6.5 Sine, Cosine and Tangent Ratios and Applications of Trigonometry
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section it is expected that you will be able to
- Find missing side of a right triangle using sine, cosine, or tangent ratios
- Find missing angle of a right triangle using sine, cosine, or tangent ratios
- Solve applications using right angle trigonometry
Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Ratios
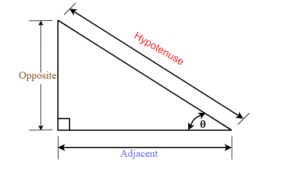
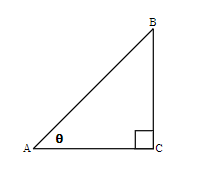
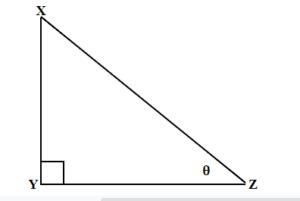
We know that any right triangle has three sides and a right angle. The side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse. The other two angles in a right triangle are acute angles (with a measure less than [latex]90[/latex] degrees). One of those angles we call reference angle and we use [latex]θ[/latex] (theta) to represent it.
The hypotenuse is always the longest side of a right triangle. The other two sides are called opposite side and adjacent side. The names of those sides depends on which of the two acute angles is being used as a reference angle.
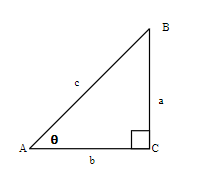
In the right triangle each side is labelled with a lowercase letter to match the uppercase letter of the opposite vertex.
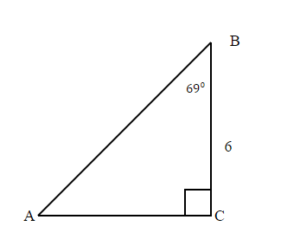
Example 6.5.1
Try It
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios are the ratios of the sides in the right triangle. For any right triangle we can define three basic trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, and tangent.
Let us refer to Figure 6.5.1 and define the three basic trigonometric ratios as:
Three Basic Trigonometric Ratios
-
-
- [latex]sine(\theta)=\frac{\text{the length of the opposite side}}{\text{the length of the hypotenuse side}}[/latex]
- [latex]cosine(\theta)=\frac{\text{the length of the adjacent side}}{\text{the length of the hypotenuse side}}[/latex]
- [latex]tangent(\theta)=\frac{\text{the length of the opposite side}}{\text{the length of the adjacent side}}[/latex]
-
Where [latex]θ[/latex] is the measure of a reference angle measured in degrees.
Very often we use the abbreviations for sine, cosine, and tangent ratios.
-
-
- [latex]sin(\theta)=\frac{opp}{hyp}[/latex]
- [latex]cos(\theta)=\frac{adj}{hyp}[/latex]
- [latex]tan(\theta)=\frac{opp}{adj}[/latex]
-
Some people remember the definition of the trigonometric ratios as SOH CAH TOA.
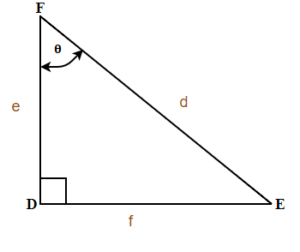
Let's use the [latex]\Delta DEF[/latex] from Example 6.5.2 to find the three ratios.
Example 6.5.2
Try It
Solution
[latex]\begin{align*}sin(\theta)&=\frac{z}{y}\\[2ex]cos(\theta)&=\frac{x}{y}\\[2ex]tan(\theta)&=\frac{z}{x}\end{align*}[/latex]
In Example 6.5.2, our reference angles can be angle [latex]E[/latex] or angle [latex]F[/latex]. Using the definition of trigonometric ratios, we can write [latex]sin(E)=\frac{e}{d}[/latex], [latex]cos(E)=\frac{f}{d}[/latex], and [latex]tan(E)=\frac{e}{f}[/latex].
When calculating we will usually round the ratios to four decimal places and at the end our final answer to one decimal place unless stated otherwise.
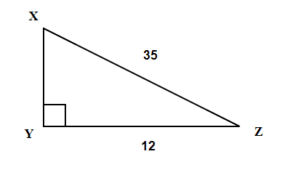
Example 6.5.3
For the given triangle find the sine, cosine and tangent ratios. If necessary round to four decimal places.
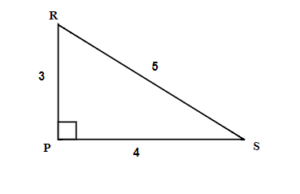
Solution
We have two possible reference angles: [latex]R[/latex] and [latex]S[/latex].
Using the definitions, the trigonometric ratios for angle [latex]R[/latex] are:
- [latex]sin(R)=\frac{4}{5}=0.8[/latex]
- [latex]cos(R)=\frac{3}{5}=0.6[/latex]
- [latex]tan(R)=\frac{4}{3}=1.3333...[/latex]
Using the definitions, the trigonometric ratios for angle [latex]S[/latex]:
- [latex]sin(S)=\frac{3}{5}=0.6[/latex]
- [latex]cos(S)=\frac{4}{5}=0.8[/latex]
- [latex]tan(S)=\frac{3}{4}=0.75[/latex]
Try It
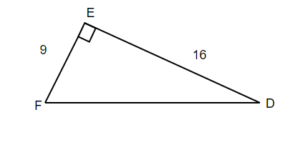
3) For the given triangle find the sine, cosine, and tangent ratios. If necessary round to four decimal places.
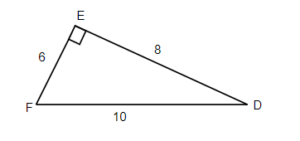
Solution
- [latex]sin(F)=\frac{8}{10}=0.8[/latex]
- [latex]cos(F)=\frac{6}{10}=0.6[/latex]
- [latex]tan(F)=\frac{8}{6}=1.3333...[/latex]
- [latex]sin(D)=\frac{6}{10}=0.6[/latex]
- [latex]cos(D)=\frac{8}{10}=0.8[/latex]
- [latex]tan(D)=\frac{6}{8}=0.75[/latex]
Now, let us use a scientific calculator to find the trigonometric ratios. Can you find the sin, cos, and tan buttons on your calculator? To find the trigonometric ratios make sure your calculator is in Degree Mode.
Example 6.5.4
Using a calculator find the trigonometric ratios. If necessary, round to 4 decimal places.
a) [latex]sin(30^\circ)[/latex]
b) [latex]cos(45^\circ)[/latex]
c) [latex]tan(60^\circ)[/latex]
Solution
Make sure your calculator is in Degree Mode.
a. Using a calculator find that [latex]sin(30^\circ)=0.5[/latex]
b. Using a calculator find that [latex]cos(45^\circ)=0.7071[/latex] Rounded to 4 decimal places.
c. Using a calculator find that [latex]tan(60^\circ)=1.7321[/latex] Rounded to 4 decimal places.
Try It
4) Find the trigonometric ratios. If necessary, round to 4 decimal places.
a. [latex]sin(60^\circ)[/latex]
b. [latex]cos(30^\circ)[/latex]
c. [latex]tan(45^\circ)[/latex]
Solution:
a. [latex]sin(60^\circ)=0.8660[/latex]
b. [latex]cos(30^\circ)=0.8660[/latex]
c. [latex]tan(45^\circ)=1[/latex]
Finding Missing Sides of a Right Triangle
In this section you will be using trigonometric ratios to solve right triangle problems. We will adapt our problem solving strategy for trigonometry applications. In addition, since those problems will involve the right triangle, it is helpful to draw it (if the drawing is not given) and label it with the given information. We will include this in the first step of the problem solving strategy for trigonometry applications.
HOW TO:
Solve Trigonometry Applications
- Read the problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
- Identify what we are looking for.
- Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
- Find the required trigonometric ratio.
- Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
- Check the answer by substituting it back into the ratio in step 4 and by making sure it makes sense in the context of the problem.
- Answer the question with a complete sentence
In the next few examples, having given the measure of one acute angle and the length of one side of the right triangle, we will solve the right triangle for the missing sides.
Example 6.5.5
Find the missing sides. Round your final answer to two decimal places
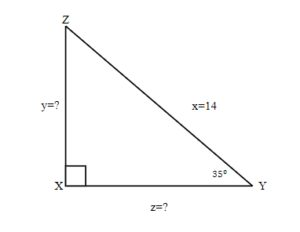
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Angle [latex]Y[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]y[/latex] is opposite side, [latex]z[/latex] is adjacent side, and [latex]x=14[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
a. The opposite side.
b. Adjacent side.
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}y&=&?\\z&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;sin(35^\circ)&=& \frac{y}{14}\\[3ex]\text{b.}\;cos(35^\circ)&=&\frac{z}{14}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;14\;sin(35^\circ)&=&y\\8.03&=&y\\[3ex]\text{b.}\;14\;sin(35^\circ)&=&z\\11.47&=&z\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{align*}\text{a.}\;0.57&\overset?=8.03 \divsymbol14\\ 0.57&=0.57\checkmark\\[3ex] \text{b.}\;0.82&\overset?=11.47 \divsymbol14\\ 0.82&=0.82 \checkmark \end{align*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
a. The opposite side is [latex]8.03[/latex].
b. The adjacent side is [latex]11.47[/latex].
Try It
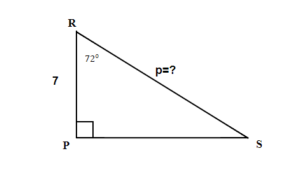
Example 6.5.6
Find the hypotenuse. Round your final answer to one decimal place.
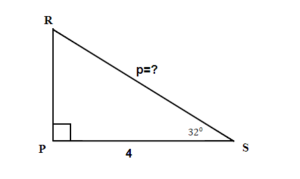
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Angle [latex]S[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]R[/latex] is opposite side, [latex]r=4[/latex] is the adjacent side, and [latex]P[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
The hypotenuse.
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}p&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}cos(32^\circ)&=&\frac{4}{p}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}0.8480&=&\frac{4}{p}\\p&=&4.7170\;\;\text{Rounding the ratios to 4 decimal places}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}0.8480&\overset?=&\frac{4}{4.7170}\\0.8480&=&0.8480\checkmark\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
The hypotenuse is [latex]4.7[/latex]. Round final answer to one decimal place.
Try It
Finding Missing Angles of a Right Triangle
Sometimes we have a right triangle with only the sides given. How can we find the missing angles? To find the missing angles, we use the inverse of the trigonometric ratios. The inverse buttons [latex]sin^{-1}[/latex], [latex]cos^{-1}[/latex], and [latex]tan^{-1}[/latex] are on your scientific calculator.
Example 6.5.7
Find the angles. Round your final answer to one decimal place.
a. [latex]sin(A)=0.5[/latex]
b. [latex]cos(B)=0.9735[/latex]
c. [latex]tan(C)=2.89358[/latex]
Solution
Use your calculator and press the 2nd FUNCTION key and then press the SIN, COS, or TAN key
a. [latex]\begin{align*}A&=sin^{-1}(0.5)\\\angle{A}&=30^\circ\end{align*}[/latex]
b. [latex]\begin{align*}B&=cos^{-1}(0.9735)\\\angle{B}&=13.2^\circ\end{align*}[/latex] Rounded to one decimal place
c. [latex]\begin{align*}C&=tan^{-1}(2.89358)\\\angle{C}&=70.9^\circ\end{align*}[/latex] Rounded to one decimal place
Try It
7) Find the angles. Round your final answer to one decimal place.
a. [latex]sin(X)=1[/latex]
b. [latex]cos(Y)=0.375[/latex]
c. [latex]tan(Z)=1.676767[/latex]
Solution
a. [latex]\angle{X}=90^\circ[/latex]
b. [latex]\angle{Y}=68^\circ[/latex]
c. [latex]\angle{Z}=59.2^\circ[/latex]
In the example below we have a right triangle with two sides given. Our acute angles are missing. Let us see what the steps are to find the missing angles.
Example 6.5.8
Find the missing [latex]\angle T[/latex] . Round your final answer to one decimal place.
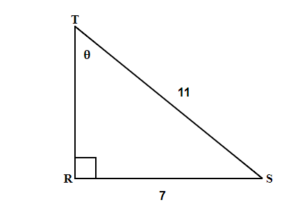
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Angle [latex]T[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]t=7[/latex] is the opposite side, [latex]s[/latex] is adjacent side, and [latex]r=11[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
Angle [latex]T[/latex].
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\angle T&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\sin(T)\;&=&\;\frac7{11}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}sin(T)&=&0.6364\\T&=&sin^{-1}(0.6364)\\\angle T&=&39.5239^\circ\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{align*}sin\left(39.523^\circ\right)&\overset?=0.6364\\0.6364&=0.6364\checkmark\end{align*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
The missing angle [latex]T[/latex] is [latex]39.5^\circ[/latex].
Try It
Example 6.5.9
Find the missing angle [latex]A[/latex]. Round your final answer to one decimal place.
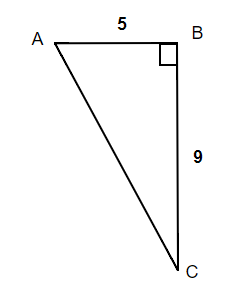
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Angle [latex]A[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]a=9[/latex] is the opposite side, [latex]c=5[/latex] is the adjacent side, and [latex]b[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
Angle [latex]A[/latex].
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\angle A&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan A&=&\frac{9}{5}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan(A)&=&1.8\\A&=&tan^{-1}(1.8)\\\angle A&=&60.9^\circ\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan\;60.9^\circ&\overset?=&\;1.8\\1.8&=&1.8 \checkmark\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
The missing angle [latex]A[/latex] is [latex]60.9^\circ[/latex].
Try It
Solving a Right Triangle
From the section before we know that any triangle has three sides and three interior angles. In a right triangle, when all six parts of the triangle are known, we say that the right triangle is solved.
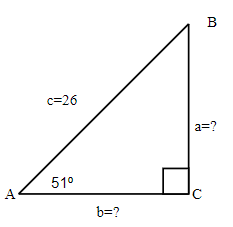
Example 6.5.10
Solve the right triangle. Round your final answer to one decimal place.
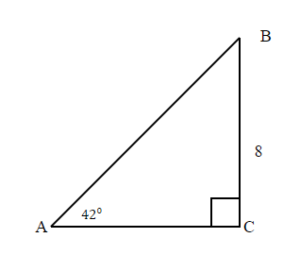
Solution
Since the sum of angles in any triangle is [latex]180^\circ[/latex], the measure of angle B can be easy calculated.
[latex]\begin{align*}\angle B&=180^\circ-90^\circ-42^\circ\\\angle B&=48^\circ\end{align*}[/latex]
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Angle [latex]A[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]a=8[/latex] is the opposite side, [latex]b[/latex] is the adjacent side, and [latex]c[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
a. The adjacent side.
b. The hypotenuse.
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;b&=&?\\ \text{b.}\;c&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;tan(42^\circ)&=&\frac{8}{b}\\[2ex] \text{b.}\;sin(42^\circ)&=&\frac{8}{c}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;0.9004&=&\frac{8}{b}\\0.9004 b&=&8\\b&=&8.8849\\[3ex]\text{b.}\;0.6691&=&\frac{8}{c}\\0.6691 c&=&8\\c&=&11.9563\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;tan(42^\circ)&\overset?=&\frac8{8.8849}\\0.9&=&0.9 \checkmark\\[3ex]\text{b.}\;sin(42^\circ)&\overset?=&\frac8{11.9563}\\0.6691&=&0.6691 \checkmark\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
a. The adjacent side is [latex]8.9[/latex]. Rounded to one decimal place.
b. The hypotenuse is [latex]12[/latex].
We solved the right triangle
[latex]\begin{align*}\angle A&=42^\circ\\\angle B&=48^\circ\\\angle C&=90^\circ\\[2ex]a&=8\\b&=8.9\\c&=12\end{align*}[/latex]
Try It
Example 6.5.11
Solve the right triangle. Round to two decimal places.
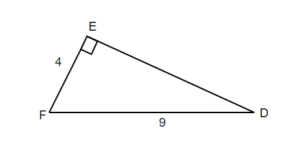
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
A drawing is given. Let angle [latex]D[/latex] be our reference angle, [latex]d=4[/latex] is the opposite side, [latex]f[/latex] is the adjacent side, and [latex]e=9[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
a. Angle D.
b. The adjacent.
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;\angle D&=&?\\[2ex] \text{b.}\;f&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\text{a.}\;sin(D)&=&\frac{4}{9}\\[2ex] \text{b.}\;4^2+f^2&=&9^2\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{align*} &\text{a.}&sin(D)&=0.4444\\ &\;&D&=sin{-1}{0.4444}\\ &\;&\angle D&=26.3850^\circ\\[3ex] &\text{b.}&16+f^2&=81\\ &\;&f^2&=81-16\\ &\;&f^2&=65\\ &\;&f&=\sqrt{65}\\ &\;&f&=8.06 \end{align*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{align*} &\text{a.}&sin(26.3850^\circ)&\overset?=\frac49\\ &\;&0.4444&=0.4444\checkmark\\[3ex] &\text{b.}&4^2+8.06^2&\overset?=9^2\\ &\;&81&=81\checkmark \end{align*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
a. The missing angle [latex]D[/latex] is [latex]26.39^\circ[/latex].
b. The adjacent side is [latex]8.06[/latex]. Rounded to two decimal places.
The missing angle [latex]\begin{eqnarray*}F&=&180^\circ - 90^\circ - 26.39^\circ\\F&=&63.61^\circ\end{eqnarray*}[/latex].
We solved the right triangle
[latex]\begin{align*}\angle D\ &=26.39^\circ\\\angle E\ &=90^\circ\\\angle F\ &=63.61^\circ\\[2ex]d &=4\\e &=9\\f &=8.06\end{align*}[/latex]
Try It
Solve Applications Using Trigonometric Ratios
In the previous examples we were able to find missing sides and missing angles of a right triangle. Now, let's use the trigonometric ratios to solve real-life problems.
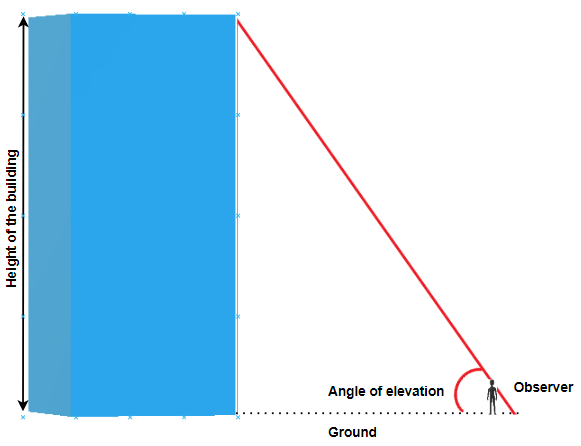
Many applications of trigonometric ratios involve understanding of an angle of elevation or angle of depression.
The angle of elevation is an angle between the horizontal line (ground) and the observer's line of sight.
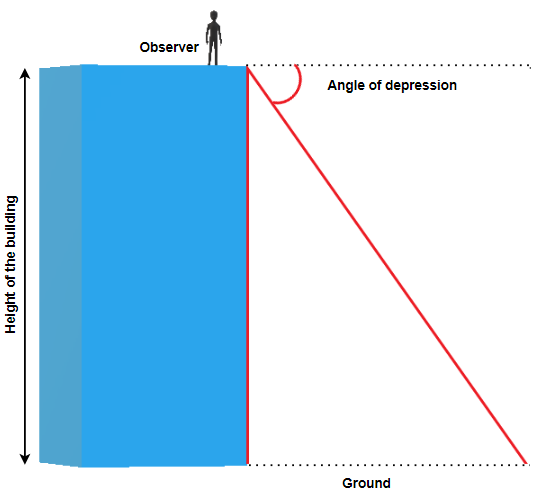
The angle of depression is the angle between horizontal line (that is parallel to the ground) and the observer's line of sight.
Example 6.5.12
James is standing [latex]31[/latex] metres away from the base of the Harbour Centre in Vancouver. He looks up to the top of the building at a [latex]78^\circ[/latex] angle. How tall is the Harbour Centre?
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
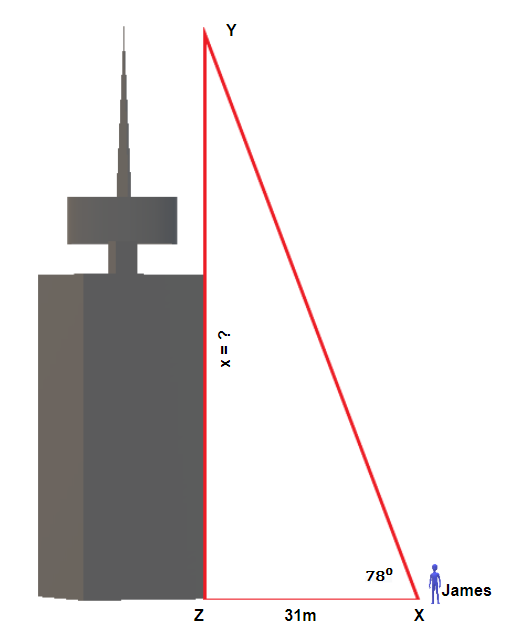
Angle [latex]X[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]x[/latex] is opposite side, [latex]y=31[/latex]m is the adjacent side, and [latex]z[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
The opposite side.
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}x&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan(78^\circ)&=&\frac{x}{31}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}4.7046&=&\frac{x}{31}\\x&=&145.8426\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}4.7046&\overset?=&\frac{145.8426}{31}\\4.7046&=&4.7046 \checkmark\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
The Harbour Centre is [latex]145.8426[/latex] metres or rounded to 146 metres.
Try It
12) Marta is standing [latex]23[/latex] metres away from the base of the tallest apartment building in Prince George and looks at the top of the building at a [latex]62^\circ[/latex] angle. How tall is the building?
Solution
[latex]43.3[/latex] metres
Example 6.5.13
Thomas is standing at the top of the building that is [latex]45[/latex] metres high and looks at her friend that is standing on the ground, [latex]22[/latex] metres from the base of the building. What is the angle of depression?
Solution
Step 1: Read problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
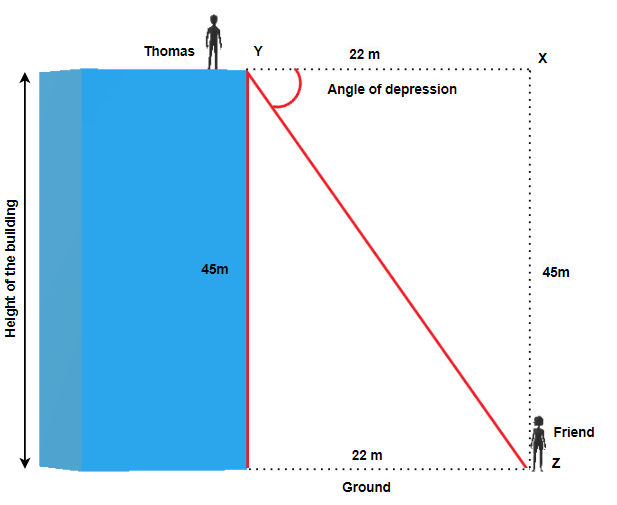
Angle [latex]Y[/latex] is our reference angle, [latex]y=45[/latex]m is the opposite side, [latex]z=22[/latex]m is the adjacent side, and [latex]x[/latex] is the hypotenuse.
Step 2: Identify what you are looking for.
The angle [latex]Y[/latex].
Step 3: Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}\angle Y&=&?\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 4: Find the required trigonometric ratio.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan(Y)&=&\frac{45}{22}\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 5: Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
[latex]\begin{eqnarray*}tan(Y)&=&2.0455\\Y&=&tan^{-1}(2.0455)\\\angle\;Y&=&63.9470^\circ\end{eqnarray*}[/latex]
Step 6: Check the answer in the problem and by making sure it makes sense.
[latex]\begin{align*}tan(63.9470^\circ)&\overset?=\;2.0455\\2.0455&=2.0455\checkmark\end{align*}[/latex]
Step 7: Answer the question with a complete sentence.
The angle of depression is [latex]63.9470^\circ[/latex] or [latex]64.0^\circ[/latex] rounded to one decimal place.
Try It
13) Hemanth is standing on the top of a cliff [latex]250[/latex] feet above the ground and looks at his friend that is standing on the ground, [latex]40[/latex] feet from the base of the cliff. What is the angle of depression?
Solution
[latex]80.9^\circ[/latex]
Key Concepts
- Three Basic Trigonometric Ratios: (Where [latex]θ[/latex] is the measure of a reference angle measured in degrees).
- [latex]sine\;\theta=\frac{\text{the length of the opposite side}}{\text{the length of the hypotenuse side}}[/latex]
- [latex]cosine\;\theta=\frac{\text{the length of the adjacent side}}{\text{the length of the hypotenuse side}}[/latex]
- [latex]tangent\;\theta=\frac{\text{the length of the opposite side}}{\text{the length of the adjacent side}}[/latex]
- Problem-Solving Strategy for Trigonometry Applications
- Read the problem and make sure all the words and ideas are understood. Draw the right triangle and label the given parts.
- Identify what we are looking for.
- Label what we are looking for by choosing a variable to represent it.
- Find the required trigonometric ratio.
- Solve the ratio using good algebra techniques.
- Check the answer by substituting it back into the ratio solved in step 5 and by making sure it makes sense in the context of the problem.
- Answer the question with a complete sentence.
Self Check
a. After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.
b. Overall, after looking at the checklist, do you think you are well-prepared for the next section? Why or why not?