Part 2: Fuels and Combustion
Fuels and Combustion
Natural Gas
Properties: The primary component of natural gas is methane (CH4), the shortest and lightest hydrocarbon molecule. Natural gas also contains heavier gaseous hydrocarbons (higher value byproducts)
-
-
-
- Ethane (C3H6)
- Propane (C3H8)
- Butane (C4H10)
- Other sulphur containing gases.
-
-
Component Typical wt. %
-
-
-
-
- Methane (CH4) 70-90
- Ethane (C2H6) 5-15
- Propane (C3H8) and Butane (C4H10) < 5
- CO2, N2, H2S, He, etc. balance
-
-
-
Natural gas also contains and is the primary market source of helium!
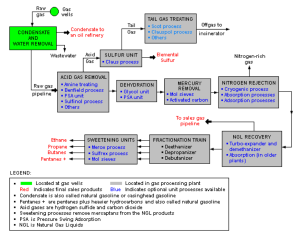
Natural Gas Processing
The by-products of natural gas are separated. H2S is removed from sour gas by sweetening. Sweetening also removes carbon dioxide, sulphur compounds and mercaptans.
The gas transmission company conditions the product by:
- Removing water and liquid hydrocarbons.
- Taking out hydrogen sulphide and inert gases.
- Removing dirt and foreign matter
- Adding an odourant for safety
Thus, the gas reaching the customer is nearly pure fuel.
Natural Gas Distribution

Major Canadian Pipelines
Natural Gas Systems
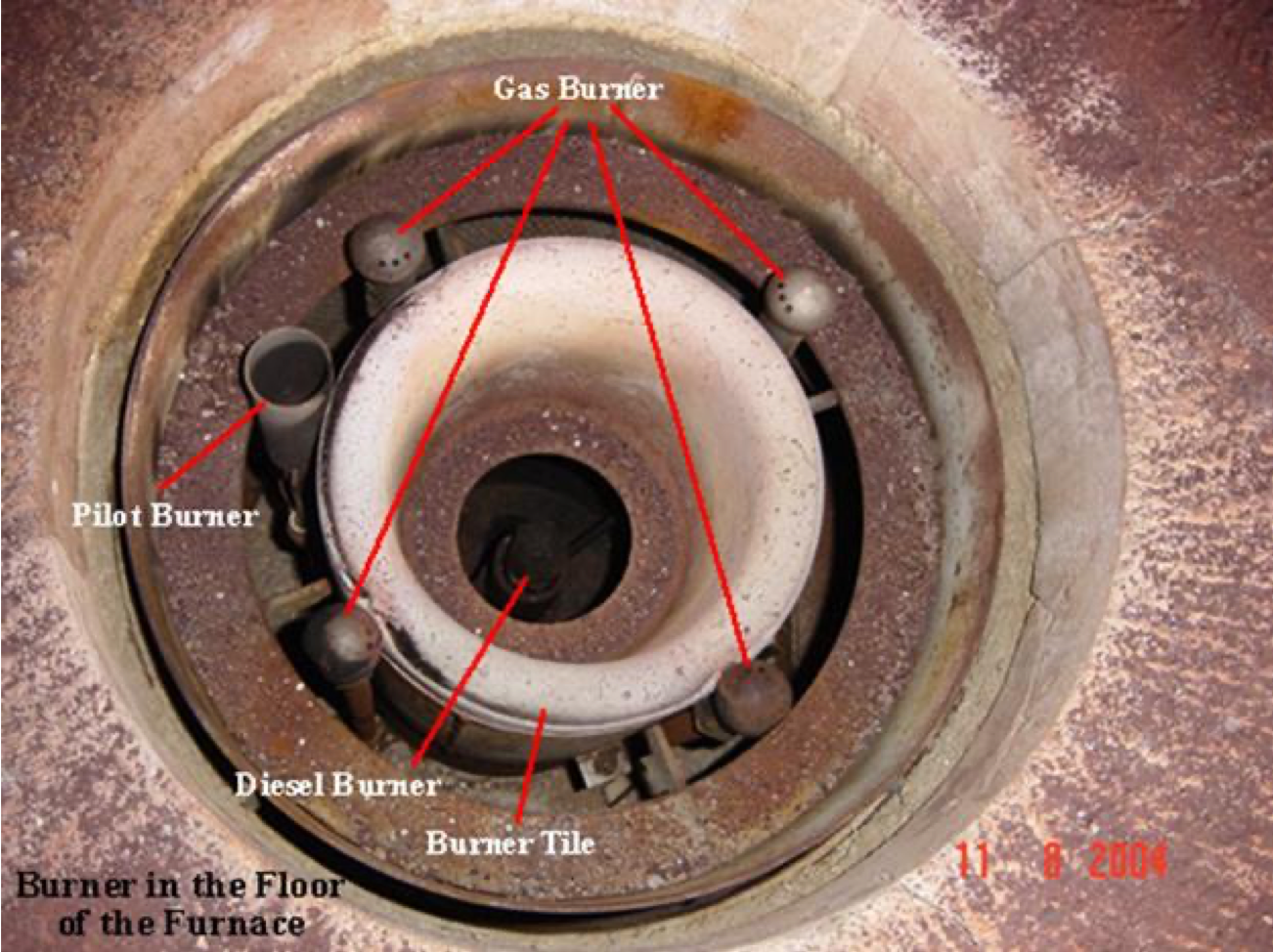
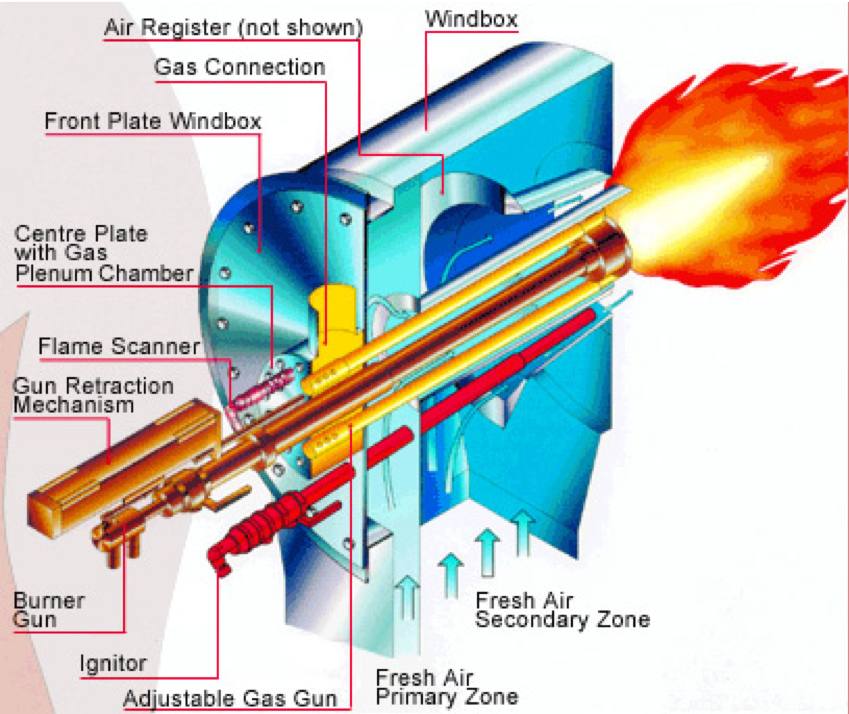
Burners
The pilot burner is positioned to light either the gas inner spuds or the oil atomizer. The gas header supplies the gas inner spuds and the outer spuds, which extend beyond the burner throat. Spuds are the gas nozzles that give the flame its location and shape.
Gas Piping Systems
Gas piping requirements:
-
- A pitch (slope) of at least 2.5 cm over a 15 m length
- A drip leg at low points where condensate can collect and be drained.
- Expansion bends in long runs of 100 mm or larger piping.
- Branch connections are attached to the top or sides of main horizontal pipes.
- Branch connections should be equipped with manual shut-off valves, or plug cocks.
- Emergency Shut-off valves on lines to individual buildings should be placed outside buildings and location of these are plainly marked.
- Gas shut-off valves are gate valves or full opening plug cocks.