25 3.4 Honeybee Venom and Melittin Induce Breast Cancer Cell Death
Overview
The potency of both honeybee venom and melittin peptide on the SUM159 cell lines of the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) cells have scientifically been tested in this study. The following sections will touch upon the various methods that show how authors conclude honeybee venom and melittin induce cancer cell death.
Cell Death: Analysis by Flow Cytometry
To examine the outcome or state of the cell after the treatment with honeybee venom and melittin, the authors targeted specific biomarkers responsible for each event: intact (live), dead, apoptotic, and necrotic.
| Types of Cell Death | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Apoptosis | an active form of cell death mediated by an intracellular cue thereby bypassing inflammation; a “programmed” cell death. |
| Necrosis | a passive form of cell death caused by external factors such as infections that result in uncontrolled inflammatory cascades; characterized by dense tissue matter. |
Biomarkers for Apoptosis and Necrosis: Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
Cell death can occur by a myriad of different stimuli or molecular mechanisms such as apoptosis or necrosis. Therefore, it is important to distinguish between the two by targeting specific markers that help to confirm the event of cell death in the experimental system (Fink and Cookson, 2005).
Common Apoptosis Marker

The target method in this study was the loss of membrane asymmetry/phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure using flow cytometry analysis of annexin V binding (Duffy et al., 2020). During apoptosis, this can be visualized as the fluorescent-tagged PS from the inner membrane undergo a conformational change that causes them to translocate to the outer membrane layer (Wlodkowic et al., 2009).

Concept and Methodology Review
Melittin Induces Apoptosis in SUM159 Cells
Propidium iodide (PI), a red fluorescent dye can be used to detect cell viability as they cannot stain live cells due to their intact membrane (Rosenberg et al., 2019). In combination with flow cytometry analysis of annexin V binding, the different cell populations can be quantified. The SUM159 cells treated with IC50 of melittin have substantially more late apoptotic cells compared to untreated control and honeybee venom groups (Duffy et al., 2020). This is indicated by the greater fluorescence intensity in the upper right portion of the flow cytometry (An+, PI+).

Cell Death Kinetics and Morphology: Quantification by Cell Viability Assay and Visualization using Microscopy

IC50 of melittin reduced cell viability of both aggressive breast cancer cell lines, SKBR3 and SUM159 over a period of 1 hr compared to the control. However, after 30 mins, the authors observed that SUM159 of the TNBC subset responded much more robustly compared to the SKBR3 of HER2. In addition, they observed a loss of volume and shrinkage of the plasma cell membrane, which is another hallmark of apoptosis (Duffy et al., 2020).
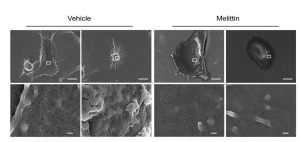
Key Takeaways
- Honeybee venom and melittin induce cell death in both breast cancer cell subsets.
- However, melittin induces more late apoptotic cells compared to Honeybee venom.
- This can be analyzed using Flow cytometry analysis of annexin V binding.
- Melittin has a more potent effect on SUM159 compared to SKBR3 with respect to time.
- Loss of membrane asymmetry and shrinkage is a hallmark of apoptotic cell death.
References
- Fink, S. L., & Cookson, B. T. (2005). Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infection and immunity, 73(4), 1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.4.1907-1916.2005
- Rosenberg, M., Azevedo, N. F., & Ivask, A. (2019). Propidium iodide staining underestimates viability of adherent bacterial cells. Scientific reports, 9(1), 6483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42906-3
- Wlodkowic, D., Skommer, J., & Darzynkiewicz, Z. (2009). Flow cytometry-based apoptosis detection. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 559, 19–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-017-5_2
