Chapter 3.2: Angles
Learning Objectives
In this section you will:
- Draw angles in standard position.
- Convert between degrees and radians.
- Find coterminal angles.
- Find the length of a circular arc.
- Use linear and angular speed to describe motion on a circular path.
A golfer swings to hit a ball over a sand trap and onto the green. An airline pilot maneuvers a plane toward a narrow runway. A dress designer creates the latest fashion. What do they all have in common? They all work with angles, and so do all of us at one time or another. Sometimes we need to measure angles exactly with instruments. Other times we estimate them or judge them by eye. Either way, the proper angle can make the difference between success and failure in many undertakings. In this section, we will examine properties of angles.
Drawing Angles in Standard Position
Properly defining an angle first requires that we define a ray. A ray is a directed line segment. It consists of one point on a line and all points extending in one direction from that point. The first point is called the endpoint of the ray. We can refer to a specific ray by stating its endpoint and any other point on it. The ray in (Figure) can be named as ray EF, or in symbol form ![]()

An angle is the union of two rays having a common endpoint. The endpoint is called the vertex of the angle, and the two rays are the sides of the angle. The angle in (Figure) is formed from ![]() and
and ![]() . Angles can be named using a point on each ray and the vertex, such as angle DEF, or in symbol form
. Angles can be named using a point on each ray and the vertex, such as angle DEF, or in symbol form ![]()

Greek letters are often used as variables for the measure of an angle. (Figure) is a list of Greek letters commonly used to represent angles, and a sample angle is shown in (Figure).
| theta | phi | alpha | beta | gamma |

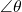
Angle creation is a dynamic process. We start with two rays lying on top of one another. We leave one fixed in place, and rotate the other. The fixed ray is the initial side, and the rotated ray is the terminal side. In order to identify the different sides, we indicate the rotation with a small arrow close to the vertex as in (Figure).

As we discussed at the beginning of the section, there are many applications for angles, but in order to use them correctly, we must be able to measure them. The measure of an angle is the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side. Probably the most familiar unit of angle measurement is the degree. One degree is ![]() of a circular rotation, so a complete circular rotation contains
of a circular rotation, so a complete circular rotation contains ![]() degrees. An angle measured in degrees should always include the unit “degrees” after the number, or include the degree symbol
degrees. An angle measured in degrees should always include the unit “degrees” after the number, or include the degree symbol ![]() For example,
For example, ![]()
To formalize our work, we will begin by drawing angles on an x–y coordinate plane. Angles can occur in any position on the coordinate plane, but for the purpose of comparison, the convention is to illustrate them in the same position whenever possible. An angle is in standard position if its vertex is located at the origin, and its initial side extends along the positive x-axis. See (Figure).

If the angle is measured in a counterclockwise direction from the initial side to the terminal side, the angle is said to be a positive angle. If the angle is measured in a clockwise direction, the angle is said to be a negative angle.
Drawing an angle in standard position always starts the same way—draw the initial side along the positive x-axis. To place the terminal side of the angle, we must calculate the fraction of a full rotation the angle represents. We do that by dividing the angle measure in degrees by ![]() For example, to draw a
For example, to draw a ![]() angle, we calculate that
angle, we calculate that ![]() So, the terminal side will be one-fourth of the way around the circle, moving counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. To draw a
So, the terminal side will be one-fourth of the way around the circle, moving counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. To draw a ![]() angle, we calculate that
angle, we calculate that ![]() So the terminal side will be 1 complete rotation around the circle, moving counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. In this case, the initial side and the terminal side overlap. See (Figure).
So the terminal side will be 1 complete rotation around the circle, moving counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. In this case, the initial side and the terminal side overlap. See (Figure).

Since we define an angle in standard position by its terminal side, we have a special type of angle whose terminal side lies on an axis, a quadrantal angle. This type of angle can have a measure of ![]() or
or ![]() See (Figure).
See (Figure).

Quadrantal Angles
An angle is a quadrantal angle if its terminal side lies on an axis, including ![]() or
or ![]()
How To
Given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position.
- Express the angle measure as a fraction of
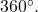
- Reduce the fraction to simplest form.
- Draw an angle that contains that same fraction of the circle, beginning on the positive x-axis and moving counterclockwise for positive angles and clockwise for negative angles.
Drawing an Angle in Standard Position Measured in Degrees
- Sketch an angle of
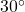 in standard position.
in standard position. - Sketch an angle of
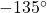 in standard position.
in standard position.
Show Solution
-
Divide the angle measure by
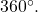
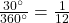
To rewrite the fraction in a more familiar fraction, we can recognize that
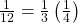
One-twelfth equals one-third of a quarter, so by dividing a quarter rotation into thirds, we can sketch a line at
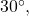 as in (Figure).
as in (Figure).
Figure 8. -
Divide the angle measure by
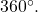
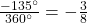
In this case, we can recognize that
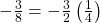
Negative three-eighths is one and one-half times a quarter, so we place a line by moving clockwise one full quarter and one-half of another quarter, as in (Figure).

Figure 9.
Try It
Show an angle of ![]() on a circle in standard position.
on a circle in standard position.
Show Solution

Converting Between Degrees and Radians
Dividing a circle into 360 parts is an arbitrary choice, although it creates the familiar degree measurement. We may choose other ways to divide a circle. To find another unit, think of the process of drawing a circle. Imagine that you stop before the circle is completed. The portion that you drew is referred to as an arc. An arc may be a portion of a full circle, a full circle, or more than a full circle, represented by more than one full rotation. The length of the arc around an entire circle is called the circumference of that circle.
The circumference of a circle is ![]() If we divide both sides of this equation by
If we divide both sides of this equation by ![]() we create the ratio of the circumference, which is always
we create the ratio of the circumference, which is always ![]() to the radius, regardless of the length of the radius. So the circumference of any circle is
to the radius, regardless of the length of the radius. So the circumference of any circle is ![]() times the length of the radius. That means that if we took a string as long as the radius and used it to measure consecutive lengths around the circumference, there would be room for six full string-lengths and a little more than a quarter of a seventh, as shown in (Figure).
times the length of the radius. That means that if we took a string as long as the radius and used it to measure consecutive lengths around the circumference, there would be room for six full string-lengths and a little more than a quarter of a seventh, as shown in (Figure).

This brings us to our new angle measure. One radian is the measure of a central angle of a circle that intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of that circle. A central angle is an angle formed at the center of a circle by two radii. Because the total circumference equals ![]() times the radius, a full circular rotation is
times the radius, a full circular rotation is ![]() radians.
radians.
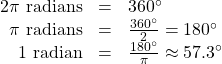
See (Figure). Note that when an angle is described without a specific unit, it refers to radian measure. For example, an angle measure of 3 indicates 3 radians. In fact, radian measure is dimensionless, since it is the quotient of a length (circumference) divided by a length (radius) and the length units cancel.

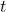 sweeps out a measure of one radian. Note that the length of the intercepted arc is the same as the length of the radius of the circle.
sweeps out a measure of one radian. Note that the length of the intercepted arc is the same as the length of the radius of the circle.Relating Arc Lengths to Radius
An arc length ![]() is the length of the curve along the arc. Just as the full circumference of a circle always has a constant ratio to the radius, the arc length produced by any given angle also has a constant relation to the radius, regardless of the length of the radius.
is the length of the curve along the arc. Just as the full circumference of a circle always has a constant ratio to the radius, the arc length produced by any given angle also has a constant relation to the radius, regardless of the length of the radius.
This ratio, called the radian measure, is the same regardless of the radius of the circle—it depends only on the angle. This property allows us to define a measure of any angle as the ratio of the arc length ![]() to the radius r. See (Figure).
to the radius r. See (Figure).
If ![]() then
then ![]()

 equals the radius
equals the radius 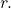 (b) An angle of 2 radians has an arc length
(b) An angle of 2 radians has an arc length 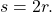 (c) A full revolution is
(c) A full revolution is 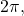 or about 6.28 radians.
or about 6.28 radians.To elaborate on this idea, consider two circles, one with radius 2 and the other with radius 3. Recall the circumference of a circle is ![]() where
where ![]() is the radius. The smaller circle then has circumference
is the radius. The smaller circle then has circumference ![]() and the larger has circumference
and the larger has circumference ![]() Now we draw a
Now we draw a ![]() angle on the two circles, as in (Figure).
angle on the two circles, as in (Figure).

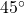 angle contains one-eighth of the circumference of a circle, regardless of the radius.
angle contains one-eighth of the circumference of a circle, regardless of the radius.Notice what happens if we find the ratio of the arc length divided by the radius of the circle.
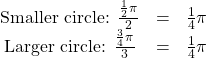
Since both ratios are ![]() the angle measures of both circles are the same, even though the arc length and radius differ.
the angle measures of both circles are the same, even though the arc length and radius differ.
Radians
One radian is the measure of the central angle of a circle such that the length of the arc between the initial side and the terminal side is equal to the radius of the circle. A full revolution ![]() equals
equals ![]() radians. A half revolution
radians. A half revolution ![]() is equivalent to
is equivalent to ![]() radians.
radians.
The radian measure of an angle is the ratio of the length of the arc subtended by the angle to the radius of the circle. In other words, if ![]() is the length of an arc of a circle, and
is the length of an arc of a circle, and ![]() is the radius of the circle, then the central angle containing that arc measures
is the radius of the circle, then the central angle containing that arc measures ![]() radians. In a circle of radius 1, the radian measure corresponds to the length of the arc.
radians. In a circle of radius 1, the radian measure corresponds to the length of the arc.
A measure of 1 radian looks to be about ![]() Is that correct?
Is that correct?
Yes. It is approximately ![]() Because
Because ![]() radians equals
radians equals ![]() radian equals
radian equals ![]()
Using Radians
Because radian measure is the ratio of two lengths, it is a unitless measure. For example, in (Figure), suppose the radius were 2 inches and the distance along the arc were also 2 inches. When we calculate the radian measure of the angle, the “inches” cancel, and we have a result without units. Therefore, it is not necessary to write the label “radians” after a radian measure, and if we see an angle that is not labeled with “degrees” or the degree symbol, we can assume that it is a radian measure.
Considering the most basic case, the unit circle (a circle with radius 1), we know that 1 rotation equals 360 degrees, ![]() We can also track one rotation around a circle by finding the circumference,
We can also track one rotation around a circle by finding the circumference, ![]() and for the unit circle
and for the unit circle ![]() These two different ways to rotate around a circle give us a way to convert from degrees to radians.
These two different ways to rotate around a circle give us a way to convert from degrees to radians.
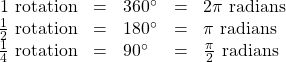
Identifying Special Angles Measured in Radians
In addition to knowing the measurements in degrees and radians of a quarter revolution, a half revolution, and a full revolution, there are other frequently encountered angles in one revolution of a circle with which we should be familiar. It is common to encounter multiples of 30, 45, 60, and 90 degrees. These values are shown in (Figure). Memorizing these angles will be very useful as we study the properties associated with angles.

Now, we can list the corresponding radian values for the common measures of a circle corresponding to those listed in (Figure), which are shown in (Figure). Be sure you can verify each of these measures.

Finding a Radian Measure
Find the radian measure of one-third of a full rotation.
Show Solution
For any circle, the arc length along such a rotation would be one-third of the circumference. We know that
So,
The radian measure would be the arc length divided by the radius.
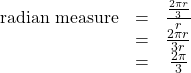
Try It
Find the radian measure of three-fourths of a full rotation.
Show Solution
![]()
Converting Between Radians and Degrees
Because degrees and radians both measure angles, we need to be able to convert between them. We can easily do so using a proportion where ![]() is the measure of the angle in degrees and
is the measure of the angle in degrees and ![]() is the measure of the angle in radians.
is the measure of the angle in radians.
This proportion shows that the measure of angle ![]() in degrees divided by 180 equals the measure of angle
in degrees divided by 180 equals the measure of angle ![]() in radians divided by
in radians divided by ![]() Or, phrased another way, degrees is to 180 as radians is to
Or, phrased another way, degrees is to 180 as radians is to ![]()
Converting between Radians and Degrees
To convert between degrees and radians, use the proportion
![]()
Converting Radians to Degrees
Convert each radian measure to degrees.
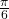
- 3
Show Solution
Because we are given radians and we want degrees, we should set up a proportion and solve it.
- We use the proportion, substituting the given information.
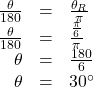
- We use the proportion, substituting the given information.
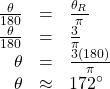
Try It
Convert ![]() radians to degrees.
radians to degrees.
Show Solution
![]()
Converting Degrees to Radians
Convert ![]() degrees to radians.
degrees to radians.
Show Solution
In this example, we start with degrees and want radians, so we again set up a proportion, but we substitute the given information into a different part of the proportion.
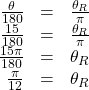
Analysis
Another way to think about this problem is by remembering that ![]() Because
Because ![]() we can find that
we can find that ![]() is
is ![]()
Try It
Convert ![]() to radians.
to radians.
Show Solution
![]()
Finding Coterminal Angles
Converting between degrees and radians can make working with angles easier in some applications. For other applications, we may need another type of conversion. Negative angles and angles greater than a full revolution are more awkward to work with than those in the range of ![]() to
to ![]() or
or ![]() to
to ![]() It would be convenient to replace those out-of-range angles with a corresponding angle within the range of a single revolution.
It would be convenient to replace those out-of-range angles with a corresponding angle within the range of a single revolution.
It is possible for more than one angle to have the same terminal side. Look at (Figure). The angle of ![]() is a positive angle, measured counterclockwise. The angle of
is a positive angle, measured counterclockwise. The angle of ![]() is a negative angle, measured clockwise. But both angles have the same terminal side. If two angles in standard position have the same terminal side, they are coterminal angles. Every angle greater than
is a negative angle, measured clockwise. But both angles have the same terminal side. If two angles in standard position have the same terminal side, they are coterminal angles. Every angle greater than ![]() or less than
or less than ![]() is coterminal with an angle between
is coterminal with an angle between ![]() and
and ![]() and it is often more convenient to find the coterminal angle within the range of
and it is often more convenient to find the coterminal angle within the range of ![]() to
to ![]() than to work with an angle that is outside that range.
than to work with an angle that is outside that range.

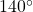 and an angle of
and an angle of 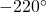 are coterminal angles.
are coterminal angles.Any angle has infinitely many coterminal angles because each time we add ![]() to that angle—or subtract
to that angle—or subtract ![]() from it—the resulting value has a terminal side in the same location. For example,
from it—the resulting value has a terminal side in the same location. For example, ![]() and
and ![]() are coterminal for this reason, as is
are coterminal for this reason, as is ![]()
An angle’s reference angle is the measure of the smallest, positive, acute angle ![]() formed by the terminal side of the angle
formed by the terminal side of the angle ![]() and the horizontal axis. Thus positive reference angles have terminal sides that lie in the first quadrant and can be used as models for angles in other quadrants. See (Figure) for examples of reference angles for angles in different quadrants.
and the horizontal axis. Thus positive reference angles have terminal sides that lie in the first quadrant and can be used as models for angles in other quadrants. See (Figure) for examples of reference angles for angles in different quadrants.

Coterminal and Reference Angles
Coterminal angles are two angles in standard position that have the same terminal side.
An angle’s reference angle is the size of the smallest acute angle, ![]() formed by the terminal side of the angle
formed by the terminal side of the angle ![]() and the horizontal axis.
and the horizontal axis.
How To
Given an angle greater than ![]() find a coterminal angle between
find a coterminal angle between ![]() and
and ![]()
- Subtract
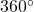 from the given angle.
from the given angle. - If the result is still greater than
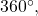 subtract
subtract 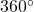 again till the result is between
again till the result is between 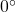 and
and 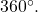
- The resulting angle is coterminal with the original angle.
Finding an Angle Coterminal with an Angle of Measure Greater Than 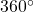
Find the least positive angle ![]() that is coterminal with an angle measuring
that is coterminal with an angle measuring ![]() where
where ![]()
Show Solution
An angle with measure ![]() is coterminal with an angle with measure
is coterminal with an angle with measure ![]() but
but ![]() is still greater than
is still greater than ![]() so we subtract
so we subtract ![]() again to find another coterminal angle:
again to find another coterminal angle: ![]()
The angle ![]() is coterminal with
is coterminal with ![]() To put it another way,
To put it another way, ![]() equals
equals ![]() plus two full rotations, as shown in (Figure).
plus two full rotations, as shown in (Figure).

Try It
Find an angle ![]() that is coterminal with an angle measuring
that is coterminal with an angle measuring ![]() where
where ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
How To
Given an angle with measure less than ![]() find a coterminal angle having a measure between
find a coterminal angle having a measure between ![]() and
and ![]()
- Add
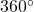 to the given angle.
to the given angle. - If the result is still less than
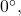 add
add 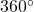 again until the result is between
again until the result is between 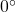 and
and 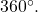
- The resulting angle is coterminal with the original angle.
Finding an Angle Coterminal with an Angle Measuring Less Than 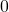
Show the angle with measure ![]() on a circle and find a positive coterminal angle
on a circle and find a positive coterminal angle ![]() such that
such that ![]()
Show Solution
Since ![]() is half of
is half of ![]() we can start at the positive horizontal axis and measure clockwise half of a
we can start at the positive horizontal axis and measure clockwise half of a ![]() angle.
angle.
Because we can find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting a full rotation of ![]() we can find a positive coterminal angle here by adding
we can find a positive coterminal angle here by adding ![]()
We can then show the angle on a circle, as in (Figure).

Try It
Find an angle ![]() that is coterminal with an angle measuring
that is coterminal with an angle measuring ![]() such that
such that ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
Finding Coterminal Angles Measured in Radians
We can find coterminal angles measured in radians in much the same way as we have found them using degrees. In both cases, we find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting one or more full rotations.
How To
Given an angle greater than ![]() find a coterminal angle between 0 and
find a coterminal angle between 0 and ![]()
- Subtract
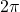 from the given angle.
from the given angle. - If the result is still greater than
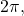 subtract
subtract 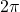 again until the result is between
again until the result is between 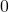 and
and 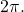
- The resulting angle is coterminal with the original angle.
Finding Coterminal Angles Using Radians
Find an angle ![]() that is coterminal with
that is coterminal with ![]() where
where ![]()
Show Solution
When working in degrees, we found coterminal angles by adding or subtracting 360 degrees, a full rotation. Likewise, in radians, we can find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting full rotations of ![]() radians:
radians:
The angle ![]() is coterminal, but not less than
is coterminal, but not less than ![]() so we subtract another rotation.
so we subtract another rotation.
The angle ![]() is coterminal with
is coterminal with ![]() as shown in (Figure).
as shown in (Figure).

Try It
Find an angle of measure ![]() that is coterminal with an angle of measure
that is coterminal with an angle of measure ![]() where
where ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
Determining the Length of an Arc
Recall that the radian measure ![]() of an angle was defined as the ratio of the arc length
of an angle was defined as the ratio of the arc length ![]() of a circular arc to the radius
of a circular arc to the radius ![]() of the circle,
of the circle, ![]() From this relationship, we can find arc length along a circle, given an angle.
From this relationship, we can find arc length along a circle, given an angle.
Arc Length on a Circle
In a circle of radius r, the length of an arc ![]() subtended by an angle with measure
subtended by an angle with measure ![]() in radians, shown in (Figure), is
in radians, shown in (Figure), is

How To
Given a circle of radius ![]() calculate the length
calculate the length ![]() of the arc subtended by a given angle of measure
of the arc subtended by a given angle of measure ![]()
- If necessary, convert
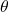 to radians.
to radians. - Multiply the radius
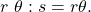
Finding the Length of an Arc
Assume the orbit of Mercury around the sun is a perfect circle. Mercury is approximately 36 million miles from the sun.
- In one Earth day, Mercury completes 0.0114 of its total revolution. How many miles does it travel in one day?
- Use your answer from part (a) to determine the radian measure for Mercury’s movement in one Earth day.
Show Solution
- Let’s begin by finding the circumference of Mercury’s orbit.
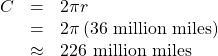
Since Mercury completes 0.0114 of its total revolution in one Earth day, we can now find the distance traveled.
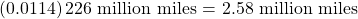
- Now, we convert to radians.

Try It
Find the arc length along a circle of radius 10 units subtended by an angle of ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
Finding the Area of a Sector of a Circle
In addition to arc length, we can also use angles to find the area of a sector of a circle. A sector is a region of a circle bounded by two radii and the intercepted arc, like a slice of pizza or pie. Recall that the area of a circle with radius ![]() can be found using the formula
can be found using the formula ![]() If the two radii form an angle of
If the two radii form an angle of ![]() measured in radians, then
measured in radians, then ![]() is the ratio of the angle measure to the measure of a full rotation and is also, therefore, the ratio of the area of the sector to the area of the circle. Thus, the area of a sector is the fraction
is the ratio of the angle measure to the measure of a full rotation and is also, therefore, the ratio of the area of the sector to the area of the circle. Thus, the area of a sector is the fraction ![]() multiplied by the entire area. (Always remember that this formula only applies if
multiplied by the entire area. (Always remember that this formula only applies if ![]() is in radians.)
is in radians.)
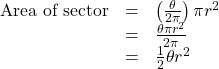
Area of a Sector
The area of a sector of a circle with radius ![]() subtended by an angle
subtended by an angle ![]() measured in radians, is
measured in radians, is
See (Figure).

How To
Given a circle of radius ![]() find the area of a sector defined by a given angle
find the area of a sector defined by a given angle ![]()
- If necessary, convert
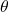 to radians.
to radians. - Multiply half the radian measure of
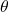 by the square of the radius
by the square of the radius 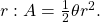
Finding the Area of a Sector
An automatic lawn sprinkler sprays a distance of 20 feet while rotating 30 degrees, as shown in (Figure). What is the area of the sector of grass the sprinkler waters?

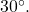
Show Solution
First, we need to convert the angle measure into radians. Because 30 degrees is one of our special angles, we already know the equivalent radian measure, but we can also convert:
The area of the sector is then
So the area is about ![]()
Try It
In central pivot irrigation, a large irrigation pipe on wheels rotates around a center point. A farmer has a central pivot system with a radius of 400 meters. If water restrictions only allow her to water 150 thousand square meters a day, what angle should she set the system to cover? Write the answer in radian measure to two decimal places.
Show Solution
1.88
Use Linear and Angular Speed to Describe Motion on a Circular Path
In addition to finding the area of a sector, we can use angles to describe the speed of a moving object. An object traveling in a circular path has two types of speed. Linear speed is speed along a straight path and can be determined by the distance it moves along (its displacement) in a given time interval. For instance, if a wheel with radius 5 inches rotates once a second, a point on the edge of the wheel moves a distance equal to the circumference, or ![]() inches, every second. So the linear speed of the point is
inches, every second. So the linear speed of the point is ![]() in./s. The equation for linear speed is as follows where
in./s. The equation for linear speed is as follows where ![]() is linear speed,
is linear speed, ![]() is displacement, and
is displacement, and ![]() is time.
is time.
Angular speed results from circular motion and can be determined by the angle through which a point rotates in a given time interval. In other words, angular speed is angular rotation per unit time. So, for instance, if a gear makes a full rotation every 4 seconds, we can calculate its angular speed as ![]() 90 degrees per second. Angular speed can be given in radians per second, rotations per minute, or degrees per hour for example. The equation for angular speed is as follows, where
90 degrees per second. Angular speed can be given in radians per second, rotations per minute, or degrees per hour for example. The equation for angular speed is as follows, where ![]() (read as omega) is angular speed,
(read as omega) is angular speed, ![]() is the angle traversed, and
is the angle traversed, and ![]() is time.
is time.
Combining the definition of angular speed with the arc length equation, ![]() we can find a relationship between angular and linear speeds. The angular speed equation can be solved for
we can find a relationship between angular and linear speeds. The angular speed equation can be solved for ![]() giving
giving ![]() Substituting this into the arc length equation gives:
Substituting this into the arc length equation gives:
Substituting this into the linear speed equation gives:
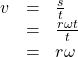
Angular and Linear Speed
As a point moves along a circle of radius ![]() its angular speed,
its angular speed, ![]() is the angular rotation
is the angular rotation ![]() per unit time,
per unit time, ![]()
The linear speed, ![]() of the point can be found as the distance traveled, arc length
of the point can be found as the distance traveled, arc length ![]() per unit time,
per unit time, ![]()
When the angular speed is measured in radians per unit time, linear speed and angular speed are related by the equation
This equation states that the angular speed in radians, ![]() representing the amount of rotation occurring in a unit of time, can be multiplied by the radius
representing the amount of rotation occurring in a unit of time, can be multiplied by the radius ![]() to calculate the total arc length traveled in a unit of time, which is the definition of linear speed.
to calculate the total arc length traveled in a unit of time, which is the definition of linear speed.
How To
Given the amount of angle rotation and the time elapsed, calculate the angular speed.
- If necessary, convert the angle measure to radians.
- Divide the angle in radians by the number of time units elapsed:
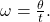
- The resulting speed will be in radians per time unit.
Finding Angular Speed
A water wheel, shown in (Figure), completes 1 rotation every 5 seconds. Find the angular speed in radians per second.

Show Solution
The wheel completes 1 rotation, or passes through an angle of ![]() radians in 5 seconds, so the angular speed would be
radians in 5 seconds, so the angular speed would be ![]() radians per second.
radians per second.
Try It
An old vinyl record is played on a turntable rotating clockwise at a rate of 45 rotations per minute. Find the angular speed in radians per second.
Show Solution
![]() rad/s
rad/s
How To
Given the radius of a circle, an angle of rotation, and a length of elapsed time, determine the linear speed.
- Convert the total rotation to radians if necessary.
- Divide the total rotation in radians by the elapsed time to find the angular speed: apply
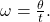
- Multiply the angular speed by the length of the radius to find the linear speed, expressed in terms of the length unit used for the radius and the time unit used for the elapsed time: apply
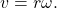
Finding a Linear Speed
A bicycle has wheels 28 inches in diameter. A tachometer determines the wheels are rotating at 180 RPM (revolutions per minute). Find the speed the bicycle is traveling down the road.
Show Solution
Here, we have an angular speed and need to find the corresponding linear speed, since the linear speed of the outside of the tires is the speed at which the bicycle travels down the road.
We begin by converting from rotations per minute to radians per minute. It can be helpful to utilize the units to make this conversion:
Using the formula from above along with the radius of the wheels, we can find the linear speed:
Remember that radians are a unitless measure, so it is not necessary to include them.
Finally, we may wish to convert this linear speed into a more familiar measurement, like miles per hour.
Try It
A satellite is rotating around Earth at 0.25 radian per hour at an altitude of 242 km above Earth. If the radius of Earth is 6378 kilometers, find the linear speed of the satellite in kilometers per hour.
Show Solution
1655 kilometers per hour
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with angles, arc length, and areas of sectors.
Key Equations
| arc length | |
| area of a sector | |
| angular speed | |
| linear speed | |
| linear speed related to angular speed |
Key Concepts
- An angle is formed from the union of two rays, by keeping the initial side fixed and rotating the terminal side. The amount of rotation determines the measure of the angle.
- An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side lies along the positive x-axis. A positive angle is measured counterclockwise from the initial side and a negative angle is measured clockwise.
- To draw an angle in standard position, draw the initial side along the positive x-axis and then place the terminal side according to the fraction of a full rotation the angle represents. See (Figure).
- In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. See (Figure).
- To convert between degrees and radians, use the proportion
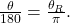 See (Figure) and (Figure).
See (Figure) and (Figure). - Two angles that have the same terminal side are called coterminal angles.
- We can find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting
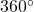 or
or 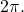 See (Figure) and (Figure).
See (Figure) and (Figure). - Coterminal angles can be found using radians just as they are for degrees. See (Figure).
- The length of a circular arc is a fraction of the circumference of the entire circle. See (Figure).
- The area of sector is a fraction of the area of the entire circle. See (Figure).
- An object moving in a circular path has both linear and angular speed.
- The angular speed of an object traveling in a circular path is the measure of the angle through which it turns in a unit of time. See (Figure).
- The linear speed of an object traveling along a circular path is the distance it travels in a unit of time. See (Figure).
Section Exercises
Verbal
1. Draw an angle in standard position. Label the vertex, initial side, and terminal side.
Show Solution

2. Explain why there are an infinite number of angles that are coterminal to a certain angle.
3. State what a positive or negative angle signifies, and explain how to draw each.
Show Solution
Whether the angle is positive or negative determines the direction. A positive angle is drawn in the counterclockwise direction, and a negative angle is drawn in the clockwise direction.
4. How does radian measure of an angle compare to the degree measure? Include an explanation of 1 radian in your paragraph.
5. Explain the differences between linear speed and angular speed when describing motion along a circular path.
Show Solution
Linear speed is a measurement found by calculating distance of an arc compared to time. Angular speed is a measurement found by calculating the angle of an arc compared to time.
Graphical
For the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure.
6. ![]()
7. ![]()
Show Solution

8. ![]()
9. ![]()
Show Solution

10. ![]()
Show Solution
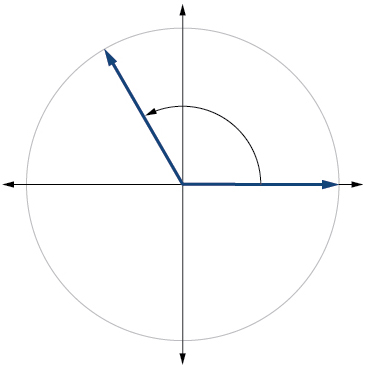
12. ![]()
13. ![]()
Show Solution

14. ![]()
15. ![]()
Show Solution

16. ![]()
17. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

18. ![]()
19. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

20. ![]()
21. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()

For the following exercises, refer to (Figure). Round to two decimal places.

22. Find the arc length.
23. Find the area of the sector.
Show Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, refer to (Figure). Round to two decimal places.

24. Find the arc length.
25. Find the area of the sector.
Show Solution
![]()
Algebraic
For the following exercises, convert angles in radians to degrees.
26. ![]() radians
radians
27. ![]() radians
radians
Show Solution
![]()
28. ![]() radians
radians
29. ![]() radians
radians
Show Solution
![]()
30. ![]() radians
radians
31. ![]() radians
radians
Show Solution
![]()
32. ![]() radians
radians
For the following exercises, convert angles in degrees to radians.
33. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() radians
radians
34. ![]()
35. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() radians
radians
36. ![]()
37. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() radians
radians
38. ![]()
39. ![]()
Show Solution
![]() radians
radians
For the following exercises, use the given information to find the length of a circular arc. Round to two decimal places.
40. Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 12 inches subtended by a central angle of ![]() radians.
radians.
41. Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 5.02 miles subtended by the central angle of ![]()
Show Solution
![]() miles
miles
42. Find the length of the arc of a circle of diameter 14 meters subtended by the central angle of ![]()
43. Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 10 centimeters subtended by the central angle of ![]()
Show Solution
![]() centimeters
centimeters
44. Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 5 inches subtended by the central angle of ![]()
45. Find the length of the arc of a circle of diameter 12 meters subtended by the central angle is ![]()
Show Solution
![]() meters
meters
For the following exercises, use the given information to find the area of the sector. Round to four decimal places.
46. A sector of a circle has a central angle of ![]() and a radius 6 cm.
and a radius 6 cm.
47. A sector of a circle has a central angle of ![]() and a radius of 20 cm.
and a radius of 20 cm.
Show Solution
104.7198 cm2
48. A sector of a circle with diameter 10 feet and an angle of ![]() radians.
radians.
49. A sector of a circle with radius of 0.7 inches and an angle of ![]() radians.
radians.
Show Solution
0.7697 in2
For the following exercises, find the angle between ![]() and
and ![]() that is coterminal to the given angle.
that is coterminal to the given angle.
50. ![]()
51. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
52. ![]()
53. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, find the angle between 0 and ![]() in radians that is coterminal to the given angle.
in radians that is coterminal to the given angle.
54. ![]()
55. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
56. ![]()
57. ![]()
Show Solution
![]()
Real-World Applications
58. A truck with 32-inch diameter wheels is traveling at 60 mi/h. Find the angular speed of the wheels in rad/min. How many revolutions per minute do the wheels make?
59. A bicycle with 24-inch diameter wheels is traveling at 15 mi/h. Find the angular speed of the wheels in rad/min. How many revolutions per minute do the wheels make?
Show Solution
![]() rad/min
rad/min ![]() RPM
RPM
60. A wheel of radius 8 inches is rotating 15^{\circ}/s. What is the linear speed ![]() the angular speed in RPM, and the angular speed in rad/s?
the angular speed in RPM, and the angular speed in rad/s?
61. A wheel of radius ![]() inches is rotating
inches is rotating ![]() rad/s. What is the linear speed
rad/s. What is the linear speed ![]() the angular speed in RPM, and the angular speed in deg/s?
the angular speed in RPM, and the angular speed in deg/s?
Show Solution
![]() in./s, 4.77 RPM ,
in./s, 4.77 RPM , ![]() deg/s
deg/s
62. A CD has diameter of 120 millimeters. When playing audio, the angular speed varies to keep the linear speed constant where the disc is being read. When reading along the outer edge of the disc, the angular speed is about 200 RPM (revolutions per minute). Find the linear speed.
63. When being burned in a writable CD-R drive, the angular speed of a CD is often much faster than when playing audio, but the angular speed still varies to keep the linear speed constant where the disc is being written. When writing along the outer edge of the disc, the angular speed of one drive is about 4800 RPM (revolutions per minute). Find the linear speed if the CD has diameter of 120 millimeters.
Show Solution
![]()
64. A person is standing on the equator of Earth (radius 3960 miles). What are his linear and angular speeds?
65. Find the distance along an arc on the surface of Earth that subtends a central angle of 5 minutes
![]() . The radius of Earth is 3960 miles.
. The radius of Earth is 3960 miles.
Show Solution
![]() miles
miles
Find the distance along an arc on the surface of Earth that subtends a central angle of 7 minutes
66. ![]() . The radius of Earth is
. The radius of Earth is ![]() miles.
miles.
67. Consider a clock with an hour hand and minute hand. What is the measure of the angle the minute hand traces in ![]() minutes?
minutes?
Show Solution
![]()
Extensions
68. Two cities have the same longitude. The latitude of city A is 9.00 degrees north and the latitude of city B is 30.00 degree north. Assume the radius of the earth is 3960 miles. Find the distance between the two cities.
69. A city is located at 40 degrees north latitude. Assume the radius of the earth is 3960 miles and the earth rotates once every 24 hours. Find the linear speed of a person who resides in this city.
Show Solution
794 miles per hour
70. A city is located at 75 degrees north latitude. Assume the radius of the earth is 3960 miles and the earth rotates once every 24 hours. Find the linear speed of a person who resides in this city.
71. Find the linear speed of the moon if the average distance between the earth and moon is 239,000 miles, assuming the orbit of the moon is circular and requires about 28 days. Express answer in miles per hour.
Show Solution
2,234 miles per hour
72. A bicycle has wheels 28 inches in diameter. A tachometer determines that the wheels are rotating at 180 RPM (revolutions per minute). Find the speed the bicycle is travelling down the road.
73. A car travels 3 miles. Its tires make 2640 revolutions. What is the radius of a tire in inches?
Show Solution
11.5 inches
74. A wheel on a tractor has a 24-inch diameter. How many revolutions does the wheel make if the tractor travels 4 miles?
Show Solution
3361 revolutions
Glossary
- angle
- the union of two rays having a common endpoint
- angular speed
- the angle through which a rotating object travels in a unit of time
- arc length
- the length of the curve formed by an arc
- area of a sector
- area of a portion of a circle bordered by two radii and the intercepted arc; the fraction
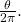 multiplied by the area of the entire circle
multiplied by the area of the entire circle
- coterminal angles
- description of positive and negative angles in standard position sharing the same terminal side
- degree
- a unit of measure describing the size of an angle as one-360th of a full revolution of a circle
- initial side
- the side of an angle from which rotation begins
- linear speed
- the distance along a straight path a rotating object travels in a unit of time; determined by the arc length
- measure of an angle
- the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side
- negative angle
- description of an angle measured clockwise from the positive x-axis
- positive angle
- description of an angle measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis
- quadrantal angle
- an angle whose terminal side lies on an axis
- radian measure
- the ratio of the arc length formed by an angle divided by the radius of the circle
- radian
- the measure of a central angle of a circle that intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of that circle
- ray
- one point on a line and all points extending in one direction from that point; one side of an angle
- reference angle
- the measure of the acute angle formed by the terminal side of the angle and the horizontal axis
- standard position
- the position of an angle having the vertex at the origin and the initial side along the positive x-axis
- terminal side
- the side of an angle at which rotation ends
- vertex
- the common endpoint of two rays that form an angle

