18 Emerging Adulthood

Emerging adulthood is the period between the late teens and early twenties; ages 18-25, although some researchers have included up to age 29 in the definition (Society for the Study of Emerging Adulthood, 2016). Jeffrey Arnett (2000) argues that emerging adulthood is neither adolescence nor is it young adulthood. Individuals in this age period have left behind the relative dependency of childhood and adolescence, but have not yet taken on the responsibilities of adulthood. “Emerging adulthood is a time of life when many different directions remain possible, when little about the future is decided for certain, when the scope of independent exploration of life’s possibilities is greater for most people than it will be at any other period of the life course” (Arnett, 2000, p. 469).
Arnett has identified five characteristics of emerging adulthood that distinguishes it from adolescence and young adulthood (Arnett, 2006).
- It is the age of identity exploration.
- In 1950, Erik Erikson proposed that it was during adolescence that humans wrestled with the question of identity. Yet, even Erikson (1968) commented on a trend during the 20th century of a “prolonged adolescence” in industrialized societies. Today, most identity development occurs during the late teens and early twenties rather than adolescence. It is during emerging adulthood that people are exploring their career choices and ideas about intimate relationships, setting the foundation for adulthood.
- Arnett also described this time period as the age of instability (Arnett, 2000; Arnett, 2006).
- Exploration generates uncertainty and instability. Emerging adults change jobs, relationships, and residences more frequently than other age groups.
- This is also the age of self-focus.
- Being self-focused is not the same as being “self- centered.” Adolescents are more self-centered than emerging adults. Arnett reports that in his research, he found emerging adults to be very considerate of the feelings of others, especially their parents. They now begin to see their parents as people not just parents, something most adolescents fail to do (Arnett, 2006). Nonetheless, emerging adults focus more on themselves, as they realize that they have few obligations to others and that this is the time where they can do what they want with their life.
-
This is also the age of feeling in-between.
-
When asked if they feel like adults, more 18 to 25 year-olds answer “yes and no” than do teens or adults over the age of 25 (Arnett, 2001). Most emerging adults have gone through the changes of puberty, are typically no longer in high school, and many have also moved out of their parents’ home. Thus, they no longer feel as dependent as they did as teenagers. Yet, they may still be financially dependent on their parents to some degree, and they have not completely attained some of the indicators of adulthood, such as finishing their education, obtaining a good full-time job, being in a committed relationship, or being responsible for others. It is not surprising that Arnett found that 60% of 18 to 25 year-olds felt that in some ways they were adults, but in some ways they were not (Arnett, 2001).
-
-
Emerging adulthood is the age of possibilities.
-
It is a time period of optimism as more 18 to 25 year-olds feel that they will someday get to where they want to be in life. Arnett (2000, 2006) suggests that this optimism is because these dreams have yet to be tested. For example, it is easier to believe that you will eventually find your soul mate when you have yet to have had a serious relationship. It may also be a chance to change directions, for those whose lives up to this point have been difficult. The experiences of children and teens are influenced by the choices and decisions of their parents. If the parents are dysfunctional, there is little a child can do about it. In emerging adulthood, people can move out and move on. They have the chance to transform their lives and move away from unhealthy environments. Even those whose lives were happier and more fulfilling as children, now have the opportunity in emerging adulthood to become independent and make decisions about the direction they would like their life to take.
-
Cultural Variations in Emerging Adulthood
The five features proposed in the theory of emerging adulthood originally were based on research involving about 300 Americans between ages 18 and 29 from various ethnic groups, social classes, and geographical regions (Arnett, 2004). To what extent does the theory of emerging adulthood apply to Canada and elsewhere?
The answer to this question depends greatly on what part of the world is considered. Demographers make a useful distinction between the developing countries that comprise the majority of the world’s population and the economically developed countries that are part of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), including the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand. The current population of OECD countries (also called developed countries) is 1.2 billion, about 18% of the total world population (United Nations Development Programme, 2011). The rest of the human population resides in developing countries, which have much lower median incomes, much lower median educational attainment, and much higher incidence of illness, disease, and early death. Let us consider emerging adulthood in other OECD countries, as little is known about the experiences of 18-25 year-olds in developing countries.
The same demographic changes as described above for the United States have taken place in other OECD countries as well. This is true of participation in postsecondary education, as well as median ages for entering marriage and parenthood (UNdata, 2010). However, there is also substantial variability in how emerging adulthood is experienced across OECD countries. Europe is the region where emerging adulthood is longest and most leisurely. The median ages for entering marriage and parenthood are near 30 in most European countries (Douglass, 2007). Europe today is the location of the most affluent, generous, and egalitarian societies in the world, in fact, in human history (Arnett, 2007). Governments pay for tertiary education, assist young people in finding jobs, and provide generous unemployment benefits for those who cannot find work. In northern Europe, many governments also provide housing support. Emerging adults in European societies make the most of these advantages, gradually making their way to adulthood during their twenties while enjoying travel and leisure with friends.

The lives of Asian emerging adults in developed countries, such as Japan and South Korea, are in some ways similar to the lives of emerging adults in Europe and in some ways strikingly different. Like European emerging adults, Asian emerging adults tend to enter marriage and parenthood around age 30 (Arnett, 2011). Like European emerging adults, Asian emerging adults in Japan and South Korea enjoy the benefits of living in affluent societies with generous social welfare systems that provide support for them in making the transition to adulthood, including free university education and substantial unemployment benefits.
However, in other ways, the experience of emerging adulthood in Asian OECD countries is markedly different than in Europe. Europe has a long history of individualism, and today’s emerging adults carry that legacy with them in their focus on self-development and leisure during emerging adulthood. In contrast, Asian cultures have a shared cultural history emphasizing collectivism and family obligations.
Although Asian cultures have become more individualistic in recent decades, as a consequence of globalization, the legacy of collectivism persists in the lives of emerging adults. They pursue identity explorations and self-development during emerging adulthood, like their American and European counterparts, but within narrower boundaries set by their sense of obligations to others, especially their parents (Phinney & Baldelomar, 2011). For example, in their views of the most important criteria for becoming an adult, emerging adults in the United States and Europe consistently rank financial independence among the most important markers of adulthood. In contrast, emerging adults with an Asian cultural background especially emphasize becoming capable of supporting parents financially as among the most important criteria (Arnett, 2003; Nelson, Badger, & Wu, 2004). This sense of family obligation may curtail their identity explorations in emerging adulthood to some extent, as they pay more heed to their parents’ wishes about what they should study, what job they should take, and where they should live than emerging adults do in the West (Rosenberger, 2007).
When does Adulthood Begin?
According to Rankin and Kenyon (2008), historically the process of becoming an adult was more clearly marked by rites of passage. For many individuals, marriage and becoming a parent were considered entry into adulthood. However, these role transitions are no longer considered as the important markers of adulthood (Arnett, 2001). Economic and social changes have resulted in increase in young adults attending college (Rankin & Kenyon, 2008) and a delay in marriage and having children (Arnett & Taber, 1994; Laursen & Jensen-Campbell, 1999) Consequently, current research has found financial independence and accepting responsibility for oneself to be the most important markers of adulthood in Western culture across age (Arnett, 2001) and ethnic groups (Arnett, 2004).
In looking at college students’ perceptions of adulthood, Rankin and Kenyon (2008) found that some students still view rites of passage as important markers. College students who had placed more importance on role transition markers, such as parenthood and marriage, belonged to a fraternity/sorority, were traditionally aged (18–25), belonged to an ethnic minority, were of a traditional marital status; i.e., not cohabitating, or belonged to a religious organization, particularly for men. These findings supported the view that people holding collectivist or more traditional values place more importance on role transitions as markers of adulthood. In contrast, older college students and those cohabitating did not value role transitions as markers of adulthood as strongly.
Living Arrangements in Emerging and Early Adulthood

In 2014, for the first time in more than 130 years, adults 18 to 34 were more likely to be living in their parents’ home than they were to be living with a spouse or partner in their own household (Fry, 2016). The current trend is that young Canadians and Americans are not choosing to settle down romantically before age 35. Since 1880, living with a romantic partner was the most common living arrangement among young adults. In 1960, 62% of America’s 18- to 34-year-olds were living with a spouse or partner in their own household, while only 20% were living with their parents.
By 2014, 31.6% of early adults were living with a spouse or partner in their own household, while 32.1% were living in the home of their parent(s). Another 14% of early adults lived alone, were a single parent, or lived with one or more roommates. The remaining 22% lived in the home of another family member (such as a grandparent, in-law, or sibling), a non-relative, or in group quarters (e.g., college dormitories). Comparing ethnic groups, 36% of black and Hispanic early adults lived at home, while 30% of white young adults lived at home.
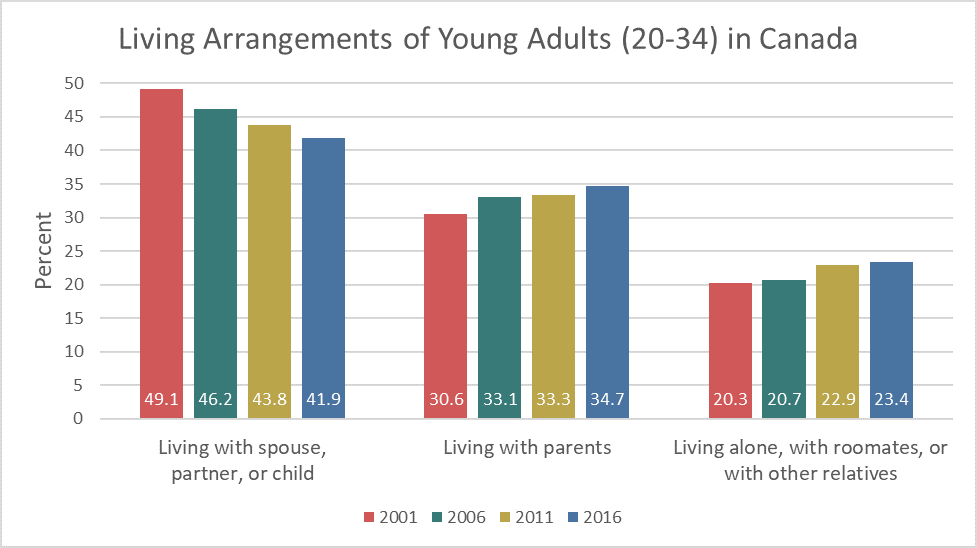
Gender differences in living arrangements are also noted in that young men are living with parents at a higher rate than young women (55.7% versus 44.3% in Canada in 2011, according to Statistics Canada). In 2014, 35% of young American men were residing with their parents, while 28% were living with a spouse or partner in their own household. Young women were more likely to be living with a spouse or partner (35%) than living with their parents (29%). Additionally, more young women (16%) than young men (13%) were heading up a household without a spouse or partner, primarily because women are more likely to be single parents living with their children. Lastly, young men (25%) are more likely than young women (19%) to be living in the home of another family member, a non-relative, or in some type of group quarters (Fry, 2016).
What are some factors that help explain these changes in living arrangements? First, early adults are postponing marriage or choosing not to marry or cohabitate. Lack of employment and lower wages have especially contributed to males residing with their parents. Men who are employed are less likely to live at home. Wages for young men (adjusting for inflation) have been falling since 1970 and correlate with the rise in young men living with their parents. The recent recession and recovery (2007-present) has also contributed to the increase in early adults living at home. College enrollments increased during the recession, which further increased early adults living at home. However, once early adults possess a college degree, they are more likely to establish their own households (Fry, 2016).
Media Attributions
- Group of friends taking a selfie © Rawpixel Ltd is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- 034-OECDcountries © Joowwww is licensed under a Public Domain license
- 033-YoungAsianCouple © Matthew Kenwrick is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- 030-YoungAdultRoommates © Robert Judge
- 033-YoungAdultLivingArrangementsCAN

