulas
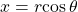 and
and 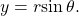 See (Figure) and (Figure).
See (Figure) and (Figure). - To convert from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, use one or more of the formulas:
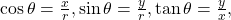 and
and 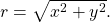 See (Figure).
See (Figure). - Transforming equations between polar and rectangular forms means making the appropriate substitutions based on the available formulas, together with algebraic manipulations. See (Figure), (Figure), and (Figure).
- Using the appropriate substitutions makes it possible to rewrite a polar equation as a rectangular equation, and then graph it in the rectangular plane. See (Figure), (Figure), and (Figure).
Section Exercises
Verbal
1. How are polar coordinates different from rectangular coordinates?
Show Solution
For polar coordinates, the point in the plane depends on the angle from the positive x-axis and distance from the origin, while in Cartesian coordinates, the point represents the horizontal and vertical distances from the origin. For each point in the coordinate plane, there is one representation, but for each point in the polar plane, there are infinite representations.
2. How are the polar axes different from the x– and y-axes of the Cartesian plane?
3. Explain how polar coordinates are graphed.
Show Solution
Determine ![]() for the point, then move
for the point, then move ![]() units from the pole to plot the point. If
units from the pole to plot the point. If ![]() is negative, move
is negative, move ![]() units from the pole in the opposite direction but along the same angle. The point is a distance of
units from the pole in the opposite direction but along the same angle. The point is a distance of ![]() away from the origin at an angle of
away from the origin at an angle of ![]() from the polar axis.
from the polar axis.
4. How are the points ![]() and
and ![]() related?
related?
5. Explain why the points ![]() and
and ![]() are the same.
are the same.
Show Solution
The point ![]() has a positive angle but a negative radius and is plotted by moving to an angle of
has a positive angle but a negative radius and is plotted by moving to an angle of ![]() and then moving 3 units in the negative direction. This places the point 3 units down the negative y-axis. The point
and then moving 3 units in the negative direction. This places the point 3 units down the negative y-axis. The point ![]() has a negative angle and a positive radius and is plotted by first moving to an angle of
has a negative angle and a positive radius and is plotted by first moving to an angle of ![]() and then moving 3 units down, which is the positive direction for a negative angle. The point is also 3 units down the negative y-axis.
and then moving 3 units down, which is the positive direction for a negative angle. The point is also 3 units down the negative y-axis.
Algebraic
For the following exercises, convert the given polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates with ![]() and
and ![]() Remember to consider the quadrant in which the given point is located when determining
Remember to consider the quadrant in which the given point is located when determining ![]() for the point.
for the point.
6. ![]()
7. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
9. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
10. ![]()
For the following exercises, convert the given Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates with ![]() Remember to consider the quadrant in which the given point is located.
Remember to consider the quadrant in which the given point is located.
11. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
13. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
14. ![]()
15. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, convert the given Cartesian equation to a polar equation.
16. ![]()
17. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
18. ![]()
19. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
20. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
22. ![]()
23. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
24. ![]()
25. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
26. ![]()
27. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, convert the given polar equation to a Cartesian equation. Write in the standard form of a conic if possible, and identify the conic section represented.
28. ![]()
29. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() or
or ![]() circle
circle
30. ![]()
31. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() line
line
32. ![]()
33. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() line
line
34. ![]()
35. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() hyperbola
hyperbola
37. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() circle
circle
38. ![]()
39. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() line
line
Graphical
For the following exercises, find the polar coordinates of the point.
40. 

Show Solution
![]()
42. 

Show Solution
![]()

For the following exercises, plot the points.
45. ![]()
Show Solution

46. ![]()
Show Solution

48. ![]()
49. ![]()
Show Solution

50. ![]()
51. ![]()
Show Solution

52. ![]()
53. ![]()
Show Solution

54. ![]()
For the following exercises, convert the equation from rectangular to polar form and graph on the polar axis.
Show Solution
![]()

56. ![]()
57. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

58. ![]()
59. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

60. ![]()
61. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

For the following exercises, convert the equation from polar to rectangular form and graph on the rectangular plane.
62. ![]()
63. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

Show Solution
![]()

66. ![]()
67. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

68. ![]()
Technology
69. Use a graphing calculator to find the rectangular coordinates of ![]() Round to the nearest thousandth.
Round to the nearest thousandth.
Show Solution
![]()
70. Use a graphing calculator to find the rectangular coordinates of ![]() Round to the nearest thousandth.
Round to the nearest thousandth.
71. Use a graphing calculator to find the polar coordinates of ![]() in degrees. Round to the nearest thousandth.
in degrees. Round to the nearest thousandth.
Show Solution
![]()
72. Use a graphing calculator to find the polar coordinates of ![]() in degrees. Round to the nearest hundredth.
in degrees. Round to the nearest hundredth.
73. Use a graphing calculator to find the polar coordinates of ![]() in radians. Round to the nearest hundredth.
in radians. Round to the nearest hundredth.
Show Solution
![]()
Extensions
74. Describe the graph of ![]()
75. Describe the graph of ![]()
Show Solution
A vertical line with ![]() units left of the y-axis.
units left of the y-axis.
76. Describe the graph of ![]()
77. Describe the graph of ![]()
Show Solution
A horizontal line with ![]() units below the x-axis.
units below the x-axis.
78. What polar equations will give an oblique line?
For the following exercise, graph the polar inequality.
79. ![]()
Show Solution

80. ![]()
81. ![]()
Show Solution

83. ![]()
Show Solution

84. ![]()
Glossary
- polar axis
- on the polar grid, the equivalent of the positive x-axis on the rectangular grid
- polar coordinates
- on the polar grid, the coordinates of a point labeled
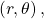 where
where 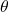 indicates the angle of rotation from the polar axis and
indicates the angle of rotation from the polar axis and  represents the radius, or the distance of the point from the pole in the direction of
represents the radius, or the distance of the point from the pole in the direction of 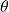
- pole
- the origin of the polar grid

