Chapter 1 – Introduction to Project Management for Human Resources
1.4. Aspects of Project Management
The Science of Project Management
Project management has been around for centuries if not millennia. From the building of the pyramids to the construction of the great buildings of 19th century London, people have developed ways to breakdown large projects into smaller more manageable chunks, schedule the work and obtain the materials needed for the projects. During that time, many tools were developed to manage projects. However, it was not until the large, highly complex defence projects undertaken by the United States during the 1950s drove a push for a more scientific and data-driven, management approach to projects, and which was the beginning of the science of modern-day project management.
HR in Focus
Project management for HR professionals improves effectiveness and productivity for the HR department, the entire company and its employees. Project management improves work flow and processes. HR project management has never been more important than in today’s work world. Wise hiring, managing the changing work culture, and day-to-day operations are all project management priorities.
The Art of Project Management
The art of project management is specific to the skills that are used in projects. When communication and managing people are the priority, this would be the ‘art’. Even though the logistics of assumptions, planning, design, and scheduling are considered the ‘science’, these components cannot be managed in a scientific method. They are guided by the skills and experience of the project manager and the project team.
Project Management Institute
The Project Management Institute started in 1969 as an effort to share best practices, and today, it is a non-profit organization with over 500,000 members. PMI has chapters throughout the world, each offers additional benefits in the form of professional development and networking opportunities (PMI, 2022).
The PMI has codified the standards for project management in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) guide. The PMBOK is best used as a reference guide; it is not recommended for cover-to-cover reading. The PMBOK Guide has been recognized as a Standard by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
The PMBOK guide is organized into nine knowledge domains:
- Project Integration Management
- Project Scope Management
- Project Time Management
- Project Cost Management
- Project Quality Management
- Project Human Resource Management
- Project Communications Management
- Project Risk Management
- Project Procurement Management
- Project Stakeholder Management
(Project Manager, 2019)
Managing a project includes identifying your project’s requirements and writing down what everyone needs from the project. What are the objectives for your project? When everyone understands the goal, it’s much easier to keep them all on the right path. Make sure you set mutually agreed-upon goals to avoid team conflicts later on. Understanding and addressing the needs of everyone affected by the project means the end result of your project is far more likely to satisfy your stakeholders. Last but not least, as project manager, you will also be balancing the many competing project constraints.
Project Constraints
On any project, you will have a number of project constraints that are competing for your attention. They are cost, scope, quality, risk, resources, and time. When one changes, something else has to change. It is the trade-off.
- Cost is the budget approved for the project, including all necessary expenses needed to deliver the project. Within organizations, project managers have to balance between not running out of money and not underspending because many projects receive funds or grants that have contract clauses with a “use it or lose it” approach to project funds. Poorly executed budget plans can result in a last-minute rush to spend the allocated funds. For virtually all projects, cost is ultimately a limiting constraint; few projects can go over budget without eventually requiring corrective action.
- Scope is what the project is trying to achieve. It entails all the work involved in delivering the project outcomes and the processes used to produce them. It is the reason for and the purpose of the project.
- Quality is a combination of the standards and criteria to which the project’s products must be delivered for them to perform effectively. The product must perform to provide the functionality expected, solve the identified problem, and deliver the benefit and value expected. It must also meet other performance requirements, or service levels, such as availability, reliability, and maintainability, and have acceptable finish and polish. Quality on a project is controlled through quality assurance (QA), which is the process of evaluating overall project performance on a regular basis to provide confidence that the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards.
- Risk is defined by potential external events that will have a negative impact on your project if they occur. Risk refers to the combination of the probability that the event will occur and the impact on the project if the event occurs. If the combination of the probability of the occurrence and the impact on the project is too high, you should identify the potential event as a risk and put a proactive plan in place to manage the risk.
- Resources are required to carry out the project tasks. They can be people, equipment, facilities, funding, or anything else capable of definition (usually other than labour) required for the completion of a project activity.
- Time is defined as the time to complete the project. Time is often the most frequent project oversight in developing projects. This is reflected in missed deadlines and incomplete deliverables. Proper control of the schedule requires the careful identification of tasks to be performed and accurate estimations of their durations, the sequence in which they are going to be done, and how people and other resources are to be allocated. Any schedule should take into account vacations and holidays.
Project Priority
Triple constraint traditionally consisted of only time, cost, and scope. These are the primary competing project constraints that you have to be most aware of. The triple constraint is illustrated in the form of a triangle to visualize the project work and see the relationship between the scope/quality, schedule/time, and cost/resource (Figure 1-2).
Projects may have additional constraints, and as the project manager, one needs to balance the needs of these constraints against the needs of the stakeholders and your project goals. For instance, if the sponsor wants to add functionality to the original scope, more money is needed to finish the project. On the other hand, if the budget is cut, there will be a reduction of the quality of the scope. Further, if there are not appropriate resources to work on the project tasks, the schedule may need to be extended and take much longer to finish the work.
In summary, the constraints are all dependent on each other. Think of all of these constraints as the classic carnival game of Whac-a-Mole. Each time you try to push one mole back in the hole, another one pops out. The best advice is to rely on your project team to keep these moles in place.
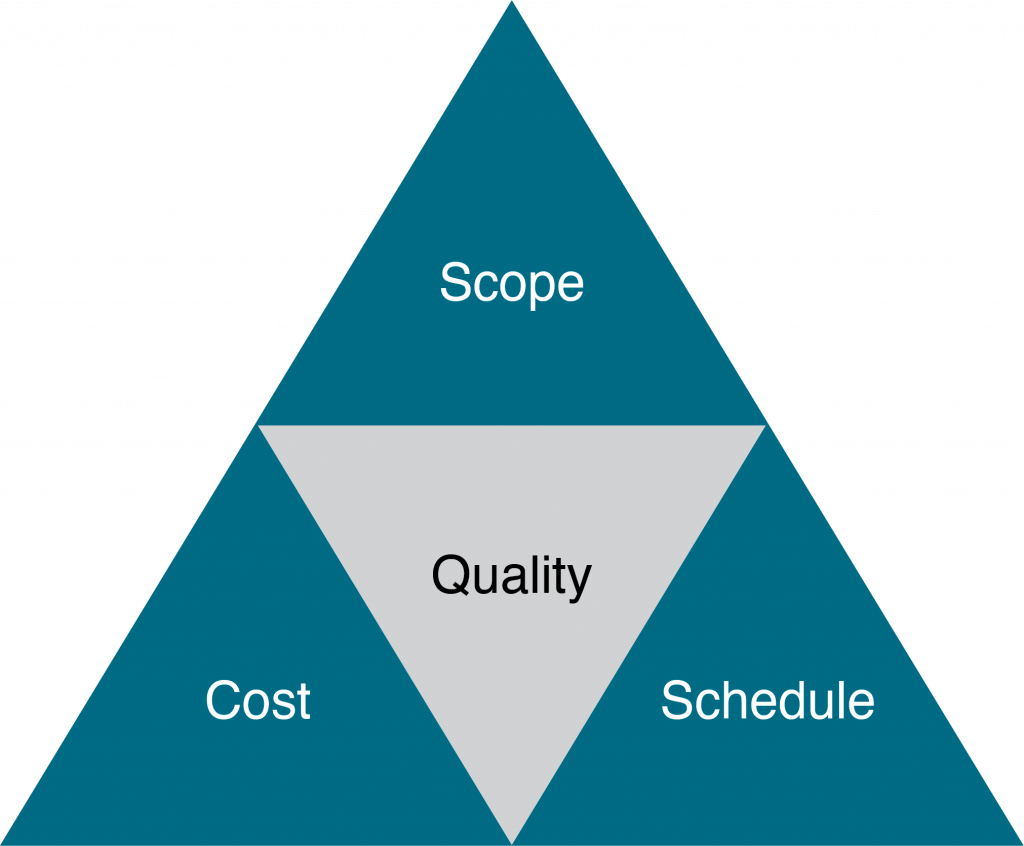
In this triangle, each side represents one of the constraints (or related constraints) wherein any changes to any one side cause a change in the other sides. The best projects have a perfectly balanced triangle. Maintaining this balance is difficult because projects are prone to change. For example, if scope increases, cost and time may increase disproportionately. Alternatively, if the amount of money you have for your project decreases, you may be able to do as much, but your time may increase.
“1.4. Aspects of Project Management” from Essentials of Project Management by Adam Farag is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

