6.4 Trade Harmonization
Learning Objective
3. Introduce Harmonized commodity classification system and its use in international trade.
Trade Harmonization
According to United Nations Trade Facilitation Implementation Guide, harmonization is
"the alignment of national procedures, operations and documents with international conventions, standards and practices. It can come from adopting and implementing the same standards as partner countries, either as part of a regional integration process or as a result of business decisions."
Trade harmonization becomes even more important in international trade where multiple countries, languages and systems are involved. In simple words, Harmonization of trade implies standardized processes and procedures to facilitate and simplify trade. This section will cover the standardization of product classifications and documentation.
Standardization of Product Classification
Correct product classification is crucial as it helps prepare accurate documentation, calculate tariffs and taxes and completion of customs formalities. World Customs Organization (WCO) established a standardized product classification system in 1983 known worldwide as ‘Harmonized System (HS) Coding. HS Coding categorizes goods into approximately 5,000 commodity groups, used in by more than 200 countries worldwide. It is also known as the HS code or HTS — the Harmonized Tariff Schedule code (Zurkow, 2016).
The HS is organized logically by economic activity or component material. The HS is organized into 21 sections subdivided into 99 chapters. The 99 HS chapters are further subdivided into 1,244 headings and 5224 subheadings (Wikipedia, 2022). Section and Chapter titles describe broad categories of goods, while headings and subheadings describe products in more detail. Generally, HS sections and chapters are arranged according to a product's degree of manufacture or technological complexity. Natural commodities, such as live animals and vegetables are described in the early sections of the HS. In contrast, more evolved goods such as machinery and precision instruments are described in later sections.
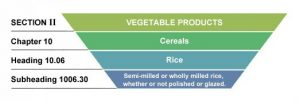
Generally, the HS code consists of 6-digits. The first two digits designate the HS Chapter. The second two digits represent the HS heading. The third two digits designate the HS subheading. HS code 1006.30, for example, indicates Chapter 10 (Cereals), Heading 06 (Rice), and Subheading 30 (Semi-milled or wholly milled rice, whether or not polished or glazed).
Hierarchy of Harmonized Code: Example
Note. Example of hierarchical structure of the Harmonized System for rice. From Wikimedia Commons, 2016. CC-BY-SA-4.0. [Image description].
More HS Coding Examples
Table 6.1
| Product Name | HS Code | Headings and Subheadings |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh potatoes | 701.9 | Header Potatoes, fresh or chilled, Sub header Other |
| Frozen potatoes | 710.1 | Header Vegetables (uncooked or cooked by steaming or boiling in water), frozen, Subheader Potatoes |
| Picture frames made of wood | 4414 | Subheader Wooden frames for paintings, photographs, mirrors or similar objects |
| Picture frames made of plastic | 3924.9 | Subheader Tableware, kitchenware, other household articles and hygienic or toilet articles, of plastics. Other |
| Picture frames made of glass | 7020 | Subheader Other articles of glass |
| Personal hygiene soap in the form of a bar, cake or moulded shape | 3401.11 | Subheader Soap and organic surface-active products and preparations, in the form of bars, cakes, moulded pieces or shapes, and paper, wadding, felt and nonwovens, impregnated, coated or covered with soap or detergent: For toilet use (including medicated products) |
| Liquid personal hygiene soap | 3401.20 or 3401.30 | Subheader Soap in other forms or Organic surface-active products and preparations for washing the skin, in the form of liquid or cream and put up for retail sale, whether or not containing soap |
| CO detector that captures and displays gas measurements | 9027.1 | Subheader Instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis (for example, polarimeters, refractometers, spectrometers, gas or smoke analysis apparatus; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking viscosity, porosity, expansion, surface tension or the like; instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking quantities of heat, sound or light (including exposure meters); microtomes; Gas or smoke analysis apparatus |
| CO detector that does not capture and display gas measurements | 8531.1 | Electric sound or visual signaling apparatus (for example, bells, sirens, indicator panels, burglar or fire alarms), other than those of heading 85.12 or 85.30. Burglar or fire alarms and similar apparatus. |
Note. This table gives different HS Code examples.
Use this online database to search list of products and commodities with their 6-digit, 4-digit and 2-digit HS codes: Foreign Trade Online.
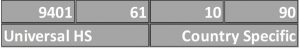
The contracting parties (such as countries participating in international trade) to the Convention on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System must agree to base their national tariff schedules on the HS nomenclature and legal notes. They can subdivide the HS nomenclature beyond 6-digits and add their legal notes according to their tariff and statistical requirements. Parties often set their customs duties at the 8-digit "tariff code" level. Statistical suffixes are often added to the 8-digit tariff code and make it 10 digits. If the number of digits is more than 8, additional digits are called the national subheading.
For example, a leather sofa can be classified as 9401.61.10.90.
HS Code Breakdown
Did You Know?
Canada has its own HS Coding System called Custom’s Tariff which is based on Harmonized System Coding developed by WCO. Visit Canadian Customs Tariff, Government of Canada website for more details.
Video: Classifying Imported Goods (2:21)
Watch this video that summarizes classification of goods in Canada.
Media 6.5 Classifying Imported Goods [Video]. Canada Border Services Agency. (URL: https://youtu.be/K4KML-rENVM)
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered above. You can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to (1) study the previous section further or (2) move on to the next section.
Check Your Understanding: Trade Harmonization
Interactive activity unavailable in this format
Text-based alternative to interactive activity available in Chapter 6.7.
Media Attributions and References
Canada Border Services Agency. (2016, March 4). Classifying imported goods [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K4KML-rENVM.
Hsmind. (2016, February 17). Hierarchy of harmonized code: Example [Hierarchy Chart]. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HS_Hierarchy_Structure_Rice.jpg.
Bi-lateral or Multi-lateral exchange of goods and services.