[in progress] Chapter 14: Historical Linguistics
14.1 Why do languages change?
A need for change
Consider the English sentence in (1):
| (1) | I found a new app for my phone that I read about on a life hack blog. |
This sentence would be readily understood by many users of English in the 2020s, but just 30 years earlier, it would have been very difficult for anyone to decode it, because some of the expressions used here did not exist or did not have the same meaning in the 1990s. For example, the word app as a short form of application had just started being used for computer programs in the previous decade (this and other etymological information for English in this chapter are from the Oxford English Dictionary Online 2024, unless otherwise noted). Smartphones were still very new, and app was not yet used to refer to programs for phones, since the very concept of installing programs on phones was not yet widespread. Online journals existed, but they would not be called blogs until the late 1990s. Finally, the term hack had long been used to refer to infiltrating computer systems, but it would not be combined with life to refer to cleverly modifying one’s routine activities until the 2000s. If we go back even further than the 1990s, the sentence in (1) would essentially be uninterpretable.
This example demonstrates one important pressure that can cause a language to change. The world around us is constantly changing, with new technology, cultural shifts, and growing scientific understanding, and we want to be able to talk about those changes. We could just use cumbersome descriptions, but the more common a concept is, the more likely we are to dedicate or adapt specialized terminology for it for more efficient communication. No one wants to keep saying clever modification to routine activities when they could get by with the much shorter expression life hack.
Variation and change
Changes in the world around us are not the only reasons that a language might change. As discussed in Section 2.5 and Chapter 10, languages naturally vary, and different linguistic variants can carry different social meanings. However, while variation may be stable over time (see Section 10.3), any given instance of sociolinguistic variation could eventually collapse, leaving older forms obsolete and forgotten, while the newer forms are now considered unremarkable rather than socially meaningful.
For example, to describe the construction of a new house, speakers of English in the 1600s could have said either the house is building or the house is in building (as depicted in Figure 14.1, left). But by the 1700s, a new variant had emerged, with some speakers saying the house is being built instead (Figure 14.1, centre). This new variant was looked down upon by the educated elite at the time, who viewed it as “clumsy” and “at war with the genius of the English tongue” (Marsh 1862: 461–465).
However, the newer form overcame the prescriptive pressure against it and has now replaced the older forms (Figure 14.1, right). The negative perception of the newer form is gone, and instead, the older forms are now the forms that would seem out of place. Today, the house is building is semantically anomalous, since houses do not normally build other structures, while the house is in building just seems ungrammatical.
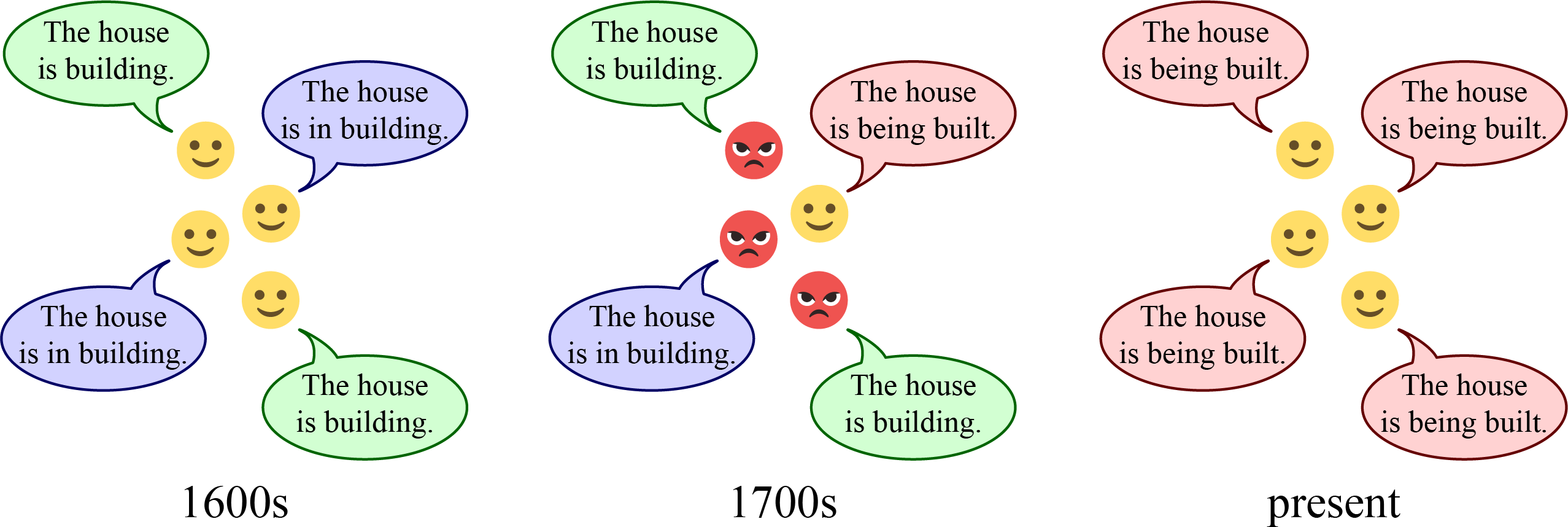
Much of the discussion in previous chapters of this textbook has focused on synchronic linguistics, which is the study of language patterns at a single point in time, such as how the house is being built is grammatical right now. In this chapter, we turn to diachronic linguistics, which is the study of changes in language patterns across two or more points in time, such as how the house is in building used to be grammatical in English 500 years ago but is no longer grammatical today.
Historical periods in a language
As changes in a language build up over time, the language may become sufficiently different that it is convenient to use distinct labels for its historical forms. The modifiers Old, Middle, and Modern may be added before a language name to indicate different periods in a language’s history, as in the periods of the history of English given in (2) (based on divisions by Baugh 1951):
| (2) | a. | Old English (AD 450–1150): The beginning of Old English corresponds to the earliest known English writing, which was mostly short runic engravings (names, greetings, prayers, graffiti, etc.) dated to the 400s. One of the most notable pieces of Old English literature is the epic poem Beowulf, of unknown authorship and date; the earliest surviving manuscript is the Nowell Codex from around 1000. |
| b. | Middle English (1150–1500): Due to influence from Norman French after the Norman conquest of England by William the Conqueror (1066), as well as influence from Old Norse after hundreds of years of Scandinavian invasions during the Viking Age (800–1150), English vocabulary and grammar underwent significant changes. There was also much regional variation in Middle English. One of the most notable pieces of Middle English literature is the collection of stories The Canterbury Tales by Geoffrey Chaucer, published shortly after his death in 1400. | |
| c. | Modern English (1500–present): A key feature of the transition from Middle to Modern English is the Great Vowel Shift, which drastically changed the pronunciation of English vowels beginning in the 1400s (see further discussion in Section 14.3). This was unfortunate timing, because the spread of printing in English in the late 1400s helped standardize the written form long before the completion of the Great Vowel Shift around 1700. The result is a significant divergence between spelling and pronunciation. Notable early pieces of Modern English literature include the works of William Shakespeare, which were written from about the 1590s to the 1610s. |
Note that this terminology is typically used only for the attested forms of a language, that is, those for which we have direct evidence from writing or audio/visual recordings. See Sections 14.8, 14.9 and 14.10 for discussion of methods we can use for exploring the nature of unattested languages for which there is no such direct evidence.
Old is typically used for the oldest attested form of a language, but for some languages, the modifier Ancient may be used in variation with Old for the oldest attested form, as with Old/Ancient Chinese and Old/Ancient Egyptian. In some cases, Ancient may instead be used for a form older than Old, as with Ancient Greek (which is not even the oldest attested form of Greek; Mycenaean Greek is earlier than Ancient Greek). For some languages, Classical may be used as a modifier to indicate a particularly notable early literary era in the history of a language, as with Classical Latin and Classical Nahuatl. Many other language-specific modifiers are traditionally used for certain periods in some languages’ histories, especially for those with extensive documentation. Some examples include Mycenaean Greek (as noted above), Biblical Hebrew (an alternate name for Old Hebrew), Vedic Sanskrit (Old Sanskrit), Old Church Slavonic (Old Bulgarian), and Vulgar Latin (for the period of Latin after Classical Latin and before Old French, Old Spanish, etc.).
The modifiers Early and Late may also added before the name of any historical period of a language to make finer distinctions within that period as needed. For example, because Modern English spans almost 600 years, it is often useful to distinguish between Early Modern English (such as Shakespearean English) and Late Modern English (the English used in this textbook), given how different they are.
There is no universal crosslinguistic timeline or particular years for the use of this terminology. It is instead based on attested differences internal to the language’s own history. For example, the earliest attestations of Old Chinese are engravings on turtle shells and ox bones that date back to 1200 BC (Boltz 1986), well before Old English, yet both are labelled Old.
In addition, there is normally no distinct single point in time at which a language transitions from one period to the next. For example, Old English is sometimes considered to have ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest. However, the influence of Norman French on Old English was not instantaneous, and distinctly Old English linguistic patterns persisted until the 12th century. The transition from one period of a language’s history to another is more like a smooth spectrum of gradual change with no sharp divisions between periods, as shown in Figure 14.2 for English.
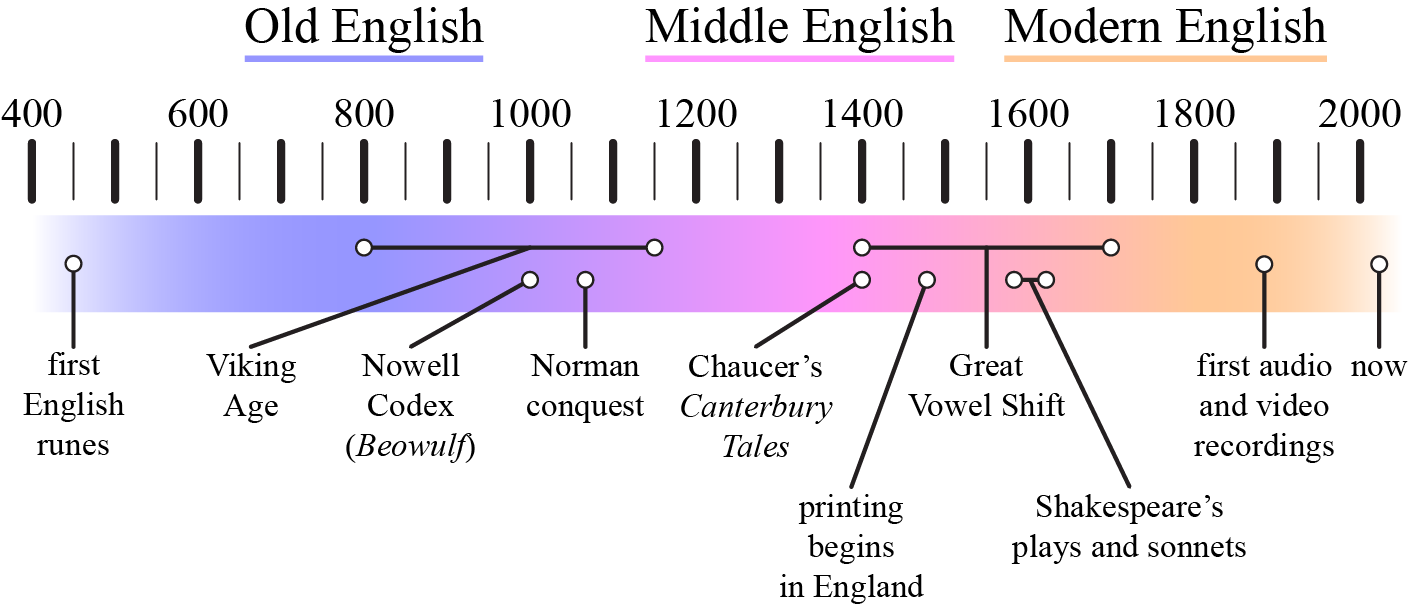
Furthermore, all languages naturally vary regardless of historical period, so there was no single consistent version of Middle English or Old Chinese or any other language. There was always some sort of variation based on class, age, gender, region, and/or other social factors. So when we talk about Middle English or Old Chinese as languages, we have to remember that they varied: the Middle English of royalty was different from the Middle English of farmers, the Old Chinese of western China was different from the Old Chinese of eastern China, and so on. Some of this variation is even attested in written records.
Notation of language change
We may represent a language change with a greater than sign > pointing from the older form on the left to the newer form on the right. For example, the change in structure from earlier the house is building to newer the house is being built could be represented as (3).
| (3) | the house is building > the house is being built |
This notation can be used for any kind of change in any aspect of a language. For example, the first vowel in the pronunciation of the word reasons used to be more like [e] in Early Modern English, so that it sounded like raisins, allowing for puns like the one in (4) from Shakespeare's Henry IV, Part 1, in which Falstaff compares reasons (raisins) to blackberries.
| (4) | If reasons were as plentiful as blackberries, […] |
The pronunciation of the vowel in reasons eventually changed to [i], while the corresponding vowel in raisins did not, ruining Shakespeare’s pun. We can notate this phonological change as reasons [rezənz] > [rizənz], with the older pronunciation on the left of the greater than sign and the newer pronunciation on the right. Sometimes, a less than sign < is used to indicate the reverse direction of a language change. Thus, we could also write reasons [rizənz] < [rezənz] to indicate the reverse direction, that the modern pronunciation [rizənz] originates from the older pronunciation [rezənz]. This means exactly the same thing as reasons [rezənz] > [rizənz].
Changes in meaning can similarly be represented with this notation. The word nice was borrowed into Middle English from Old French in the late 1200s, and its original meaning at the time in both languages was ‘silly’. Over time, its meaning in English changed in various ways, to ‘delicate’ (in the 1400s), then ‘careful’ (1500s), and eventually ‘pleasant’ (1700s). This overall sequence of change in meaning can be represented as (5).
| (5) | nice ‘silly’ > ‘delicate’ > ‘careful’ > ‘pleasant’ |
Additional information may sometimes be added to this notation, such as the name of the language or language variety at each stage. For example, to show a deeper history of the word nice, we could go back to the original Old French source and show its development from Latin, as in (6).
| (6) | Old French nice ‘silly’ < Latin nescius ‘ignorant’ |
Note the use of the less than sign < in (6), which means this should be read as going further back in time as we read from left to right. This representation is equivalent to (7), which reverses the order of the historical stages and flips the direction of the sign.
| (7) | Latin nescius ‘ignorant’ > Old French nice ‘silly’ |
The usage of the greater than sign > is similar to the usage of the arrow [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] in previous chapters: both symbols indicate some kind of linguistic change. The difference is that the greater than sign > represents a diachronic change from one time period to another, while the arrow [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] represents a synchronic change at a single point in time, such as how a phonological rule converts an underlying representation into a surface representation.
Etymology
The historical development of a word or expression is called its etymology. The etymology of nice is an example of how the modern meaning of a word can be very different from its etymological source. In this case, nice started with a negative meaning in English but eventually developed a positive meaning.
This is a reminder that a word’s meaning is defined by how the word is used now, regardless of how it may have been used 500 years ago, 50 years ago, or even 5 years ago. See also related discussion in Section 3.1 about the term phonetics and other scientific terminology. It is an etymological fallacy to make a logical argument that relies on using an etymological meaning of a word in a context where only its current meaning is what is relevant.
For example, if someone is told that their behaviour is transphobic, they may try to avoid engaging directly with the offensiveness of their actions by instead focusing on an etymological interpretation of the meaning of transphobic. A typical argument is that they could not be transphobic because they are not literally afraid of trans people.
However, this is an etymological fallacy. The suffix -phobic is used in English to refer to being averse in a more general sense, not necessarily due specifically to fear. We see this modern meaning in various words referring to social intolerance or discrimination, such as transphobic, Islamophobic, and xenophobic, as well as other words referring to physical incompatibility or intolerance, such as hydrophobic (which refers to being water-repellant, like wax and oil) and photophobic (which refers to being physically sensitive to light, which can be a symptom of some medical conditions like glaucoma and eye infections).
Other reasons for change
There are two broad categories of sources of language change, external and internal. External change is change caused by something from outside the language itself, such as cultural changes, new technology, etc. An important external source of language change is language contact, when two or more cultures who use different languages interact with each other, which results in influence between the two languages. There are many different ways that cultures may interact, some more egalitarian than others, and there are consequently many different ways that language contact can cause language change. Some of these are discussed in Section 14.7.
But in many cases, a language may change for no external reason. This is an internal change that happens spontaneously within the language due to its structure or modality. For example, when two phones are adjacent, it is often easier to pronounce them by assimilating some phonetic property from one to the other, so that they are more similar (see discussion of assimilation in Section 4.9). There is no external reason from the specific surrounding culture that causes assimilation. Assimilation is just something that is physically easier for all human bodies to do, so this is a kind of change that could happen to any language at any time (but importantly, it is not guaranteed to happen in every language).
Many internal changes likely happen during the acquisition process. The earliest claim of this idea is probably Paul 1880, and there has been much work on this topic since, such as Ohala 1981, Crain et al. 2006, and Niyogi and Berwick 2009. During acquisition, children may articulate the language in a slightly different way than their parents. The change may be subtle enough that no one really picks up on it consciously. However, the change could still be robust enough that it persists into the next generation, who themselves may then push the change just a bit further, and so on, for many generations. Ordinary language users may not notice these subtle, incremental generational changes as they are happening, but the effects may be noticeable after enough time has passed. In addition, linguists are often able to discover and measure them in real time with modern instruments and methods (see Section 10.5 for discussion).
Complexity and change
Many people believe that ancient humans must have used simpler languages, and that these languages changed over time to become more complex modern languages. But many people also believe that younger generations are ruining language by simplifying it through a combination of laziness and ignorance. These seemingly contradictory views may even be held at the same time by the same person. The result is that many people coincidentally believe that their own personal version of a language just so happens to be the best version.
In truth, language complexity and language change are not actually related. In part, this is because language complexity is not a single well-defined concept. Languages may be complex in one way but simple in another. For example, English has fairly simple verb morphology, with most verbs having only a small number of distinct forms (for example, sign, signs, signed, signing), but it has a complex vowel system with over a dozen vowels, including multiple diphthongs. In contrast, Georgian (a Karto-Zan language of the Kartvelian family, spoken in the Republic of Georgia) has only five vowels (Shosted and Chikovani 2006), but it has incredibly complex verb morphology, with as many as a dozen positions that can be filled by many different morphemes marking verb tense, agreement, etc. (Makharoblidze and Leonard 2022).
In addition, each aspect of a language can change in different ways. We find that some changes may reduce complexity, some may increase complexity, and some may have no obvious effect on complexity at all. Furthermore, while a change could continue along the same path, growing increasingly complex over time, it might instead reverse at any time, and even reverse again later, and then again, and again, oscillating back and forth between different levels of complexity. Thus, there simply is no universal relationship between language change and complexity.
Check your understanding
References
Baugh, Albert. 1951. A history of the English language. London: Routledge.
Boltz, William G. 1986. Early Chinese writing. World Archaeology 17(3): 420–436.
Crain, Stephen, Takuya Goro, and Rosalind Thornton. 2006. Language acquisition is language change. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 35(1): 31–49.
Makharoblidze, Tamar, and Jean Leo Leonard. 2022. Disentangling structural complexity in a (challenging) inflectional system: The Georgian verb. Journal of Language and Linguistic Studies 18(2): 1075–1109.
Marsh, George P. 1883. The student’s manual of the English language: Lectures on the English language. London: John Murray.
Niyogi, Partha, and Robert C. Berwick. 2009. The proper treatment of language acquisition and change in a population setting. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106(25): 10124–10129.
Ohala, John J. 1981. The listener as a source of sound change. In Roberta A. Hendrik, Carrie S. Masek, and Mary Frances Miller (eds.), Papers from the Parasession on Language and Behavior, Seventeenth Regional Meeting of the Chicago Linguistic Society, 178–203. Chicago: Chicago Linguistics Society.
Oxford English Dictionary Online. 2024. Oxford: Oxford University Press. http://www.oed.com/
Paul, Hermann. 1880. Prinzipien der Sprachgeschichte. Tubingen: Niemeyer.
Shosted, Ryan K., and Vakhtang Chikovani. 2006. Standard Georgian. Journal of the International Phonetic Association 36(2): 255–264.

