Part 6 : Powerplant Water Systems
Powerplant Water Systems
A power plant has water systems with different quality:
Raw water or makeup water- Suitable for cooling tower makeup or firewater
Filtered water or treated water- Used for fire water, cooling water makeup and supply to the demineralizers or RO units.
Cooling Water- Similar to the filtered water makeup, but it has been cycled up or concentrated 5 to 12 times. Contains chlorine, and treatment chemicals such as phosphates and polymers and dispersants.
Demineralized water- high purity water.
Steam Condensate- Similar in quality to demineralized water
Regen Waste- effluent water from regenerating the demineralizers.
Boiler Blowdown- same quality as the water recirculating in the boiler and its steam drum.
Potable Water- water suitable for human consumption.
Boiler Feed Water- water from the boiler feed water pumps to the boiler.
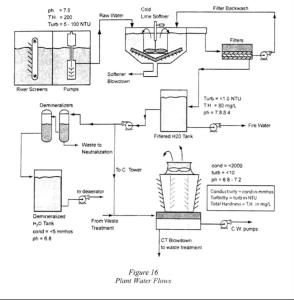
Plant Water Flows
Demineralized water
-
- It contains no suspended solids or dissolved solids (trace amounts still exist). It has no chemicals added and is suitable for makeup to the steam systems. A demineralized water storage tank is necessary, to allow for short outages to the demineralizer system.
Steam Condensate
-
- It contains no hardness, but has a low conductivity due to amines added for p1-1 control of the condensate and boiler feed water system. A condensate storage tank is often used as a back up in case of contamination or makeup supply problems.
Regen Waste
-
- It has a high conductivity (20000-40000 mmohs) as it contains high levels of dissolved solids.
Boiler Blowdown
-
- It is boiler feed water that has been cycled up 50-100 times. It contains chemicals such as polymers, phosphates and amines.
Potable Water
-
- It may be filtered water with additional testing and treatment. It may be supplied from a municipal water source or well water. Care must be taken to never connect this piping system to other plant water systems. Other plant waters must never enter the potable water system. It may have chorine added as well as the pH adjusted.
Boiler Feed Water
-
- It is a mixture of steam condensate and demineralized makeup water. It contains amines for pH control and chemical oxygen scavengers. Boiler feedwater can be used to supply steam desuperheaters if the water is phosphate free. Fig. 16 shows a typical plant water flow drawing.
Wastewater Streams and Treatment
Streams are managed in the following ways:
-
- Collected, sampled and diluted before discharge to a local waterway
- Recycling as much water as possible.
- Zero discharge plants return no water to the source stream.
The following water streams go to the wastewater treatment system.
-
-
- The water from floor drains and sample coolers
- Blowdown from the cooling tower
- The waste water from the demineralizers or reverse osmosis system
- The boiler blowdown water
-
The effluent from the wastewater system:
- The government sets the limits for suspended solids, BOD, COD and other components if the water is returned to a river or lake.
-
-
- The pH of the effluent from the wastewater system must be between 6.5 and 8.5.
- Often used for make-up for the cooling water system, or returned to a river or lake.
- When used in the cooling water system, its quality should be similar to the cooling tower makeup.
- The effluent from the wastewater system may even be used for boiler feedwater if the quality is high enough.
-
-
