Introduction to Open Educational Resources
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Provide a definition of open educational resources.
- Explain the difference between OER and other free educational materials.
- Describe the challenges and benefits of using OER in a class.
Introduction
Contact North. (2014, April 4). What are open educational resources (OER)? [Video file]. Vimeo.
Background
The open education movement was originally inspired by the open-source community, with a focus on broadening access to information through the use of free, open content. As Bliss & Smith (2017) explain in their breakdown of the history of open education:
“much of our attention focused on OER’s usefulness at providing knowledge in its original form to those who otherwise might not have access. The implicit goal was to equalize access to disadvantaged and advantaged peoples of the world – in MIT’s language, to create ‘a shared intellectual Common.’”[1]
Following the rise of open education in the early 2000s, growing interest in MOOCs, open courseware, and particularly open textbooks catapulted the movement to new heights; however, there are still many instructors who have never heard of open educational resources (OER) today.[2]
What is an OER?
Open educational resources (OER) are openly licensed, freely available educational materials that can be modified and redistributed by users. They can include any type of educational resource, from syllabi to full courses.
- Openly licensed: You can read about this more in the Copyright & Licensing chapter.
- Freely Available: The resources must be freely available online with no fee to access. Physical OER may be sold at a low cost to facilitate printing.
- Modifiable: The resource must be made available under an open license that allows for editing. Ideally, it should also be available in an editable format.[3]
The most comprehensive definition of OER available today is provided by the Hewlett Foundation:
“Open Educational Resources are teaching, learning and research materials in any medium – digital or otherwise – that reside in the public domain or have been released under an open license that permits no-cost access, use, adaptation and redistribution by others with no or limited restrictions.”[4]
With a definition so broad that it includes any educational material so long as it is free to access and open, it might be easier to ask, “What isn’t an OER?”
What is Not an OER?
If a resource is not free or openly licensed, it cannot be described as an OER. For example, most materials accessed through your library’s subscriptions cannot be altered, remixed, or redistributed. These materials require special permission to use and, therefore, cannot be considered “open.” Table 1 below explains the difference between OER and other resources often misattributed as OER.
| Material Type | Openly Licensed | Freely Available | Modifiable |
| Open educational resources | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Free online resources under all rights reserved copyright | No | Yes | No |
| Materials available through the University Library | No | Yes | No |
| Open-access articles and monographs | Yes | Yes | Maybe |
Note: Although some materials are free to access for a library’s users, that does not mean that they are free to access for everyone (including the library). Similarly, while some open access resources are made available under a copyright license that enables modification, this is not always the case.
Check Your Understanding
Consider the free materials you currently use in your classes. Are these materials OER? Why or why not?
Benefits of Using OER
San Francisco State University. (2015, December 15). AIM student perspective [Online video]. YouTube.
Benefits for Students
One of the first aspects of OER to be praised by the general public was the cost savings that they could bring to students. As Figure 1 shows, the price of college textbooks has risen greatly over the past 35 years, outpacing all other consumer goods in the Consumer Price Index by a great margin.
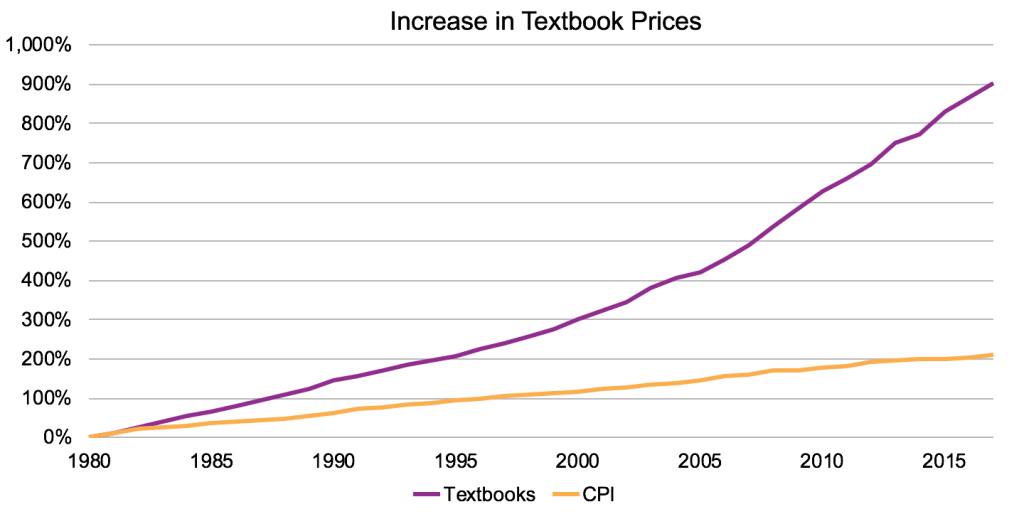
The cost of textbooks has a profound impact on college students, many of whom must wait to purchase their course materials until well into the semester or choose not to purchase them at all.[5] An Iowa State University student studying Political Science and International Studies had this to share about their experience with textbook costs:
“I use discount websites to rent textbooks or I borrow necessary books from my peers; the cost of textbooks is needlessly prohibitive to students, and I try to cut costs however I can.”
The cost of textbooks might not be a major issue on its own, but it can be an insurmountable hurdle for students already struggling to get by. A recent survey found that 36% of college students are food insecure. This number is even higher for community college students, 42% of whom reported food insecurity.[6]
The problem of food and housing insecurity among college students cannot be fixed by adjusting the price of textbooks alone. There is a wide variety of reasons why these problems exist.[7] However, the unexpected additional cost of textbooks can make the difference between a student persisting in college or dropping out.
Access to a Quality Education
When you choose to share course materials openly, you are providing students with the opportunity to engage with your content before, during, and after your course. Because OER are always free to access online, students who are interested in taking a course you teach can read up on the course ahead of time and ensure that they are ready and interested in the material. Moreover, students who have already taken your course can be safe in the knowledge that their course materials will not evaporate at the end of the semester and that they can continue to review the materials you provided to them for years to come.
The students who benefit from access to OER are not just the ones in your classroom. Unlike affordability initiatives like course reserves, OER are free for anyone worldwide to access, whether they have a college affiliation or not.[8] This encourages aging learners and students in the Global South to explore educational content without committing the time and money they might not have to attend college.[9]
Benefits for Instructors
Although cost savings are a major talking point in favour of adopting open educational resources, instructors can utilize OER effectively without replacing paid resources at all.[10] In fact, the freedom to adapt OER to instructional needs is often the most attractive aspect of OER. Since OER are openly licensed, educators can edit, reorder, and remix OER materials in many ways.
Use, Improve, and Share
- Adapt and revise resources already created to fit your course syllabus.
- Create an updated second edition of an existing OER.
- Tailor resources to fit your specific course context (e.g., translation, local examples).
Network and Collaborate with Peers
- Access educational resources that have been peer-reviewed by experts in your field.
- Create a new open educational resource with a team of your peers.
- Explore user reviews for a more in-depth understanding of the resources available.
Lower Costs to Improve Access to Information
- Enable all students to have equal access to your course materials.
- Provide students with the opportunity to explore course content before enrolling.

Chapter Summary
This chapter has provided a brief overview of what OER are, why they are used, and the movement surrounding them. If you are interested in learning more, please visit:
Check Your Understanding
References
Hayman, J., Perkovic, o., & Savicevic, N. (n.d.). Top 10 Myths for administrators [PDF file]. eCampusOntario.
- Bliss, T J and Smith, M. 2017. A Brief History of Open Educational Resources. In: Jhangiani, R S and Biswas-Diener, R. (Eds.) Open: The Philosophy and Practices that are Revolutionizing Education and Science (pp. 9–27). London: Ubiquity Press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/bbc.b. ↵
- Weller, M. (2014). The battle for open: How openness won and why it doesn't feel like victory. London: Ubiquity Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.5334/bam ↵
- Although all OER are openly licensed, many are released in formats that do not easily allow for adaptation. ↵
- William & Flore Hewlett Foundation. (n.d.). OER defined. Retrieved from https://hewlett.org/strategy/open-educational-resources/ ↵
- Florida Virtual Campus. (2018). 2018 student textbook and course materials survey: Executive summary. Retrieved from https://www.flbog.edu/documents_meetings/0290_1174_8926_6.3.2%2003a_FLVC_SurveyEXSUM.pdf ↵
- Romo, V. (2018, April). The survey finds that hunger and homelessness are widespread among college students. NPR: The Two-Way. Retrieved from https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2018/04/03/599197919/hunger-and-homelessness-are-widespread-among-college-students-study-finds ↵
- Goldrick-Rab, S. & Cady, C. (2018). Supporting community college completion with a culture of caring: A case study of Amarillo College. Retrieved from https://hope4college.com/supporting-community-college-completion-with-a-culture-of-caring-a-case-study-of-amarillo-college/ ↵
- Although OER are free for anyone to access, this access is still limited by who has access to the Internet. Still, since OER can be freely redistributed, some individuals have printed OER for dissemination in areas that do not have Internet access as well. ↵
- Hodgkinson-Williams, C. & Arinto, P. B. (2017). Adoption and impact of OER in the Global South. Cape Town & Ottawa: African Minds, International Development Research Centre & Research on Open Educational Resources. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.1005330 ↵
- The Benefits for Instructors section of this chapter was adapted from the SUNY OER Community Course, licensed CC BY 4.0. ↵
Free educational materials that are openly licensed to enable reuse and redistribution by users.

