26 3.5 Bioengineering at the C-Terminus of Melittin
Overview
Melittin is able to bind to plasma membranes by way of electrostatic interactions between melittin’s positively-charged C-terminus and the negatively-charged phospholipid bilayer of cells, as has been demonstrated by previous research (Hall et al., 2010). In this section, we will examine how altering the amino acid sequence at the C-terminus of melittin has important implications not only for plasma membrane affinity, but also for anticancer activity.
Anticancer Activity: Using Bioengineered DEDE-Melittin as a Research Tool
Concept and Methodology Review
TAT-melittin is a variant of melittin in which a very large positive TAT sequence has been added at the C-terminus.
Bioengineering technology allowed researchers the unique opportunity to study the importance of the positively-charged C-terminus of melittin, by way of using DEDE-melittin in which this positive charge was reversed. It was determined that DEDE-melittin demonstrated no anticancer activity on either HER2-enriched breast cancer cells or TNBC cells, which signifies that the positive charge normally at the C-terminus plays an important role in terms of bringing about toxic effects in breast cancer cells.
To verify this highly significant finding, researchers rescued the positive charge at the C-terminus by using SV40-melittin. As expected, anticancer activity was recovered when this variant was tested on T11 cells. Nevertheless, it should be noted that, in this particular situation, size matters; by also studying TAT-melittin, researchers discovered that any larger of a positive sequence at the C-terminus decreases the anticancer properties of melittin.
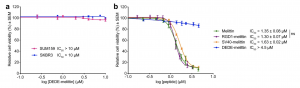
a: The impact of DEDE-melittin on the cell viability of both HER2-enriched breast cancer cells (SKBR3) and TNBC cells (SUM159). b: Comparing the impact of different melittin variants on the cell viability of squamous cell carcinoma cells (T11) (Duffy et al., 2020).
Key Takeaways
- The positively-charged C-terminus of the melittin peptide is responsible for anticancer activity.
- Replacing this positively-charged sequence with a negatively-charged sequence eliminates the anticancer properties of melittin.
- Significantly enlarging the positively-charged sequence at the C-terminus hinders anticancer activity.
References
- Hall K., Lee T., & Aguilar M. (2010). The role of electrostatic interactions in the membrane binding of melittin. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 24(1), 108-118. doi:10.1002/jmr.1032
