7 Financing of Constructed Facilities
7.1 The Financing Problem
Investment in a constructed facility represents a cost in the short term that returns benefits only over the long-term use of the facility. Thus, costs occur earlier than the benefits, and owners of facilities must obtain the capital resources to finance the costs of construction. A project cannot proceed without adequate financing, and the cost of providing adequate financing can be quite large. For these reasons, attention to project finance is an important aspect of project management. Finance is also a concern to the other organizations involved in a project such as the general contractor and material suppliers. Unless an owner immediately and completely covers the costs incurred by each participant, these organizations face financing problems of their own.
At a more general level, project finance is only one aspect of the general problem of corporate finance. If numerous projects are considered and financed together, then the net cash flow requirements constitute the corporate financing problem for capital investment. Whether project finance is performed at the project or at the corporate level does not alter the basic financing problem.
In essence, the project finance problem is to obtain funds to bridge the time between making expenditures and obtaining revenues. Based on the conceptual plan, the cost estimate and the construction plan, the cash flow of costs and receipts for a project can be estimated. Normally, this cash flow will involve expenditures in early periods. Covering this negative cash balance in the most beneficial or cost-effective fashion is the project finance problem. During planning and design, expenditures of the owner are modest, whereas substantial costs are incurred during construction. Only after the facility is complete do revenues begin. In contrast, a contractor would receive periodic payments from the owner as construction proceeds. However, a contractor also may have a negative cash balance due to delays in payment and retainage of profits or cost reimbursements on the part of the owner.
Plans considered by owners for facility financing typically have both long- and short-term aspects. In the long term, sources of revenue include sales, grants, and tax revenues. Borrowed funds must be eventually paid back from these other sources. In the short term, a wider variety of financing options exist, including borrowing, grants, corporate investment funds, payment delays and others. Many of these financing options involve the participation of third parties such as banks or bond underwriters. For private facilities such as office buildings, it is customary to have completely different financing arrangements during the construction period and during the period of facility use. During the latter period, mortgage or loan funds can be secured by the value of the facility itself. Thus, different arrangements of financing options and participants are possible at different stages of a project, so the practice of financial planning is often complicated.
On the other hand, the options for borrowing by contractors to bridge their expenditures and receipts during construction are relatively limited. For small or medium size projects, overdrafts from bank accounts are the most common form of construction financing. Usually, a maximum limit is imposed on an overdraft account by the bank on the basis of expected expenditures and receipts for the duration of construction. Contractors who are engaged in large projects often own substantial assets and can make use of other forms of financing which have lower interest charges than overdrafting.
Design-build-operate projects are those in which owners prescribe functional requirements and a contractor handles financing. Contractors are repaid over a period of time from project revenues or government payments. Sometimes this arrangement is called a “concession”. Eventually, ownership of the facilities is transferred to a government entity. Examples of this type of project are the Confederation Bridge to Prince Edward Island in Canada and Highway 407 that skirts the Greater Toronto Area (GTA).
In this chapter, we will first consider facility financing from the owner's perspective, with due consideration for its interaction with other organizations involved in a project. Later, we discuss the problems of construction financing which are crucial to the profitability and solvency of construction contractors.
7.2 Institutional Arrangements for Facility Financing
Financing arrangements differ sharply by type of owner and by the type of facility construction. As one example, many municipal projects are financed in the United States with tax exempt bonds for which interest payments to a lender are exempt from income taxes. As a result, tax exempt municipal bonds are available at lower interest charges. Different institutional arrangements have evolved for specific types of facilities and organizations.
A private corporation which plans to undertake large capital projects may use its retained earnings, seek equity partners in the project, issue bonds, offer new stocks in the financial markets, or seek borrowed funds in another fashion. Potential sources of funds would include pension funds, insurance companies, investment trusts, asset managers, commercial banks and others. Developers who invest in real estate properties for rental purposes have similar sources, plus quasi-governmental corporations such as urban development authorities. Syndicators for investment such as real estate investment trusts (REITs) as well as domestic and foreign pension funds represent relatively new entries to the financial market for building mortgage money.
Public projects may be funded by tax receipts, general revenue bonds, or special bonds with income dedicated to the specified facilities. General revenue bonds would be repaid from general taxes or other revenue sources, while special bonds would be redeemed either by special taxes or user fees collected for the project. Grants from higher levels of government are also an important source of funds for state, county, city or other local agencies.
Despite the different sources of borrowed funds, there is a rough equivalence in the actual cost of borrowing money for particular types of projects. Because lenders can participate in many different financial markets, they tend to switch towards loans that return the highest yield for a particular level of risk. As a result, borrowed funds that can be obtained from different sources tend to have very similar costs, including interest charges and issuing costs.
As a general principle, however, the costs of funds for construction will vary inversely with the risk of a loan. Lenders usually require security for a loan represented by a tangible asset. If for some reason the borrower cannot repay a loan, then the borrower can take possession of the loan security. To the extent that an asset used as security is of uncertain value, then the lender will demand a greater return and higher interest payments. Loans made for projects under construction represent considerable risk to a financial institution. If a lender acquires an unfinished facility, then it faces the difficult task of re-assembling the project team. Moreover, a default on a facility may result if a problem occurs such as foundation problems or anticipated unprofitability of the future facility. As a result of these uncertainties, construction lending for unfinished facilities commands a premium interest charge of several percent compared to mortgage lending for completed facilities.
Financing plans will typically include a reserve amount to cover unforeseen expenses, cost increases or cash flow problems. This reserve can be represented by a special reserve or a contingency amount in the project budget. In the simplest case, this reserve might represent a borrowing agreement with a financial institution to establish a line of credit in case of need. For publicly traded bonds, specific reserve funds administered by a third party may be established. The cost of these reserve funds is the difference between the interest paid to bondholders and the interest received on the reserve funds plus any administrative costs.
Finally, arranging financing may involve a lengthy period of negotiation and review. Particularly for publicly traded bond financing, specific legal requirements in the issue must be met. A typical seven-month schedule to issue revenue bonds would include the various steps outlined in Table 7-1. [1] In many cases, the speed in which funds may be obtained will determine a project's financing mechanism.
TABLE 7-1 Illustrative Process and Timing for Issuing Revenue Bonds
| Activities | Time of Activities |
| Analysis of financial alternatives Preparation of legal documents Preparation of disclosure documents Forecasts of costs and revenues Bond Ratings Bond Marketing Bond Closing and Receipt of Funds |
Weeks 0-4 Weeks 1-17 Weeks 2-20 Weeks 4-20 Weeks 20-23 Weeks 21-24 Weeks 23-26 |
Example 7-1: Example of financing options
Suppose that you represent a private corporation attempting to arrange financing for a new headquarters building. These are several options that might be considered:
-
- Use corporate equity and retained earnings: The building could be financed by directly committing corporate resources. In this case, no other institutional parties would be involved in the finance. However, these corporate funds might be too limited to support the full cost of construction.
- Construction loan and long-term mortgage: In this plan, a loan is obtained from a bank or other financial institution to finance the cost of construction. Once the building is complete, a variety of institutions may be approached to supply mortgage or long-term funding for the building. This financing plan would involve both short- and long-term borrowing, and the two periods might involve different lenders. The long-term funding would have greater security since the building would then be complete. As a result, more organizations might be interested in providing funds (including pension funds) and the interest charge might be lower. Also, this basic financing plan might be supplemented by other sources such as corporate retained earnings or assistance from a local development agency.
- Lease the building from a third party: In this option, the corporation would contract to lease space in a headquarters building from a developer. This developer would be responsible for obtaining funding and arranging construction. This plan has the advantage of minimizing the amount of funds borrowed by the corporation. Under terms of the lease contract, the corporation still might have considerable influence over the design of the headquarters building even though the developer was responsible for design and construction.
- Initiate a Joint Venture with Local Government: In many areas, local governments will help local companies with major new ventures such as a new headquarters. This help might include assistance in assembling property, low interest loans or property tax reductions. In the extreme, local governments may force sale of land through their power of eminent domain to assemble necessary plots.
7.3 Evaluation of Alternative Financing Plans
Since there are numerous different sources and arrangements for obtaining the funds necessary for facility construction, owners and other project participants require some mechanism for evaluating the different potential sources. The relative costs of different financing plans are certainly important in this regard. In addition, the flexibility of the plan and availability of reserves may be critical. As a project manager, it is important to assure adequate financing to complete a project. Alternative financing plans can be evaluated using the same techniques that are employed for the evaluation of investment alternatives.
As described in Chapter 6, the availability of different financing plans can affect the selection of alternative projects. A general approach for obtaining the combined effects of operating and financing cash flows of a project is to determine the adjusted net present value (APV) which is the sum of the net present value of the operating cash flow (NPV) and the net present value of the financial cash flow (FPV), discounted at their respective minimum attractive rates of return (MARR), i.e.,
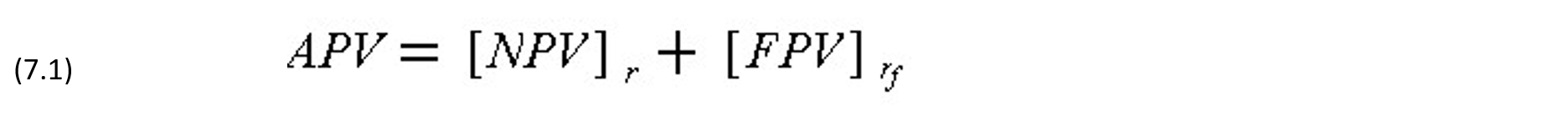
where r is the MARR reflecting the risk of the operating cash flow and rf is the MARR representing the cost of borrowing for the financial cash flow. Thus,
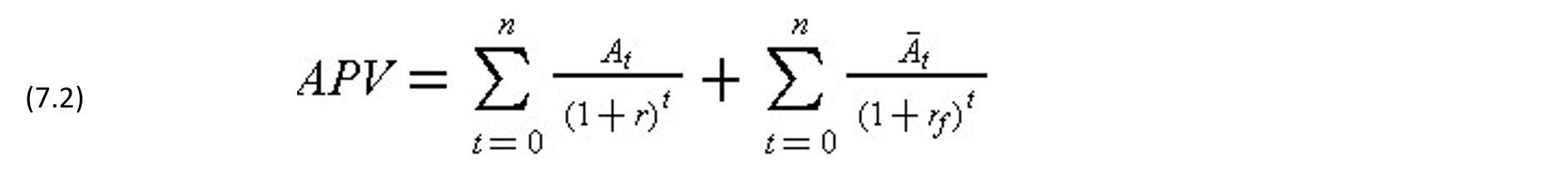
where At and Āt are respectively the operating and financial cash flows in period t.
For the sake of simplicity, we shall emphasize in this chapter the evaluation of financing plans, with occasional references to the combined effects of operating and financing cash flows. In all discussions, we shall present various financing schemes with examples limiting to cases of before-tax cash flows discounted at a before-tax MARR of r = rf for both operating and financial cash flows. Once the basic concepts of various financing schemes are clearly understood, their application to more complicated situations involving depreciation, tax liability and risk factors can be considered in combination with the principles for dealing with such topics enunciated in Chapter 6.
In this section, we shall concentrate on the computational techniques associated with the most common types of financing arrangements. More detailed descriptions of various financing schemes and the comparisons of their advantages and disadvantages will be discussed in later sections.
Typically, the interest rate for borrowing is stated in terms of annual percentage rate (A.P.R.), but the interest is accrued according to the rate for the interest period specified in the borrowing agreement. Let ip be the nominal annual percentage rate, and i be the interest rate for each of the p interest periods per year. By definition

If interest is accrued semi-annually, i.e., p = 2, the interest rate per period is ip/2; similarly, if the interest is accrued monthly, i.e., p = 12, the interest rate per period is ip/12. On the other hand, the effective annual interest rate ie is given by:
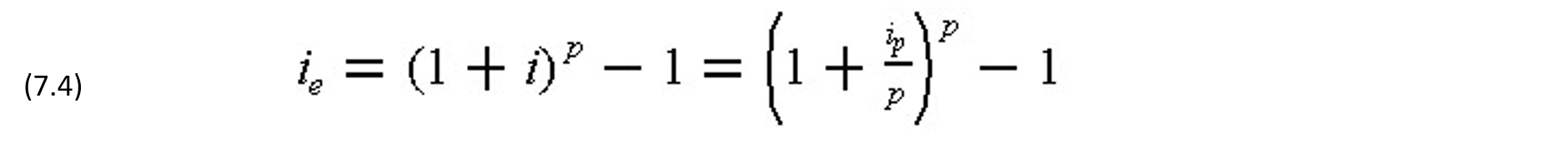
Note that the effective annual interest rate, ie, takes into account compounding within the year. As a result, ie is greater than ip for the typical case of more than one compounding period per year.
For a coupon bond, the face value of the bond denotes the amount borrowed (called principal) which must be repaid in full at a maturity or due date, while each coupon designates the interest to be paid periodically for the total number of coupons covering all periods until maturity. Let Q be the amount borrowed, and Ip be the interest payment per period which is often six months for coupon bonds. If the coupon bond is prescribed to reach maturity in n years from the date of issue, the total number of interest periods will be pn = 2n. The semi-annual interest payment is given by:

In purchasing a coupon bond, a discount from or a premium above the face value may be paid.
An alternative loan arrangement is to make a series of uniform payments including both interest and part of the principal for a pre-defined number of repayment periods. In the case of uniform payments at an interest rate i for n repayment periods, the uniform repayment amount U is given by:
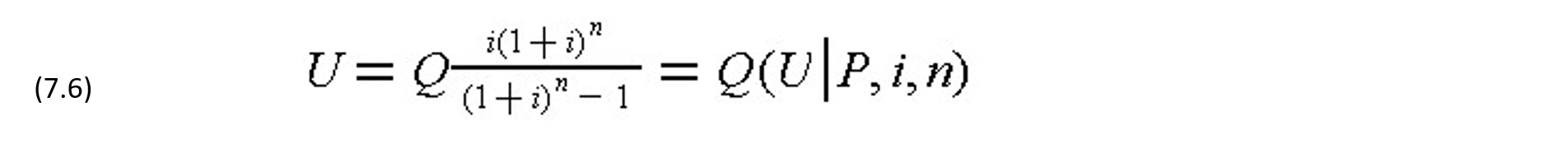
where (U|P,i,n) is a capital recovery factor which reads: "to find U, given P=1, for an interest rate i over n periods." Compound interest factors are as tabulated in Appendix A. The number of repayment periods n will clearly influence the amounts of payments in this uniform payment case. Uniform payment bonds or mortgages are based on this form of repayment.
Usually, there is an origination fee associated with borrowing for legal and other professional services which is payable upon the receipt of the loan. This fee may appear in the form of issuance charges for revenue bonds or percentage point charges for mortgages. The borrower must allow for such fees in addition to the construction cost in determining the required original amount of borrowing. Suppose that a sum of Po must be reserved at t=0 for the construction cost, and K is the origination fee. Then the original loan needed to cover both is:

If the origination fee is expressed as k percent of the original loan, i.e., K = kQ0, then:

Since interest and sometimes parts of the principal must be repaid periodically in most financing arrangements, an amount Q considerably larger than Q0 is usually borrowed in the beginning to provide adequate reserve funds to cover interest payments, construction cost increases and other unanticipated shortfalls. The net amount received from borrowing is deposited in a separate interest-bearing account from which funds will be withdrawn periodically for necessary payments. Let the borrowing rate per period be denoted by i and the interest for the running balance accrued to the project reserve account be denoted by h. Let At be the net operating cash flow for - period t (negative for construction cost in period t) and Āt be the net financial cash flow in period t (negative for payment of interest or principal or a combination of both). Then, the running balance Nt of the project reserve account can be determined by noting that at t=0,

and at t = 1,2,...,n:
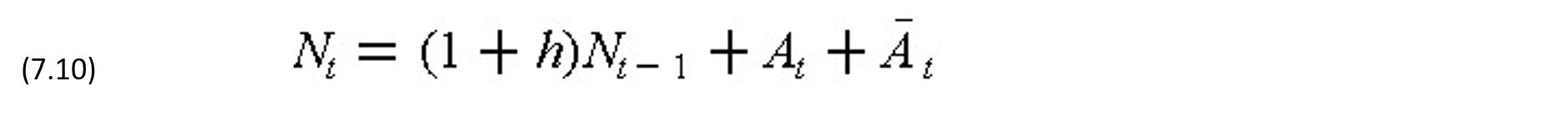
where the value of At or t may be zero for some period(s). Equations (7.9) and (7.10) are approximate in that interest might be earned on intermediate balances based on the pattern of payments during a period instead of at the end of a period.
Because the borrowing rate i will generally exceed the investment rate h for the running balance in the project account and since the origination fee increases with the amount borrowed, the financial planner should minimize the amount of money borrowed under this finance strategy. Thus, there is an optimal value for Q such that all estimated shortfalls are covered, interest payments and expenses are minimized, and adequate reserve funds are available to cover unanticipated factors such as construction cost increases. This optimal value of Q can either be identified analytically or by trial and error.
Finally, variations in ownership arrangements may also be used to provide at least partial financing. Leasing a facility removes the need for direct financing of the facility. Sale-leaseback involves sale of a facility to a third party with a separate agreement involving use of the facility for a pre-specified period of time. In one sense, leasing arrangements can be viewed as a particular form of financing. In return for obtaining the use of a facility or piece of equipment, the user (lesser) agrees to pay the owner (lesser) a lease payment every period for a specified number of periods. Usually, the lease payment is at a fixed level due every month, semi-annually, or annually. Thus, the cash flow associated with the equipment or facility use is a series of uniform payments. This cash flow would be identical to a cash flow resulting from financing the facility or purchase with sufficient borrowed funds to cover initial construction (or purchase) and with a repayment schedule of uniform amounts. Of course, at the end of the lease period, the ownership of the facility or equipment would reside with the lesser. However, the lease terms may include a provision for transferring ownership to the lesser after a fixed period.
Example 7-2: A coupon bond cash flow and cost
A private corporation wishes to borrow $10.5 million for the construction of a new building by issuing a twenty-year coupon bond at an annual percentage interest rate of 10% to be paid semi-annually, i.e. 5% per interest period of six months. The principal will be repaid at the end of 20 years. The amount borrowed will cover the construction cost of $10.331 million and an origination fee of $169,000 for issuing the coupon bond.
The interest payment per period is (5%) (10.5) = $0.525 million over a lifetime of (2) (20) = 40 interest periods. Thus, the cash flow of financing by the coupon bond consists of a $10.5 million receipt at period 0, -$0.525 million each for periods 1 through 40, and an additional -$10.5 million for period 40. Assuming a MARR of 5% per period, the net present value of the financial cash flow is given by:
[FPV]5%) = 10.5 - (0.525)(P|U, 5%, 40) - (10.5)(P|F, 5%, 40) = 0
This result is expected since the corporation will be indifferent between borrowing and diverting capital from other uses when the MARR is identical to the borrowing rate. Note that the effective annual rate of the bond may be computed according to Eq.(7.4) as follows:
ie = (1 + 0.05)2 - 1 = 0.1025 = 10.25%
If the interest payments were made only at the end of each year over twenty years, the annual payment should be:
0.525(1 + 0.05) + 0.525 = 1.076
where the first term indicates the deferred payment at the mid-year which would accrue interest at 5% until the end of the year, then:
[FPV]10.25% = 10.5 - (1.076)(P|U, 10.25%, 20) - (10.5)(P|F, 10.25%, 20) = 0
In other words, if the interest is paid at 10.25% annually over twenty years of the loan, the result is equivalent to the case of semi-annual interest payments at 5% over the same lifetime.
Example 7-3: An example of leasing versus ownership analysis
Suppose that a developer offered a building to a corporation for an annual lease payment of $10 million over a thirty-year lifetime. For the sake of simplicity, let us assume that the developer also offers to donate the building to the corporation at the end of thirty years or, alternatively, the building would then have no commercial value. Also, suppose that the initial cost of the building was $65.66 million. For the corporation, the lease is equivalent to receiving a loan with uniform payments over thirty years at an interest rate of 15% since the present value of the lease payments is equal to the initial cost at this interest rate:
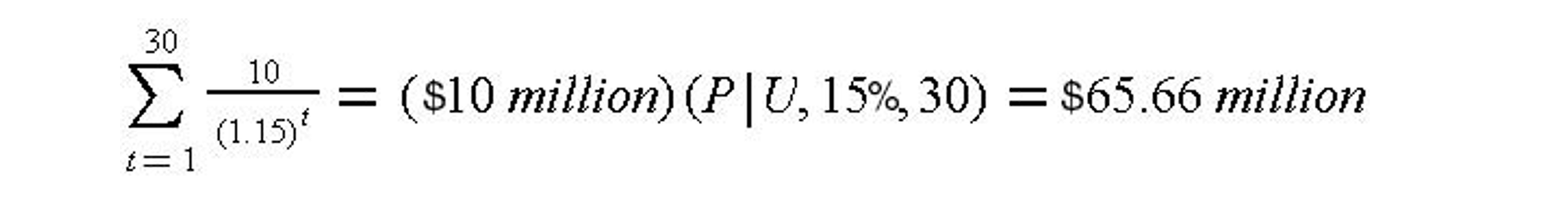
If the minimum attractive rate of return of the corporation is greater than 15%, then this lease arrangement is advantageous as a financing scheme since the net present value of the leasing cash flow would be less than the cash flow associated with construction from retained earnings. For example, with MARR equal to 20%:
[FPV]20% = $65.66 million - ($10 million)(P|U, 20%, 30) = $15.871 million
On the other hand, with MARR equal to 10%:
[FPV]10% = $65.66 million - ($10 million)(P|U, 10%, 30) = - $28.609 million
and the lease arrangement is not advantageous.
Example 7-4: Example evaluation of alternative financing plans.
Suppose that a small corporation wishes to build a headquarters building. The construction will require two years and cost a total of $12 million, assuming that $5 million is spent at the end of the first year and $7 million at the end of the second year. To finance this construction, several options are possible, including:
-
- Investment from retained corporate earnings;
- Borrowing from a local bank at an interest rate of 11.2% with uniform annual payments over twenty years to pay for the construction costs. The shortfalls for repayments on loans will come from corporate earnings. An origination fee of 0.75% of the original loan is required to cover engineer's reports, legal issues, etc; or
- A twenty-year coupon bond at an annual interest rate of 10.25% with interest payments annually, repayment of the principal in year 20, and a $169,000 origination fee to pay for the construction cost only.
The current corporate MARR is 15%, and short-term cash funds can be deposited in an account having a 10% annual interest rate.
The first step in evaluation is to calculate the required amounts and cash flows associated with these three alternative financing plans. First, investment using retained earnings will require a commitment of $5 million in year 1 and $7 million in year 2.
Second, borrowing from the local bank must yield sufficient funds to cover both years of construction plus the issuing fee. With the unused fund accumulating interest at a rate of 10%, the amount of dollars needed at the beginning of the first year for future construction cost payments is:
P0 = ($5 million)/(1.1) + ($7 million)/(1.1)2 = $10.331 million
Discounting at ten percent in this calculation reflects the interest earned in the intermediate periods. With a 10% annual interest rate, the accrued interests for the first two years from the project account of $10.331 at t=0 will be:
Year 1: I1 = (10%)(10.331 million) = $1.033 million
Year 2: I2 = (10%)(10.331 million + $1.033 million - $5.0 million) = 0.636 million
Since the issuance charge is 0.75% of the loan, the amount borrowed from the bank at t=0 to cover both the construction cost and the issuance charge is
Q0 = ($10.331 million)/(1 - 0.0075) = $ 10.409 million
The issuance charge is 10.409 - 10.331 = $ 0.078 million or $78,000. If this loan is to be repaid by annual uniform payments from corporate earnings, the amount of each payment over the twenty year life time of the loan can be calculated by Eq. (7.6) as follows:
U = ($10.409 million)[(0.112)(1.112)20]/[(1.112)20 - 1] = $1.324 million
Finally, the twenty-year coupon bond would have to be issued in the amount of $10.5 million which will reflect a higher origination fee of $169,000. Thus, the amount for financing is:
Q0 = $10.331 million + $0.169 million = $10.5 million
With an annual interest charge of 10.25% over a twenty year life time, the annual payment would be $1.076 million except in year 20 when the sum of principal and interest would be 10.5 + 1.076 = $11.576 million. The computation for this case of borrowing has been given in Example 7-2.
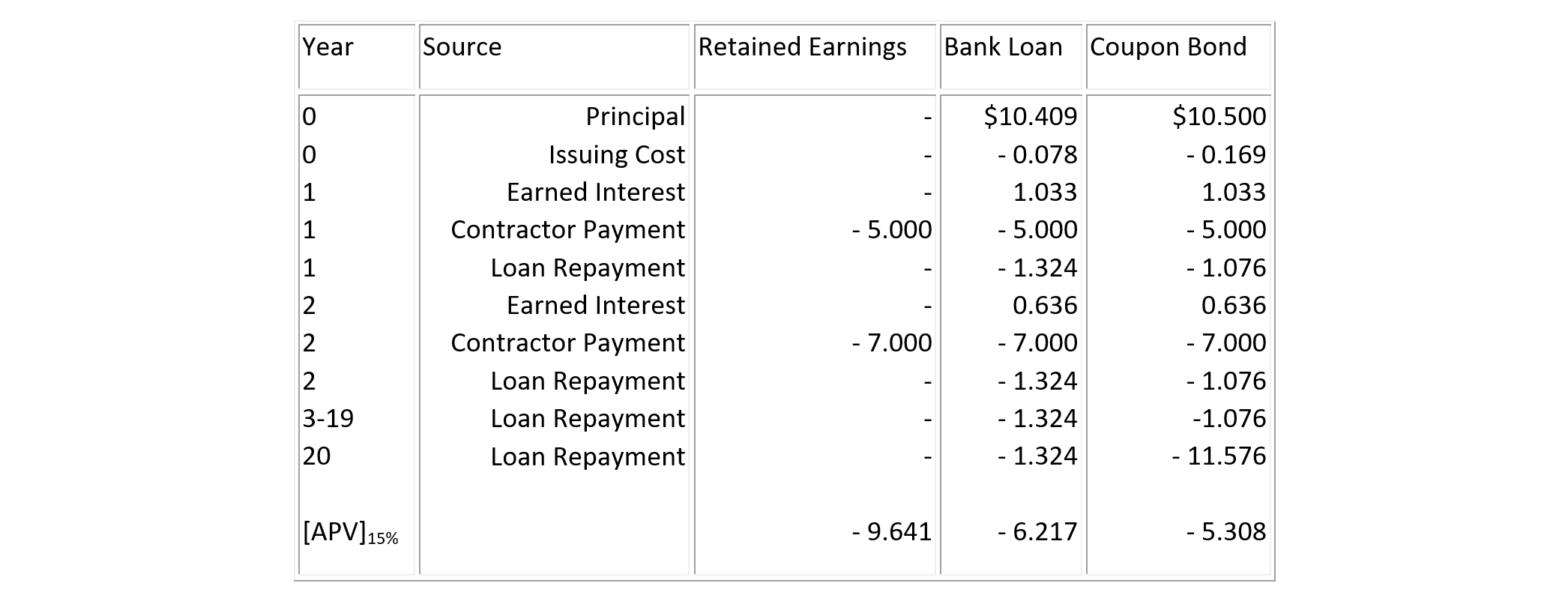
Table 7-2 summarizes the cash flows associated with the three alternative financing plans. Note that annual incomes generated from the use of this building have not been included in the computation. The adjusted net present value of the combined operating and financial cash flows for each of the three plans discounted at the corporate MARR of 15% is also shown in the table. In this case, the coupon bond is the least expensive financing plan. Since the borrowing rates for both the bank loan and the coupon bond are lower than the corporate MARR, these results are expected.
TABLE 7-2 Cash Flow Illustration of Three Alternative Financing Plans (in $ millions)
7.4 Secured Loans with Bonds, Notes and Mortgages
Secured lending involves a contract between a borrower and lender, where the lender can be an individual, a financial institution or a trust organization. Notes and mortgages represent formal contracts between financial institutions and owners. Usually, repayment amounts and timing are specified in the loan agreement. Public facilities are often financed by bond issues for either specific projects or for groups of projects. For publicly issued bonds, a trust company is usually designated to represent the diverse bond holders in case of any problems in the repayment. The borrowed funds are usually secured by granting the lender some rights to the facility or other assets in case of defaults on required payments. In contrast, corporate bonds such as debentures can represent loans secured only by the good faith and credit worthiness of the borrower.
Under the terms of many bond agreements, the borrower reserves the right to repurchase the bonds at any time before the maturity date by repaying the principal and all interest up to the time of purchase. The required repayment Rc at the end of period c is the net future value of the borrowed amount Q - less the payment Āt made at intermediate periods compounded at the borrowing rate i to period c as follows:
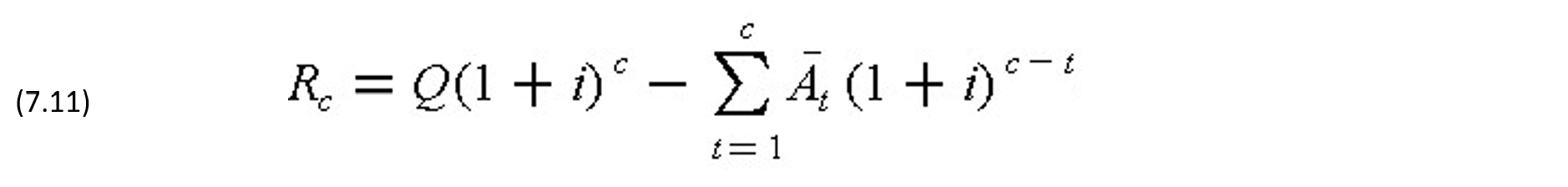
The required repayment Rc at the end of the period c can also be obtained by noting the net present value of the repayments in the remaining (n-c) periods discounted at the borrowing rate i to t = c as follows:

For coupon bonds, the required repayment Rc after the redemption of the coupon at the end of period c is simply the original borrowed amount Q. For uniform payment bonds, the required repayment Rc after the last payment at the end of period c is:
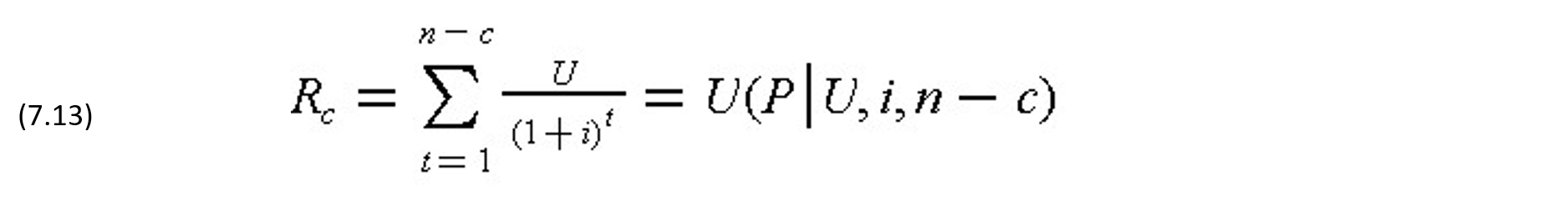
Many types of bonds can be traded in a secondary market by the bond holder. As interest rates fluctuate over time, bonds will gain or lose in value. The actual value of a bond is reflected in the market discount or premium paid relative to the original principal amount (the face value). Another indicator of this value is the yield to maturity or internal rate of return of the bond. This yield is calculated by finding the interest rate that sets the (discounted) future cash flow of the bond equal to the current market price:

where Vc is the current market value after c periods have lapsed since the - issuance of the bond, Āt is the bond cash flow in period t, and r is the market yield. Since all the bond cash flows are positive after the initial issuance, only one value of the yield to maturity will result from Eq. (7.14).
Several other factors come into play in evaluation of bond values from the lenders point of view, however. First, the lender must adjust for the possibility that the borrower may default on required interest and principal payments. In the case of publicly traded bonds, special rating companies divide bonds into different categories of risk for just this purpose. Obviously, bonds that are more likely to default will have a lower value. Secondly, lenders will typically make adjustments to account for changes in the tax code affecting their after-tax return from a bond. Finally, expectations of future inflation or deflation as well as exchange rates will influence market values.
Another common feature in borrowing agreements is to have a variable interest rate. In this case, interest payments would vary with the overall market interest rate in some pre-specified fashion. From the borrower's perspective, this is less desirable since cash flows are less predictable. However, variable rate loans are typically available at lower interest rates because the lenders are protected in some measure from large increases in the market interest rate and the consequent decrease in value of their expected repayments. Variable rate loans can have floors and ceilings on the applicable interest rate or on rate changes in each year.
Example 7-5: Example of a corporate promissory note
A corporation wishes to consider the option of financing the headquarters building in Example 7-4 by issuing a five-year promissory note which requires an origination fee for the note costing $25,000. Then a total borrowed amount needed at the beginning of the first year to pay for the construction costs and origination fee is 10.331 + 0.025 = $10.356 million. Interest payments are made annually at an annual rate of 10.8% with repayment of the principal at the end of the fifth year. Thus, the annual interest payment is (10.8%)(10.356) = $1.118 million. With the data in Example 7-4 for construction costs and accrued interests for the first two year, the combined operating and and financial cash flows in million dollars can be obtained:
Year 0, AA0 = 10.356 - 0.025 = 10.331
Year 1, AA1 = 1.033 - 5.0 - 1.118 = -5.085
Year 2, AA2 = 0.636 - 7.0 - 1.118 = -7.482
Year 3, AA3 = -1.118
Year 4, AA4 = -1.118
Year 5, AA5 = -1.118 - 10.356 = -11.474
At the current corporate MARR of 15%,
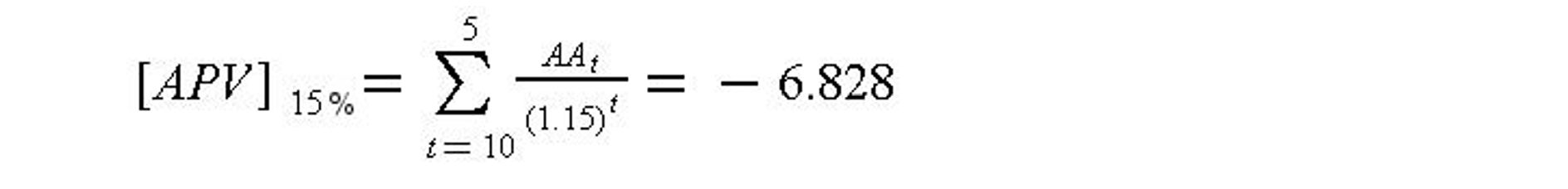
which is inferior to the 20-year coupon bond analyzed in Table 7-3.
For this problem as well as for the financing arrangements in Example 7-4, the project account is maintained to pay the construction costs only, while the interest and principal payments are repaid from corporate earnings. Consequently, the Āt terms in Eq. (7.10) will disappear when the account balance in each period is computed for this problem:
At t=0, N0 = 10.356 - 0.025 = $10.331 million
At t=1, N1 = (1 + 0.1) (10.331) - 5.0 = $6.364 million
At t=2, N2 = (1 + 0.1) (6.364) - 7.0 = $0
Example 7-6: Bond financing mechanisms.
Suppose that the net operating expenditures and receipts of a facility investment over a five-year time horizon are as shown in column 2 of Table 7-3 in which each period is six months. This is a hypothetical example with a deliberately short lifetime period to reduce the required number of calculations. Consider two alternative bond financing mechanisms for this project. Both involve borrowing $2.5 million at an issuing cost of five percent of the loan with semi-annual repayments at a nominal annual interest rate of ten percent i.e., 5% per period. Any excess funds can earn an interest of four percent each semi-annual period. The coupon bond involves only interest payments in intermediate periods, plus the repayment of the principal at the end, whereas the uniform payment bond requires ten uniform payments to cover both interests and the principal. Both bonds are subject to optional redemption by the borrower before maturity.
The operating cash flow in column 2 of Table 7-3 represents the construction expenditures in the early periods and rental receipts in later periods over the lifetime of the facility. By trial and error with Eqs. (7.9) and (7.10), it can be found that Q = $2.5 million (K = $0.125 or 5% of Q) is necessary to ensure a nonnegative balance in the project account for the uniform payment bond, as shown in Column 6 of Table 7-3. For comparison, the same amount is borrowed for the coupon bond option even though a smaller loan will be sufficient for the construction expenditures in this case.
The financial cash flow of the coupon bond can easily be derived from Q = $2.5 million and K = $0.125 million. Using Eq. (7.5), Ip = (5%)(2.5) = $0.125 million, and the repayment in Period 10 is Q + Ip = $2.625 million as shown in Column 3 of Table 7-3. The account balance for the coupon bond in Column 4 is obtained from Eqs. (7.9) and (7.10). On the other hand, the uniform annual payment U = $0.324 million for the financial cash flow of the uniform payment bond (Column 5) can be obtained from Eq. (7.6), and the bond account for this type of balance is computed by Eqs. (7.9) and (7.10).
Because of the optional redemption provision for both types of bonds, it is advantageous to gradually redeem both options at the end of period 3 to avoid interest payments resulting from i = 5% and h = 4% unless the account balance beyond period 3 is needed to fund other corporate investments. corporate earnings are available for repurchasing the bonds at end of period 3, the required repayment for coupon bond after redeeming the last coupon at the end of period 3 is simply $2.625 million. In the case of the uniform payment bond, the required payment after the last uniform payment at the end of period 3 is obtained from Equation (7-13) as:
R3 = (0.324)(P|U, 5%, 7) = (0.324)(5.7864) = $1.875 million.
TABLE 7-3 Example of Two Borrowing Cash Flows (in $ thousands)

Example 7-7: Provision of Reserve Funds
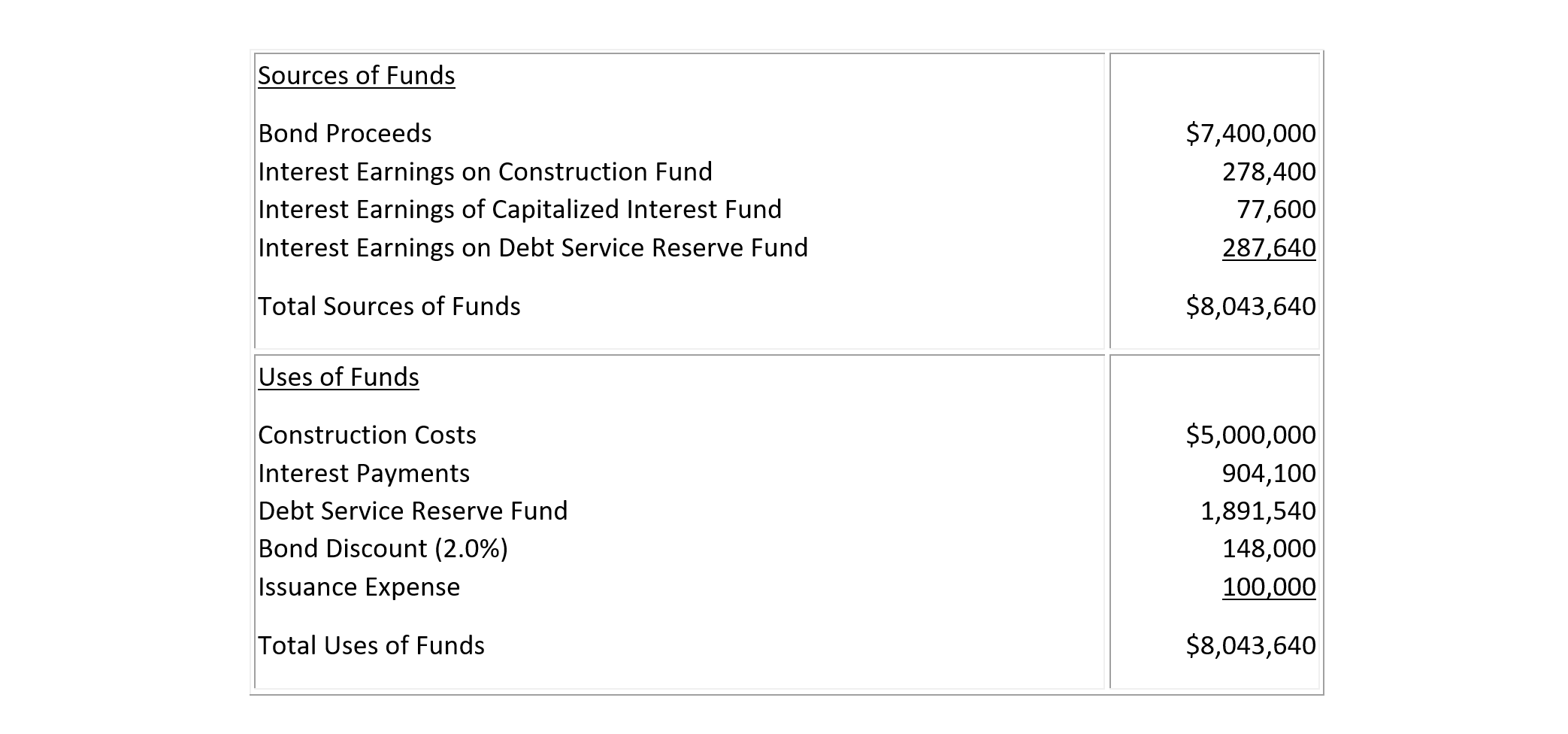
Typical borrowing agreements may include various required reserve funds. [2] Consider an eighteen-month project costing five million dollars. To finance this facility, coupon bonds will be issued to generate revenues which must be sufficient to pay interest charges during the eighteen months of construction, to cover all construction costs, to pay issuance expenses, and to maintain a debt service reserve fund. The reserve fund is introduced to assure bondholders of payments in case of unanticipated construction problems. It is estimated that a total amount of $7.4 million of bond proceeds is required, including a two percent discount to underwriters and an issuance expense of $100,000.
Three interest bearing accounts are established with the bond proceeds to separate various categories of funds:
-
- A construction fund to provide payments to contractors, with an initial balance of $4,721,600. Including interest earnings, this fund will be sufficient to cover the $5,000,000 in construction expenses.
- A capitalized interest fund to provide interest payments during the construction period.
- A debt service reserve fund to be used for retiring outstanding debts after the completion of construction.
The total sources of funds (including interest from account balances) and uses of funds are summarized in Table 7-4
TABLE 7-4 Illustrative Sources and Uses of Funds from Revenue Bonds During Construction
Example 7-8: Variable rate revenue bonds prospectus
The information in Table 7-5 is abstracted from the Prospectus for a new issue of revenue bonds for Atwood City. This prospectus language is typical for municipal bonds. Notice the provision for variable rate after the initial interest periods. The borrower reserves the right to repurchase the bond before the date for conversion to variable rate takes effect to protect itself from declining market interest rates in the future so that the borrower can obtain other financing arrangements at lower rates.
TABLE 7-5 Provision of Variable Rate for Bonds

7.5 Overdraft Accounts
Overdrafts can be arranged with a banking institution to allow accounts to have either a positive or a negative balance. With a positive balance, interest is paid on the account balance, whereas a negative balance incurs interest charges. Usually, an overdraft account will have a maximum overdraft limit imposed. Also, the interest rate h available on positive balances is less than the interest rate i charged for borrowing.
Clearly, the effects of overdraft financing depends upon the pattern of cash flows over time. Suppose that the net cash flow for period t in the account is denoted by At which is the difference between the receipt Pt and the payment Et in period t. Hence, At can either be positive or negative. The amount of overdraft at the end of period t is the cumulative net cash flow Nt which may also be positive or negative. If Nt is positive, a surplus is indicated and the subsequent interest would be paid to the borrower. Most often, Nt is negative during the early time periods of a project and becomes positive in the later periods when the borrower has received payments exceeding expenses.
If the borrower uses overdraft financing and pays the interest per period on the accumulated overdraft at a borrowing rate i in each period, then the interest per period for the accumulated overdraft Nt-1 from the previous period (t-1) is It = iNt-1 where It would be negative for a negative account balance Nt-1. For a positive account balance, the interest received is It = hNt-1 where It would be positive for a positive account balance.
The account balance Nt at each period t is the sum of receipts Pt, payments Et, interest It and the account balance from the previous period Nt-1. Thus,
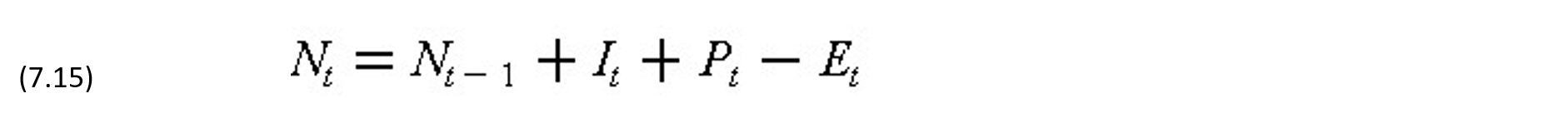
where It = iNt-1 for a negative Nt-1 and It = hNt-1 for a positive Nt-1. The net cash flow At = Pt - Et is positive for a net receipt and negative for a net payment. This equation is approximate in that the interest might be earned on intermediate balances based on the pattern of payments during the period instead of at the end of a period. The account balance in each period is of interest because there will always be a maximum limit on the amount of overdraft available.
For the purpose of separating project finances with other receipts and payments in an organization, it is convenient to establish a credit account into which receipts related to the project must be deposited when they are received, and all payments related to the project will be withdrawn from this account when they are needed. Since receipts typically lag behind payments for a project, this credit account will have a negative balance until such time when the receipts plus accrued interests are equal to or exceed payments in the period. When that happens, any surplus will not be deposited in the credit account, and the account is then closed with a zero balance. In that case, for negative Nt-1, Eq. (7.15) can be expressed as:
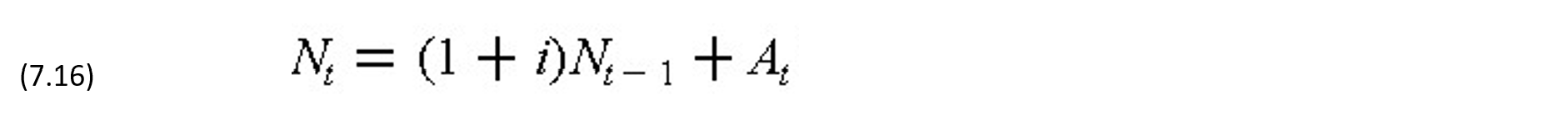
and as soon as Nt reaches a positive value or zero, the account is closed.
Example 7-9: Overdraft Financing with Grants to a Local Agency
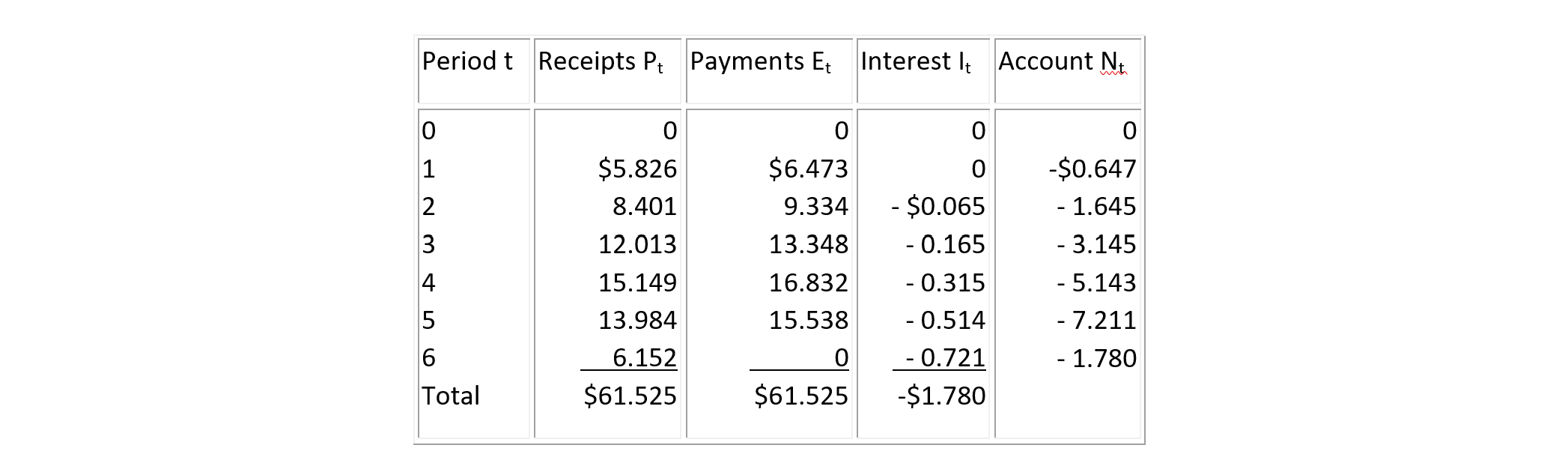
A public project which costs $61,525,000 is funded eighty percent by a federal grant and twenty percent from a state grant. The anticipated duration of the project is six years with receipts from grant funds allocated at the end of each year to a local agency to cover partial payments to contractors for that year while the remaining payments to contractors will be allocated at the end of the sixth year. The end-of-year payments are given in Table 7-6 in which t=0 refers to the beginning of the project, and each period is one year.
If this project is financed with an overdraft at an annual interest rate i = 10%, then the account balance are computed by Eq. (7.15) and the results are shown in Table 7-6.
In this project, the total grant funds to the local agency covered the cost of construction in the sense that the sum of receipts equaled the sum of construction payments of $61,525,000. However, the timing of receipts lagged payments, and the agency incurred a substantial financing cost, equal in this plan to the overdraft amount of $1,780,000 at the end of year 6 which must be paid to close the credit account. Clearly, this financing problem would be a significant concern to the local agency.
TABLE 7-6 Illustrative Payments, Receipts and Overdrafts for a Six Year Project
Example 7-10: Use of overdraft financing for a facility
A corporation is contemplating an investment in a facility with the following before-tax operating net cash flow (in thousands of dollars) at year ends:
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Cash Flow | -500 | 110 | 112 | 114 | 116 | 118 | 120 | 238 |
The MARR of the corporation before tax is 10%. The corporation will finance the facility be using $200,000 from retained earnings and by borrowing the remaining $300,000 through an overdraft credit account which charges 14% interest for borrowing. Is this proposed project including financing costs worthwhile?
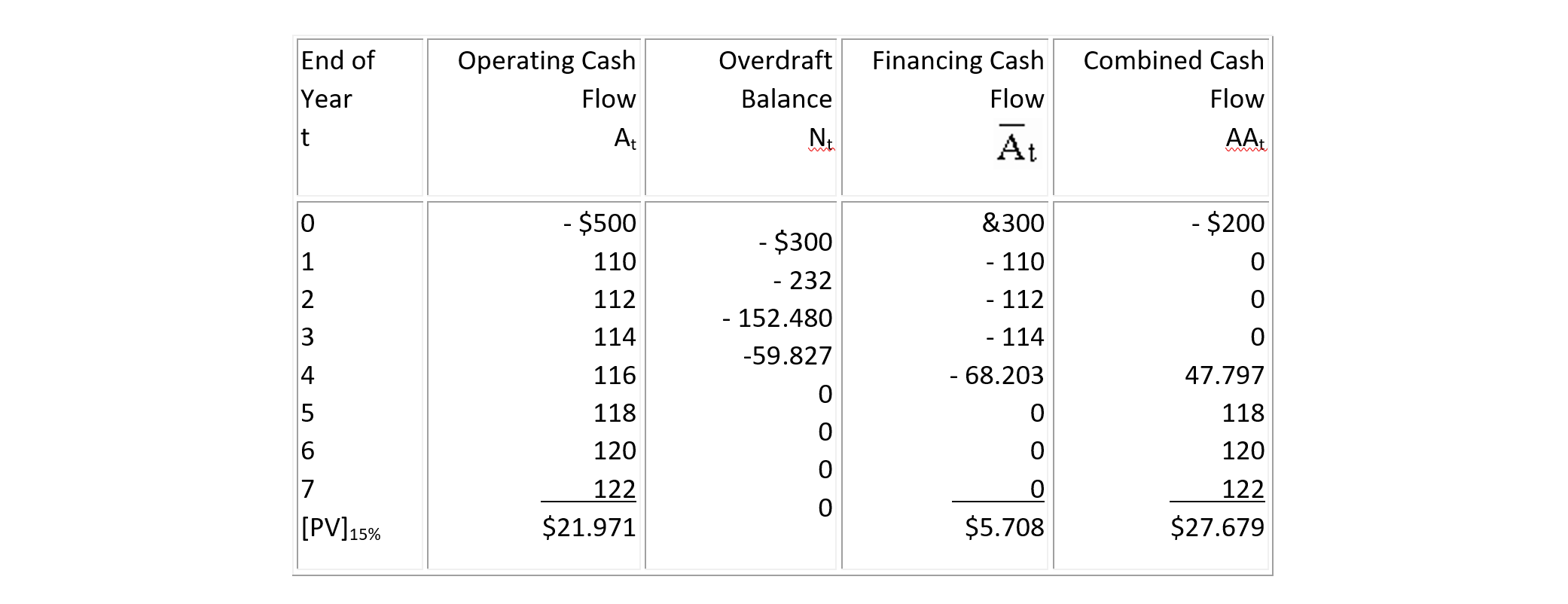
The results of the analysis of this project is shown in Table 7-7 as follows:
N0 = -500 + 200 = -300
N1 = (1.14)(-300) + 110 = -232
N2 = (1.14)(-232) + 112 = -152.48
N3 = (1.14)(-152.48) + 114 = -59.827
N4 = (1.14)(-59.827) +116 = +47.797
Since N4 is positive, it is revised to exclude the net receipt of 116 for this period. Then, the revised value for the last balance is
N4' = N4 - 116 = - 68.203
The financial cash flow Āt resulting from using overdrafts and making repayments from project receipts will be:
Ā0 = - N0 = 300
Ā1 = - A1 = -110
Ā2 = - A2 = -112
Ā3 = - A3 = -114
Ā4 = N4 - A4 = - 68.203
The adjusted net present value of the combined cash flow discounted at 15% is $27,679 as shown in Table 7-7. Hence, the project including the financing charges is worthwhile.
TABLE 7-7 Evaluation of Facility Financing Using Overdraft (in $ thousands)
7.6 Refinancing of Debts
Refinancing of debts has two major advantages for an owner. First, they allow re-financing at intermediate stages to save interest charges. If a borrowing agreement is made during a period of relatively high interest charges, then a repurchase agreement allows the borrower to re-finance at a lower interest rate. Whenever the borrowing interest rate declines such that the savings in interest payments will cover any transaction expenses (for purchasing outstanding notes or bonds and arranging new financing), then it is advantageous to do so.
Another reason to repurchase bonds is to permit changes in the operation of a facility or new investments. Under the terms of many bond agreements, there may be restrictions on the use of revenues from a particular facility while any bonds are outstanding. These restrictions are inserted to ensure bondholders that debts will be repaid. By repurchasing bonds, these restrictions are removed. For example, several bridge authorities had bonds that restricted any diversion of toll revenues to other transportation services such as transit. By repurchasing these bonds, the authority could undertake new operations. This type of repurchase may occur voluntarily even without a repurchase agreement in the original bond. The borrower may give bondholders a premium to retire bonds early.
Example 7-11: Refinancing a loan.
Suppose that the bank loan shown in Example 7-4 had a provision permitting the borrower to repay the loan without penalty at any time. Further, suppose that interest rates for new loans dropped to nine percent at the end of year six of the loan. Issuing costs for a new loan would be $50,000. Would it be advantageous to re-finance the loan at that time?
To repay the original loan at the end of year six would require a payment of the remaining principal plus the interest due at the end of year six. This amount R6 is equal to the present value of remaining fourteen payments discounted at the loan interest rate 11.2% to the end of year 6 as given in Equation (7-13) as follows:
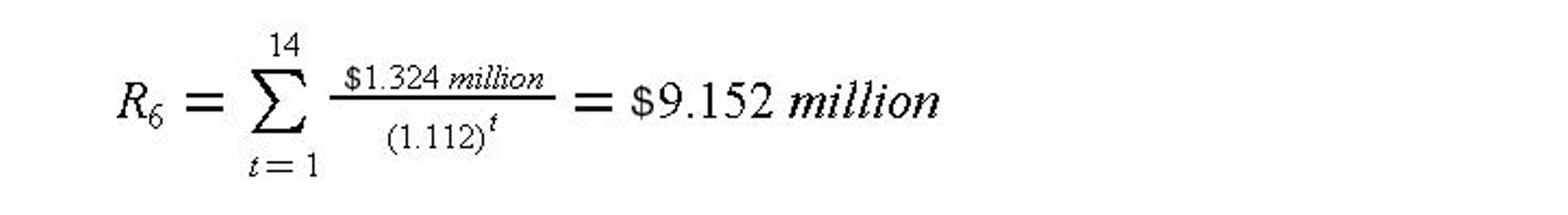
The new loan would be in the amount of $ 9.152 million plus the issuing cost of $0.05 million for a total of $ 9.202 million. Based on the new loan interest rate of 9%, the new uniform annual payment on this loan from years 7 to 20 would be:
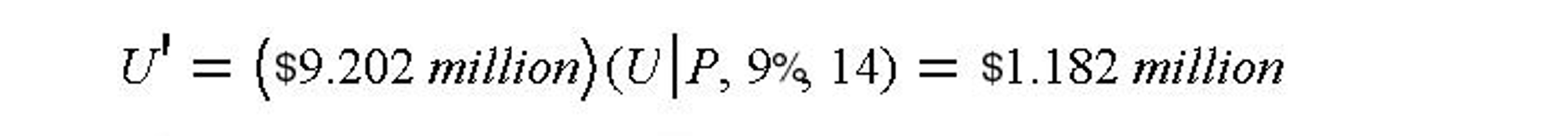
The net present value of the financial cash flow for the new loan would be obtained by discounting at the corporate MARR of 15% to the end of year six as follows:
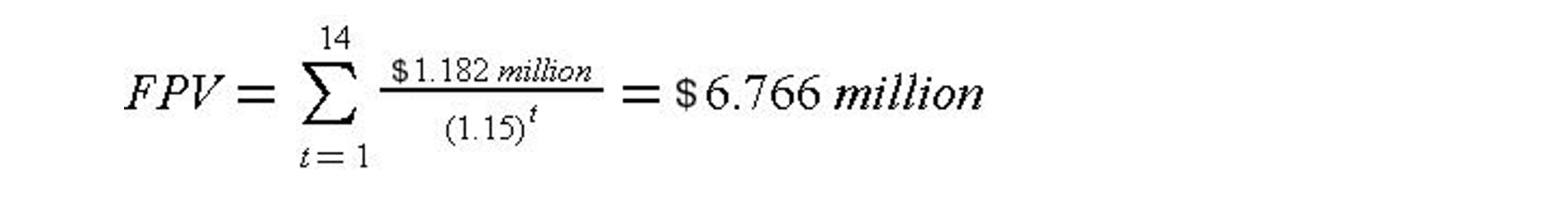
Since the annual payment on the new loan is less than the existing loan ($1.182 versus $1.324 million), the new loan is preferable.
7.7 Project versus Corporate Finance
We have focused so far on problems and concerns at the project level. While this is the appropriate viewpoint for project managers, it is always worth bearing in mind that projects must fit into broader organizational decisions and structures. This is particularly true for the problem of project finance, since it is often the case that financing is planned on a corporate or agency level, rather than a project level. Accordingly, project managers should be aware of the concerns at this level of decision making.
A construction project is only a portion of the general capital budgeting problem faced by an owner. Unless the project is very large in scope relative to the owner, a particular construction project is only a small portion of the capital budgeting problem. Numerous construction projects may be lumped together as a single category in the allocation of investment funds. Construction projects would compete for attention with equipment purchases or other investments in a private corporation.
Financing is usually performed at the corporate level using a mixture of long-term corporate debt and retained earnings. A typical set of corporate debt instruments would include the different bonds and notes discussed in this chapter. Variations would typically include different maturity dates, different levels of security interests, different currency denominations, and, of course, different interest rates.
Grouping projects together for financing influences the type of financing that might be obtained. As noted earlier, small and large projects usually involve different institutional arrangements and financing arrangements. For small projects, the fixed costs of undertaking particular kinds of financing may be prohibitively expensive. For example, municipal bonds require fixed costs associated with printing and preparation that do not vary significantly with the size of the issue. By combining numerous small construction projects, different financing arrangements become more practical.
While individual projects may not be considered at the corporate finance level, the problems and analysis procedures described earlier are directly relevant to financial planning for groups of projects and other investments. Thus, the net present values of different financing arrangements can be computed and compared. Since the net present values of different sub-sets of either investments or financing alternatives are additive, each project or finance alternative can be disaggregated for closer attention or aggregated to provide information at a higher decision-making level.
Example 7-12: Basic types of repayment schedules for loans.
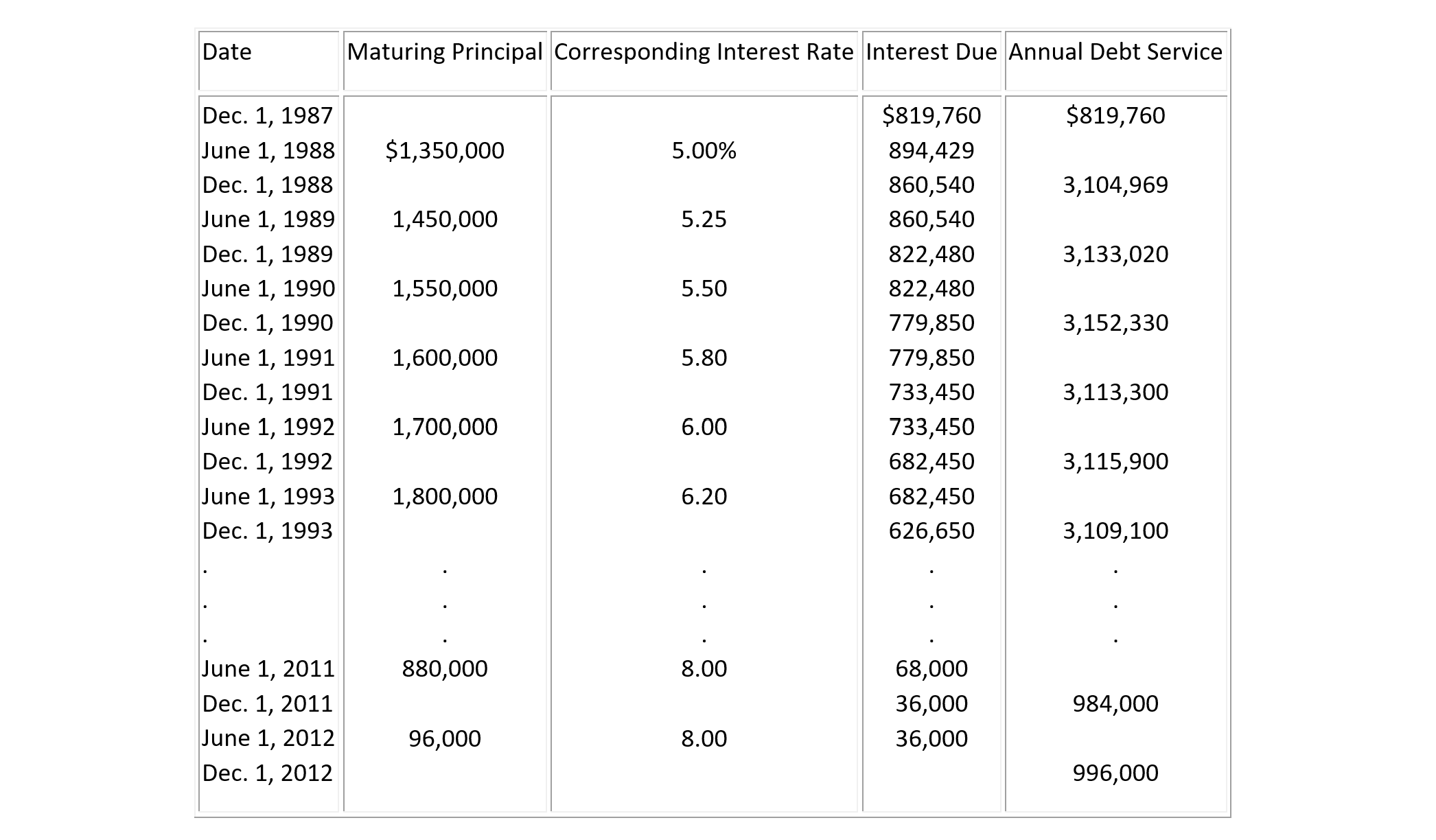
Coupon bonds are used to obtain loans which involve no payment of principal until the maturity date. By combining loans of different maturities, however, it is possible to achieve almost any pattern of principal repayments. However, the interest rates charged on loans of different maturities will reflect market forces such as forecasts of how interest rates will vary over time. As an example, Table 7-8 illustrates the cash flows of debt service for a series of coupon bonds used to fund a municipal construction project; for simplicity not all years of payments are shown in the table.
In this financing plan, a series of coupon bonds were sold with maturity dates ranging from June 1988 to June 2012. Coupon interest payments on all outstanding bonds were to be paid every six months, on December 1 and June 1 of each year. The interest rate or "coupon rate" was larger on bonds with longer maturities, reflecting an assumption that inflation would increase during this period. The total principal obtained for construction was $26,250,000 from sale of these bonds. This amount represented the gross sale amount before subtracting issuing costs or any sales discounts; the amount available to support construction would be lower. The maturity dates for bonds were selected to require relative high repayment amounts until December 1995, with a declining repayment amount subsequently. By shifting the maturity dates and amounts of bonds, this pattern of repayments could be altered. The initial interest payment (of $819,760 on December 1, 1987), reflected a payment for only a portion of a six month period since the bonds were issued in late June of 1987.
TABLE 7-8 Illustration of a Twenty-five Year Maturity Schedule for Bonds
7.8 Shifting Financial Burdens
The different participants in the construction process have quite distinct perspectives on financing. In the realm of project finance, the revenues to one participant represent an expenditure to some other participant. Payment delays from one participant result in a financial burden and a cash flow problem to other participants. It is a common occurrence in construction to reduce financing costs by delaying payments in just this fashion. Shifting payment times does not eliminate financing costs, however, since the financial burden still exists.
Traditionally, many organizations have used payment delays both to shift financing expenses to others or to overcome momentary shortfalls in financial resources. From the owner's perspective, this policy may have short term benefits, but it certainly has long term costs. Since contractors do not have large capital assets, they typically do not have large amounts of credit available to cover payment delays. Contractors are also perceived as credit risks in many cases, so loans often require a premium interest charge. Contractors faced with large financing problems are likely to add premiums to bids or not bid at all on particular work. For example, A. Maevis noted: [3]
“...there were days in New York City when city agencies had trouble attracting bidders; yet contractors were beating on the door to get work from Consolidated Edison, the local utility. Why? First, the city was a notoriously slow payer, COs (change orders) years behind, decision process chaotic, and payments made 60 days after close of estimate. Con Edison paid on the 20th of the month for work done to the first of the month. Change orders were negotiated and paid within 30 days - 60 days. If a decision was needed, it came in 10 days. The number of bids you receive on your projects are one measure of your administrative efficiency. Further, competition is bound to give you the lowest possible construction price.”
Even after bids are received and contracts signed, delays in payments may form the basis for a successful claim against an agency on the part of the contractor.
The owner of a constructed facility usually has a better credit rating and can secure loans at a lower borrowing rate, but there are some notable exceptions to this rule, particularly for construction projects in developing countries. Under certain circumstances, it is advisable for the owner to advance periodic payments to the contractor in return for some concession in the contract price. This is particularly true for large-scale construction projects with long durations for which financing costs and capital requirements are high. If the owner is willing to advance these amounts to the contractor, the gain in lower financing costs can be shared by both parties through prior agreement.
Unfortunately, the choice of financing during the construction period is often left to the contractor who cannot take advantage of all available options alone. The owner is often shielded from participation through the traditional method of price quotation for construction contracts. This practice merely exacerbates the problem by excluding the owner from participating in decisions which may reduce the cost of the project.
Under conditions of economic uncertainty, a premium to hedge the risk must be added to the estimation of construction cost by both the owner and the contractor. The larger and longer the project is, the greater is the risk. For an unsophisticated owner who tries to avoid all risks and to place the financing burdens of construction on the contractor, the contract prices for construction facilities are likely to be increased to reflect the risk premium charged by the contractors. In dealing with small projects with short durations, this practice may be acceptable particularly when the owner lacks any expertise to evaluate the project financing alternatives or the financial stability to adopt innovative financing schemes. However, for large scale projects of long duration, the owner cannot escape the responsibility of participation if it wants to avoid catastrophes of run-away costs and expensive litigation. The construction of nuclear power plants in the private sector and the construction of transportation facilities in the public sector offer ample examples of such problems. If the responsibilities of risk sharing among various parties in a construction project can be clearly defined in the planning stage, all parties can be benefited to take advantage of cost saving and early use of the constructed facility.
Example 7-13: Effects of payment delays
Table 7-9 shows an example of the effects of payment timing on the general contractor and subcontractors. The total contract price for this project is $5,100,000 with scheduled payments from the owner shown in Column 2. The general contractor's expenses in each period over the lifetime of the project are given in Column 3 while the subcontractor's expenses are shown in Column 4. If the general contractor must pay the subcontractor's expenses as well as its own at the end of each period, the net cash flow of the general contractor is obtained in Column 5, and its cumulative cash flow in Column 6.
TABLE 7-9 An Example of the Effects of Payment Timing
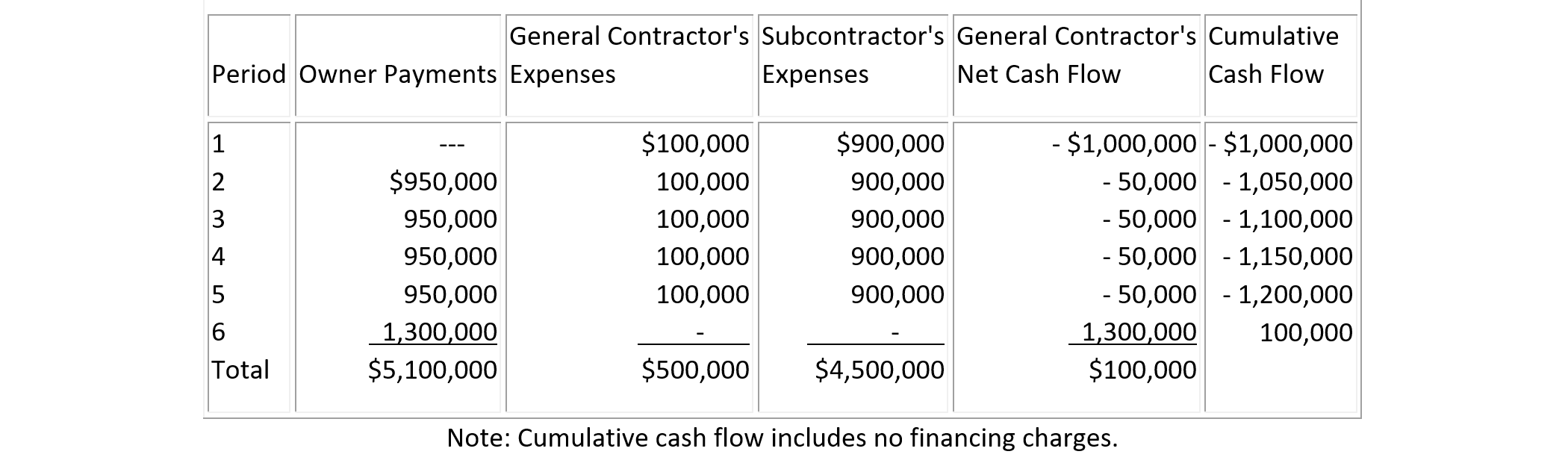
In this example, the owner withholds a five percent retainage on cost as well as a payment of $100,000 until the completion of the project. This $100,000 is equal to the expected gross profit of the contractor without considering financing costs or cash flow discounting. Processing time and contractual agreements with the owner result in a delay of one period in receiving payments. The actual construction expenses from the viewpoint of the general contractor consist of $100,000 in each construction period plus payments due to subcontractors of $900,000 in each period. While the net cash flow without regard to discounting or financing is equal to a $100,000 profit for the general contractor, financial costs are likely to be substantial. With immediate payment to subcontractors, over $1,000,000 must be financed by the contractor throughout the duration of the project. If the general contractor uses borrowing to finance its expenses, a maximum borrowing amount of $1,200,000 in period five is required even without considering intermediate interest charges. Financing this amount is likely to be quite expensive and may easily exceed the expected project profit.
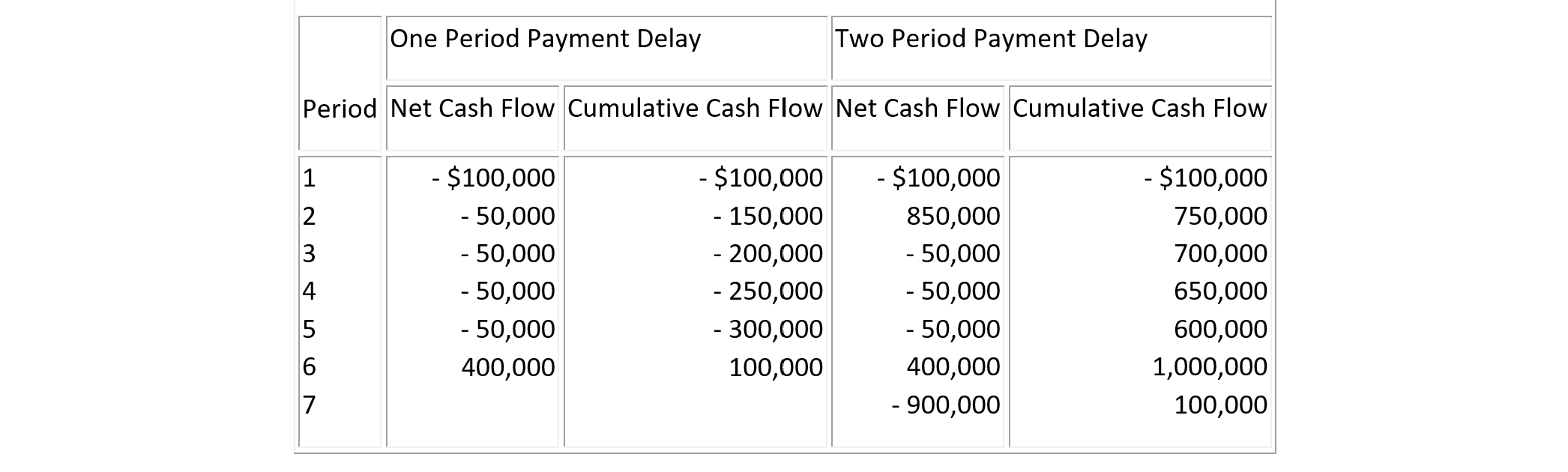
By delaying payments to subcontractors, the general contractor can substantially reduce its financing requirement. For example, Table 7-10 shows the resulting cash flows from delaying payments to subcontractors for one period and for two periods, respectively. With a one period delay, a maximum amount of $300,000 (plus intermediate interest charges) would have to be financed by the general contractor. That is, from the data in Table 7-10, the net cash flow in period 1 is -$100,000, and the net cash flow for each of the periods 2 through 5 is given by:
$950,000 - $100,000 - $900,000 = -$ 50,000
Finally, the net cash flow for period 6 is:
$1,300,000 - $900,000 = $400,000
Thus, the cumulative net cash flow from periods 1 through 5 as shown in Column 2 of Table 7-10 results in maximum shortfall of $300,000 in period 5 in Column 3. For the case of a two-period payment delay to the subcontractors, the general contractor even runs a positive balance during construction as shown in Column 5. The positive balance results from the receipt of owner payments prior to reimbursing the subcontractor's expenses. This positive balance can be placed in an interest-bearing account to earn additional revenues for the general contractor. Needless to say, however, these payment delays mean extra costs and financing problems to the subcontractors. With a two-period delay in payments from the general contractor, the subcontractors have an unpaid balance of $1,800,000, which would represent a considerable financial cost.
TABLE 7-10 An Example of the Cash Flow Effects of Delayed Payments
7.9 Construction Financing for Contractors
For a general contractor or subcontractor, the cash flow profile of expenses and incomes for a construction project typically follows the work in progress for which the contractor will be paid periodically. The markup by the contractor above the estimated expenses is included in the total contract price and the terms of most contracts generally call for monthly reimbursements of work completed less retainage. At time period 0, which denotes the beginning of the construction contract, a considerable sum may have been spent in preparation. The contractor's expenses which occur more or less continuously for the project duration are depicted by a piecewise continuous curve while the receipts (such as progress payments from the owner) are represented by a step function as shown in Fig. 7-1. The owner's payments for the work completed are assumed to lag one period behind expenses except that a withholding proportion or remainder is paid at the end of construction. This method of analysis is applicable to realistic situations where a time period is represented by one month and the number of time periods is extended to cover delayed receipts as a result of retainage.
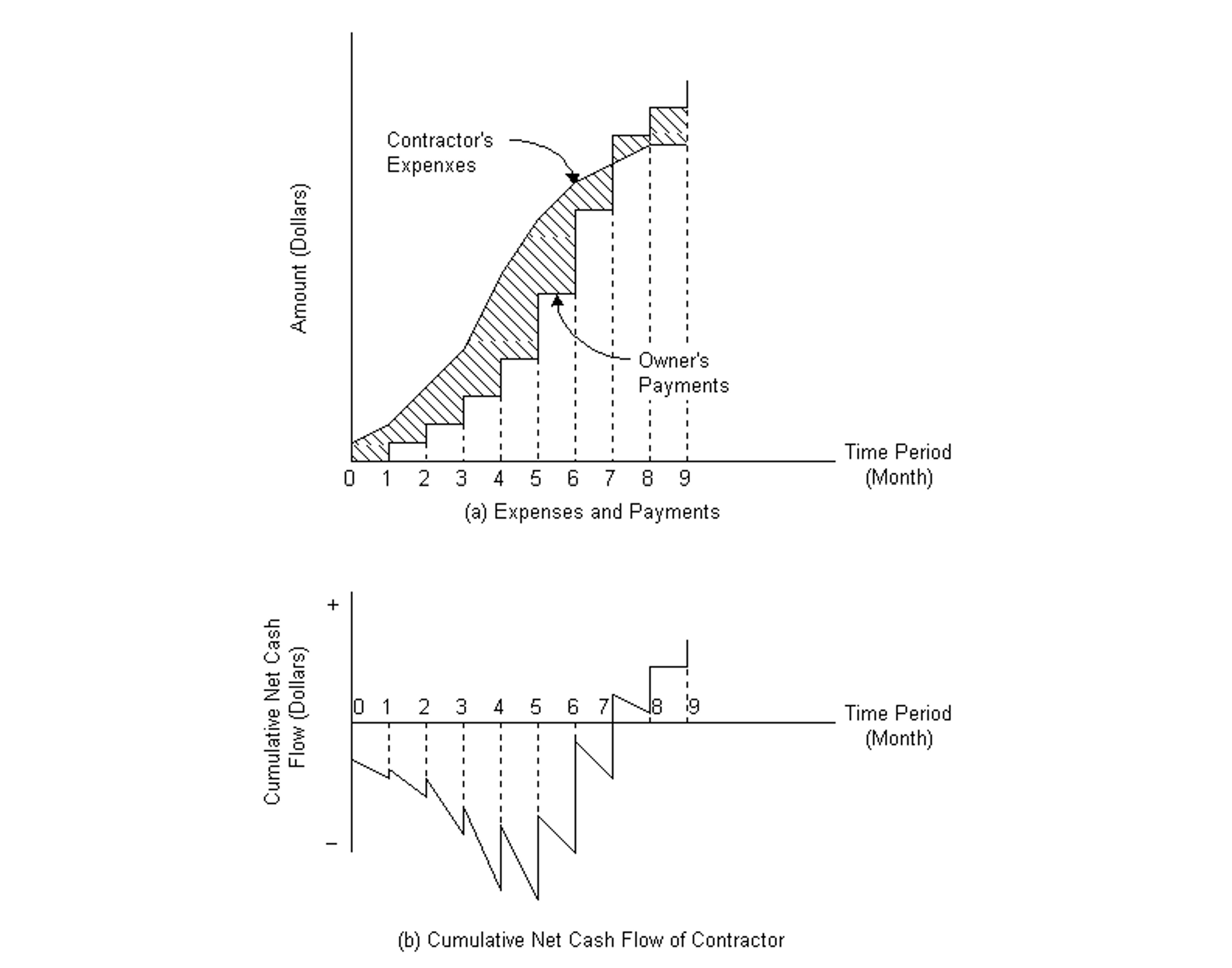
Figure 7-1 Contractor's Expenses and Owner's Payments
While the cash flow profiles of expenses and receipts are expected to vary for different projects, the characteristics of the curves depicted in Fig. 7-1 are sufficiently general for most cases. Let Et represent the contractor's expenses in period t, and Pt represent owner's payments in period t, for t=0,1,2,...,n for n=5 in this case. The net operating cash flow at the end of period t for t >= 0 is given by:

where At is positive for a surplus and negative for a shortfall.
The cumulative operating cash flow at the end of period t just before receiving payment Pt (for t >= 1) is:

where Nt-1 is the cumulative net cash flows from period 0 to period (t-1). Furthermore, the cumulative net operating cash flow after receiving payment Pt at the end of period t (for t >= 1) is:
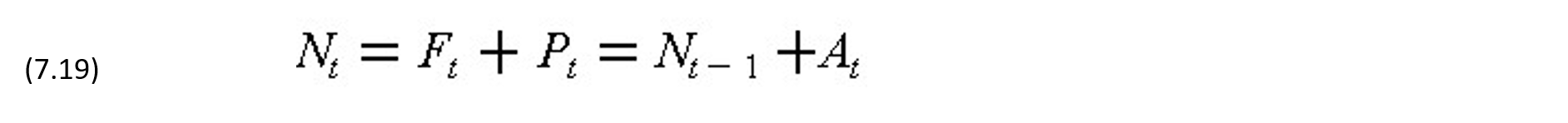
The gross operating profit G for a n-period project is defined as net operating cash flow at t=n and is given by:
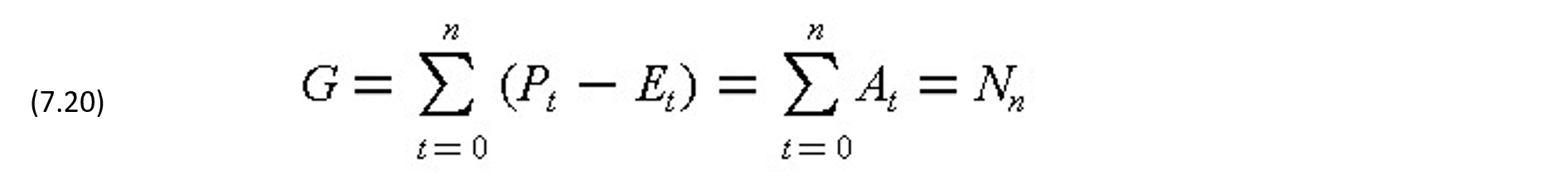
The use of Nn as a measure of the gross operating profit has the disadvantage that it is not adjusted for the time value of money.
Since the net cash flow At (for t=0,1,...,n) for a construction project represents the amount of cash required or accrued after the owner's payment is plowed back to the project at the end of period t, the internal rate of return (IRR) of this cash flow is often cited in the traditional literature in construction as a profit measure. To compute IRR, let the net present value (NPV) of At discounted at a discount rate i per period be zero, i.e.,
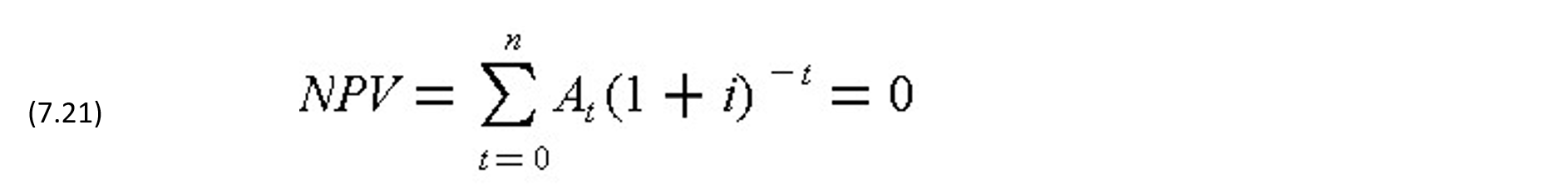
The resulting i (if it is unique) from the solution of Eq. (7.21) is the IRR of the net cash flow At. Aside from the complications that may be involved in the solution of Eq. (7.21), the resulting i = IRR has a meaning to the contractor only if the firm finances the entire project from its own equity. This is seldom if ever the case since most construction firms are highly leveraged, i.e. they have relatively small equity in fixed assets such as construction equipment, and depend almost entirely on borrowing in financing individual construction projects. The use of the IRR of the net cash flows as a measure of profit for the contractor is thus misleading. It does not represent even the IRR of the bank when the contractor finances the project through overdraft since the gross operating profit would not be given to the bank.
Since overdraft is the most common form of financing for small or medium size projects, we shall consider the financing costs and effects on profit of - the use of overdrafts. Let Ft be the cumulative cash flow before the owner's payment in period t including interest and Nt be the cumulative net cash flow in period t including interest. At t = 0 when there is no accrued interest, F0 = F0 and N0 = N0. For t >= in period t can be obtained by considering the contractor's expenses Et to be dispersed uniformly during the period.
The inclusion of interest on contractor's expenses Et during period t (for G 1) is based on the rationale that the S-shaped curve depicting the contractor's expenses in Figure 7-1 is fairly typical of actual situations, where the owner's payments are typically made at the end of well defined periods. Hence, interest on expenses during period t is approximated by one half of the amount as if the expenses were paid at the beginning of the period. In fact, Et is the accumulation of all expenses in period t and is treated - as an expense at the end of the period. Thus, the interest per period It (for t >= 1) is the combination of interest charge for Nt-1 in period t and that for one half of Et in the same period t. If Nt is negative and i is the borrowing rate for the shortfall,

If Nt is positive and h is the investment rate for the surplus,

Hence, if the cumulative net cash flow Nt is negative, the interest on the overdraft for each period t is paid by the contractor at the end of each period. If Nt is positive, a surplus is indicated and the subsequent interest would be paid to the contractor. Most often, Nt is negative during the early time periods of a project and becomes positive in the later periods when the contractor has received payments exceeding expenses.
Including the interest accrued in period t, the cumulative cash flow at the end of period t just before receiving payment Pt (for t >= 1) is:
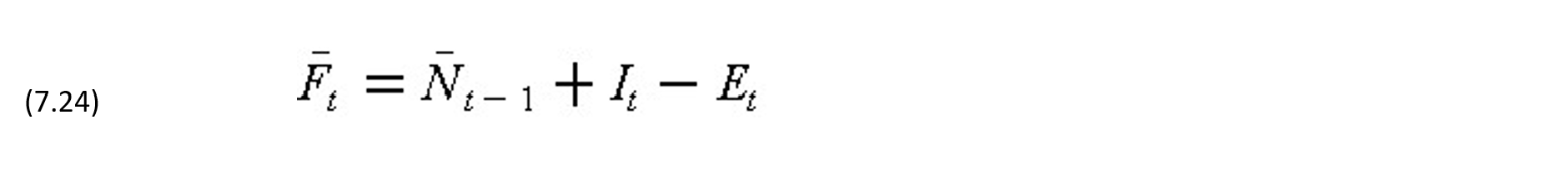
Furthermore, the cumulative net cash flow after receiving payment Pt at the end of period t (for t >= 1) is:
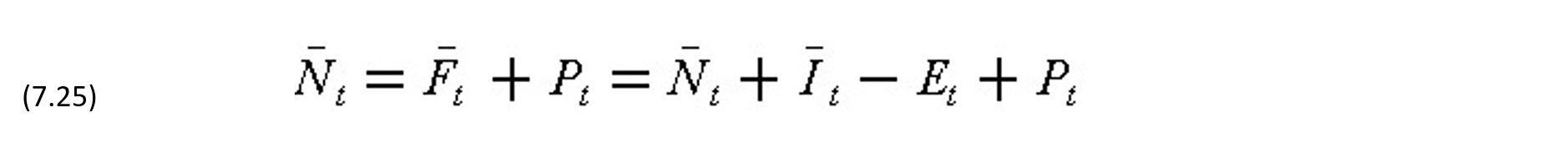
The gross operating profit G at the end of a n-period project including interest charges is:

where Nn is the cumulative net cash flow for t = n.
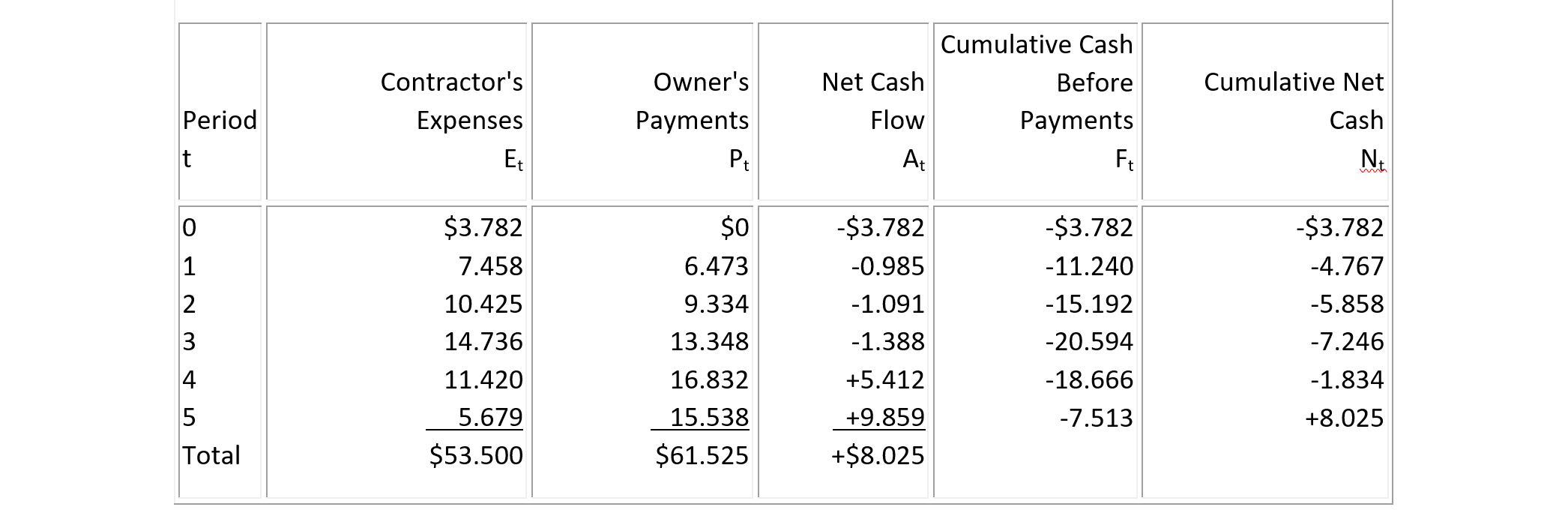
Example 7-14: Contractor's gross profit from a project
The contractor's expenses and owner's payments for a multi-year construction project are given in Columns 2 and 3, respectively, of Table 7-11. Each time period is represented by one year, and the annual interest rate i is for borrowing 11%. The computation has been carried out in Table 7-11, and the contractor's gross profit G is found to be N5 = $8.025 million in the last column of the table.
TABLE 7-11 Example of Contractor's Expenses and Owner's Payments ($ Million)
Example 7-15: Effects of Construction Financing
The computation of the cumulative cash flows including interest charges at i = 11% for Example 7-14 is shown in Table 7-12 with gross profit G = N5 = $1.384 million. The results of computation are also shown in Figure 7-2.
TABLE 7-12 Example Cumulative Cash Flows Including Interests for a Contractor ($ Million)
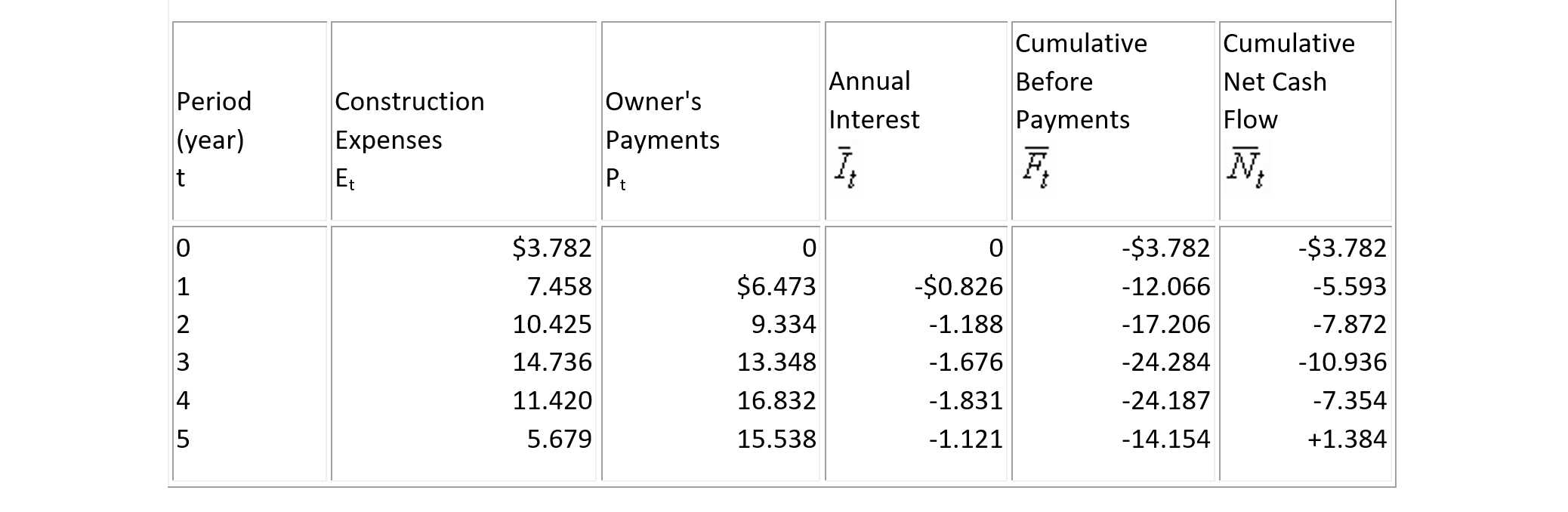
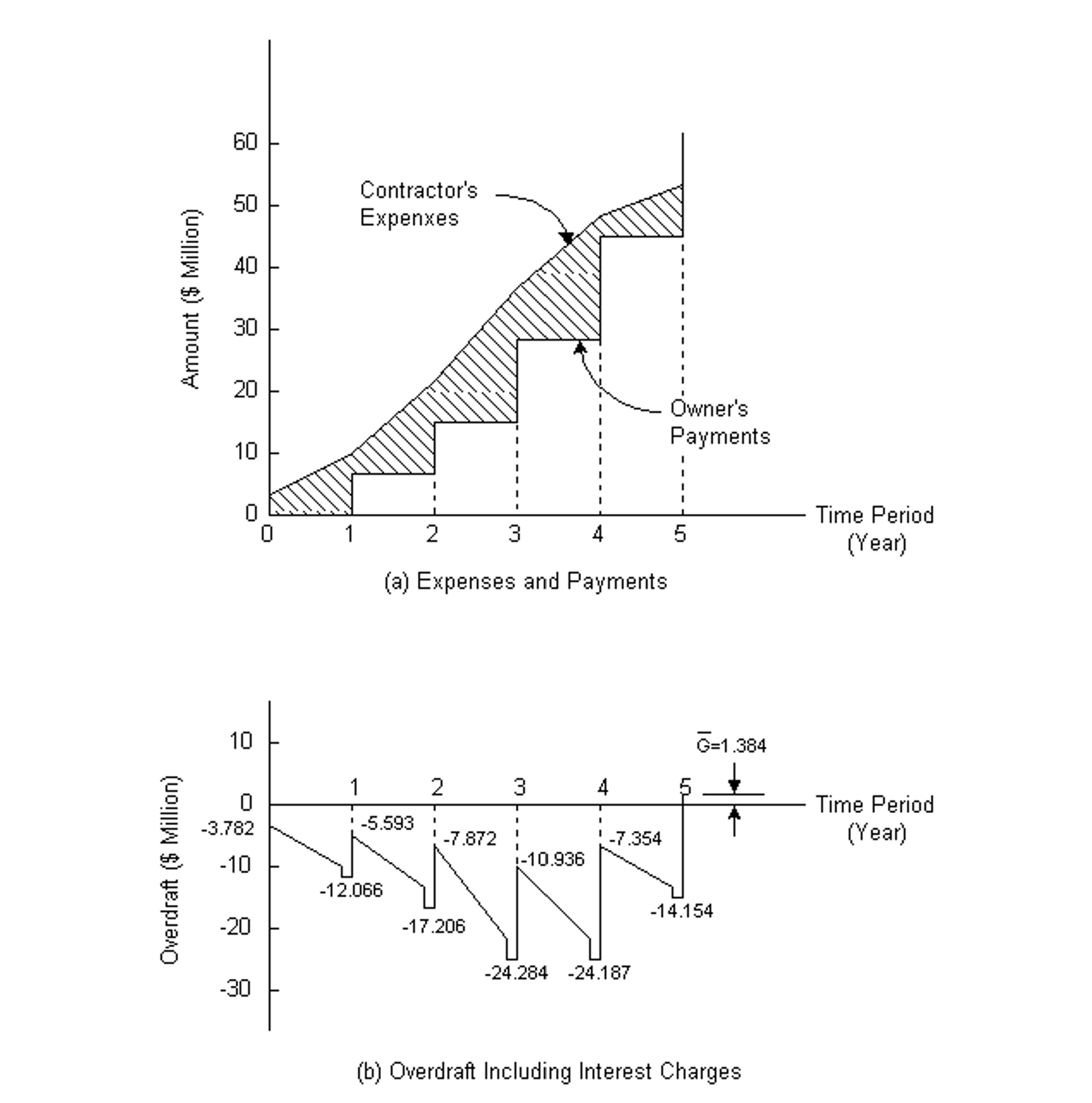
Figure 7-2 Effects of Overdraft Financing
7.10 Effects of Other Factors on a Contractor's Profits
In times of economic uncertainty, the fluctuations in inflation rates and market interest rates affect profits significantly. The total contract price is usually a composite of expenses and payments in then-current dollars at different payment periods. In this case, estimated expenses are also expressed in then-current dollars.
During periods of high inflation, the contractor's profits are particularly vulnerable to delays caused by uncontrollable events for which the owner will not be responsible. Hence, the owner's payments will not be changed while the contractor's expenses will increase with inflation.
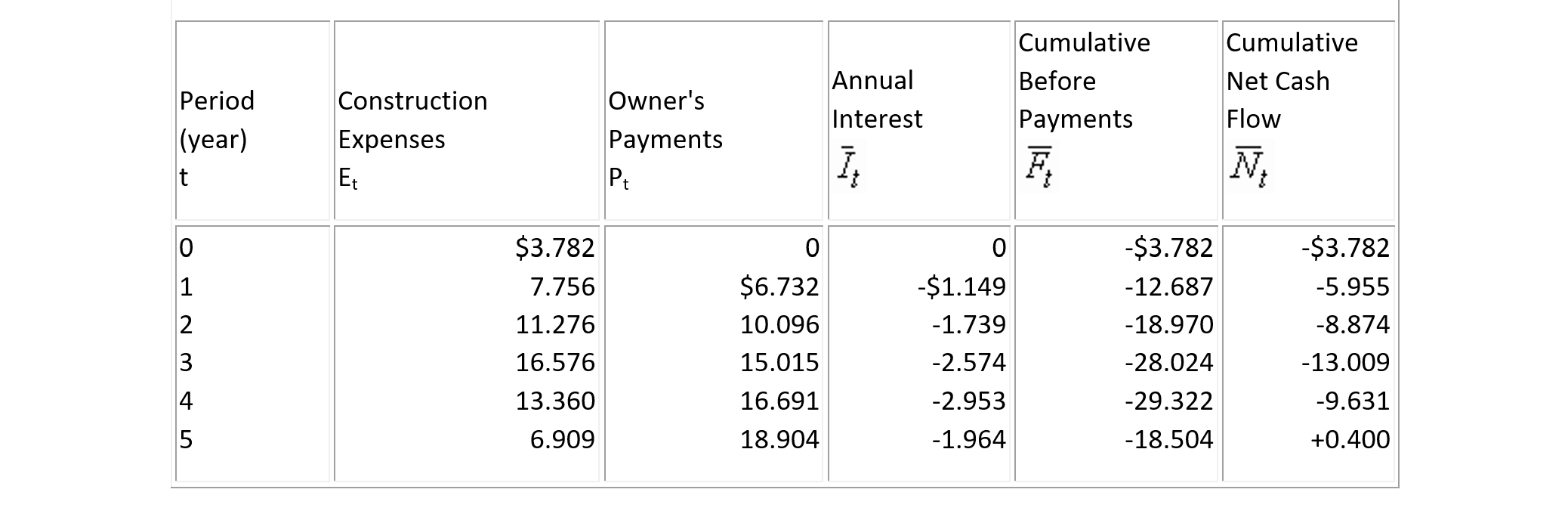
Example 7-16: Effects of Inflation
Suppose that both expenses and receipts for the construction project in the Example 7-14 are now expressed in then-current dollars (with annual inflation rate of 4%) in Table 7-13. The market interest rate reflecting this inflation is now 15%. In considering these expenses and receipts in then-current dollars and using an interest rate of 15% including inflation, we can recompute the cumulative net cash flow (with interest). Thus, the gross profit less financing costs becomes G = N5 = $0.4 million. There will be a loss rather than a profit after deducting financing costs and adjusting for the effects of inflation with this project.
TABLE 7-13 Example of Overdraft Financing Based on Inflated Dollars ($ Million)
Example 7-17: Effects of Work Stoppage at Periods of Inflation
Suppose further that besides the inflation rate of 4%, the project in Example 7-16 is suspended at the end of year 2 due to a labor strike and resumed after one year. Also, assume that while the contractor will incur higher interest expenses due to the work stoppage, the owner will not increase the payments to the contractor. The cumulative net cash flows for the cases of operation and financing expenses are recomputed and tabulated in Table 7-14. The construction expenses and receipts in then-current dollars resulting from the work stopping and the corresponding net cash flow of the project including financing (with annual interest accumulated in the overdraft to the end of the project) is shown in Fig. 7-3. It is noteworthy that, with or without the work stoppage, the gross operating profit declines in value at the end of the project as a result of inflation, but with the work stoppage it has eroded - further to a loss of $3.524 million as indicated by N6 = -3.524 in Table 7-14.
TABLE 7-14 Example of the Effects of Work Stoppage and Inflation on a Contractor ($ Million)
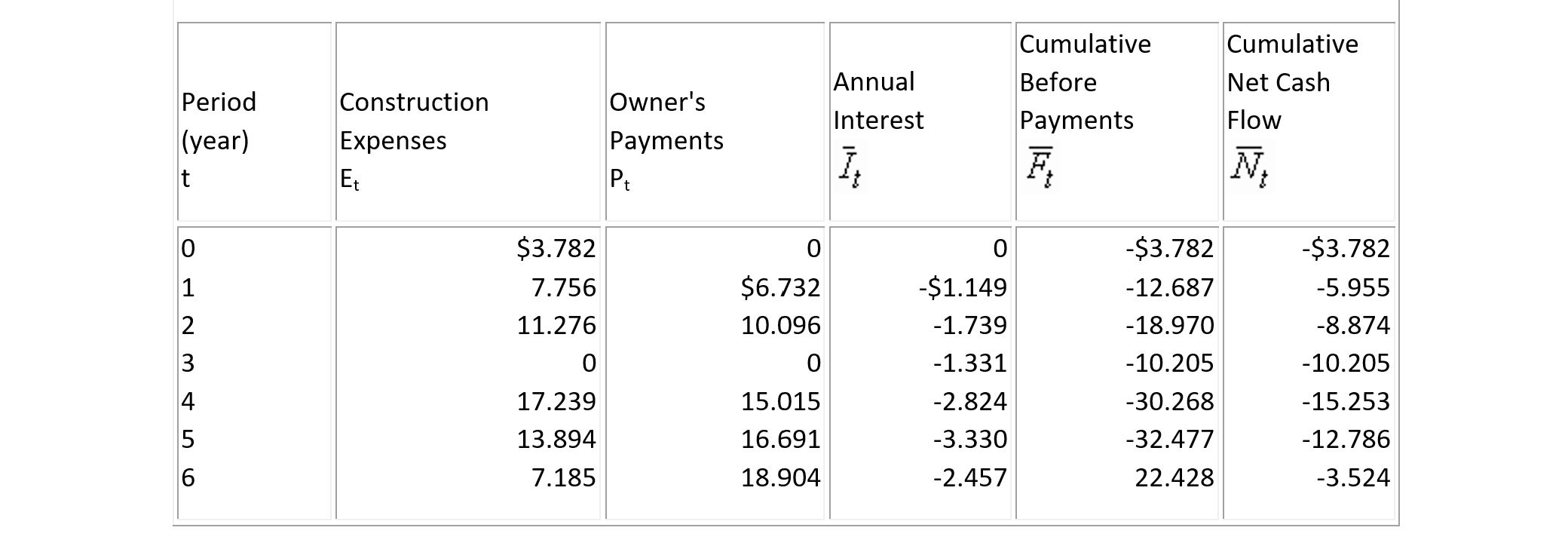
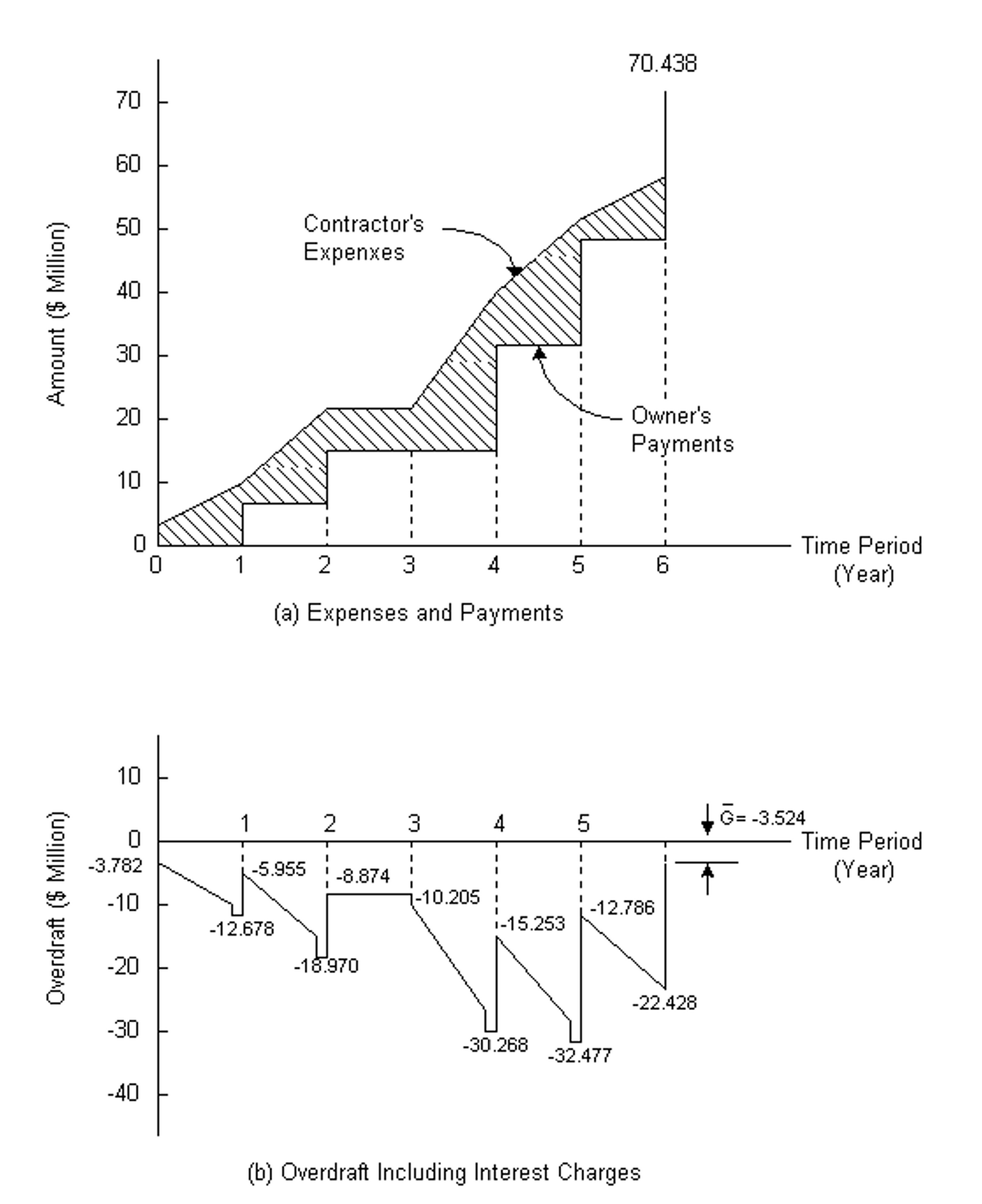
Figure 7-3 Effects of Inflation and Work Stoppage
Example 7-18: Exchange Rate Fluctuation.
Contracting firms engaged in international practice also face financial issues associated with exchange rate fluctuations. Firms are typically paid in local currencies, and the local currency may lose value relative to the contractor's home currency. Moreover, a construction contractor may have to purchase component parts in the home currency. Various strategies can be used to reduce this exchange rate risk, including:
-
- Pooling expenses and incomes from multiple projects to reduce the amount of currency exchanged.
- Purchasing futures contracts to exchange currency at a future date at a guaranteed rate. If the exchange rate does not change or changes in a favorable direction, the contractor may decide not to exercise or use the futures contract.
- Borrowing funds in local currencies and immediately exchanging the expected profit, with the borrowing paid by eventual payments from the owner.
7.11 References
- Au, T., and C. Hendrickson, "Profit Measures for Construction Projects," ASCE Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, Vol. 112, No. CO-2, 1986, pp. 273-286.
- Brealey, R. and S. Myers, Principles of Corporate Finance, McGraw-Hill, Sixth Edition, 2002.
- Collier, C.A. and D.A. Halperin, Construction Funding: Where the Money Comes From, Second Edition, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1984.
- Dipasquale, D. and C. Hendrickson, "Options for Financing a Regional Transit Authority," Transportation Research Record, No. 858, 1982, pp. 29-35.
- Kapila, Prashant and Chris Hendrickson, "Exchange Rate Risk Management in International Construction Ventures," ASCE J. of Construction Eng. and Mgmt, 17(4), October 2001.
- Goss, C.A., "Financing: The Contractor's Perspective," Construction Contracting, Vol. 62, No. 10, pp. 15-17, 1980.
7.12 Problems
(1) Compute the effective annual interest rate with a nominal annual rate of 12% and compounding periods of:
- monthly,
- quarterly, and
- semi-annually (i.e. twice a year).
(2) A corporation is contemplating investment in a facility with the following before-tax operating cash flow (in thousands of constant dollars) at year ends:
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Cash Flow | -$500 | $110 | $112 | $114 | $116 | $118 | $120 | $122 |
The MARR of the corporation before tax is 10%. The corporation will finance the facility by using $200,000 from retained earning and by borrowing the remaining amount through one of the following two plans:
- A seven year coupon bond with 5% issuance cost and 12% interest rate payable annually.
- Overdraft from a bank at 13% interest
Which financing plan is preferable?
(3) Suppose that an overseas constructor proposed to build the facility in Problem P7-2 at a cost of $550,000 (rather than $500,000), but would also arrange financing with a 5% issuing charge and uniform payments over a seven year period. This financing is available from an export bank with a special interest rate of 9%. Is this offer attractive?
(4) The original financing arrangement to obtain a $550,000 loan for a seven year project with 5% issuing charge is to repay both the loan and issue charge through uniform annual payments with a 9% annual interest rate over the seven year period. If this arrangement is to be refinanced after 2 years by coupon bonds which pays 8% nominal annual interest (4% per 6-month period) for the remaining 5 years at the end of which the principal will be due. Assuming an origination fee of 2%, determine the total amount of coupon bonds necessary for refinancing, and the interest payment per period.
(5) A public agency is contemplating construction of a facility with the following operating cash flow (in thousands of constant dollars) at year ends.
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Cash Flow | -$400 | -$200 | $280 | $300 | $320 | $340 |
The MARR of the agency is 10% including inflation. If the agency can financing this facility in one of the following two ways, which financing scheme is preferable?
- Overdraft financing at an interest rate of 12% per annum.
- Five year coupon bonds (so that all principal is repaid at the end of year 5) in the amount of $672,000 including an issuing cost of 5% and at a 10% interest rate.
(6) Suppose that the coupon bonds in Problem 5 are to be refinanced after two years by a uniform payment mortgage for the remaining three years, for an issuing cost of $10,000 in then-current dollars. If the mortgage is repaid with uniform monthly payments for 36 months and the monthly interest rate is 1%, determine the amount of monthly payment.
(7) Suppose the investment in a facility by a public agency results in a net operating cash flow at year ends (in thousands of dollars) as follows:
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Cash Flow | -$850 | -$250 | $250 | $250 | $450 | $450 | $450 |
The agency has a MARR of 9% and is not subject to tax. If the project can be financed in one of the two following ways, which financing scheme is preferable?
- Six-year uniform payment bonds at 11% interest rate for a total amount of borrowing of $875,000 which includes $25,000 of issuing cost.
- Five-year coupon bonds at 10% interest rate for a total amount of borrowing of $900,000 which includes $50,000 of issuing cost.
(8) Suppose that the five year coupon bond in Problem 7 is to be refinanced, after the payment of interest at the end of year 3, by a uniform mortgage which requires an issuance cost of 2%. If the annual interest rate is 9%, what is the uniform annual payment on the mortgage for another 5 years.
(9) A corporation plans to invest in a small project which costs a one-time expenditure of $700,000 and offers an annual return of $250,000 each in the next four years. It intends to finance this project by issuing a five year promissory note which requires an origination fee of $10,000. Interest payments are made annually at 9% with the repayment of the principal at the end of five years. If the before tax MARR of the Corporation is 11%, find the adjusted net present value of the investment in conjunction with the proposed financing.
(10) A local transportation agency is receiving a construction grant in annual installments from the federal and state governments for a construction project. However, it must make payments to the contractor periodically for construction expenditures. Suppose that all receipts and expenditures (in million dollars) are made at year ends as shown below. Determine the overdraft at the end of year 5 if the project is financed with an overdraft at an annual interest rate of 10%.
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Receipts Expenditures |
0 $1.250 |
$4.764 $6.821 |
$7.456 9.362 |
$8.287 7.744 |
$6.525 4.323 |
$2.468 0 |
(11) The operating cash flows of contractor's expenses and the owner's payments for a construction project as stipulated in the contract agreement are shown in Table 7-15. The contractor has established a line of credit from the bank at a monthly interest rate of 1.5%, and the contractor is allowed to borrow the shortfall between expense and receipt at the end of each month but must deposit any excess of net operating cash flow to reduce the loan amount. Assuming that there is no inflation, determine the cumulative net cash flow including interest due to overdrafting. Also find the contractor's gross profit.
Table 7-15
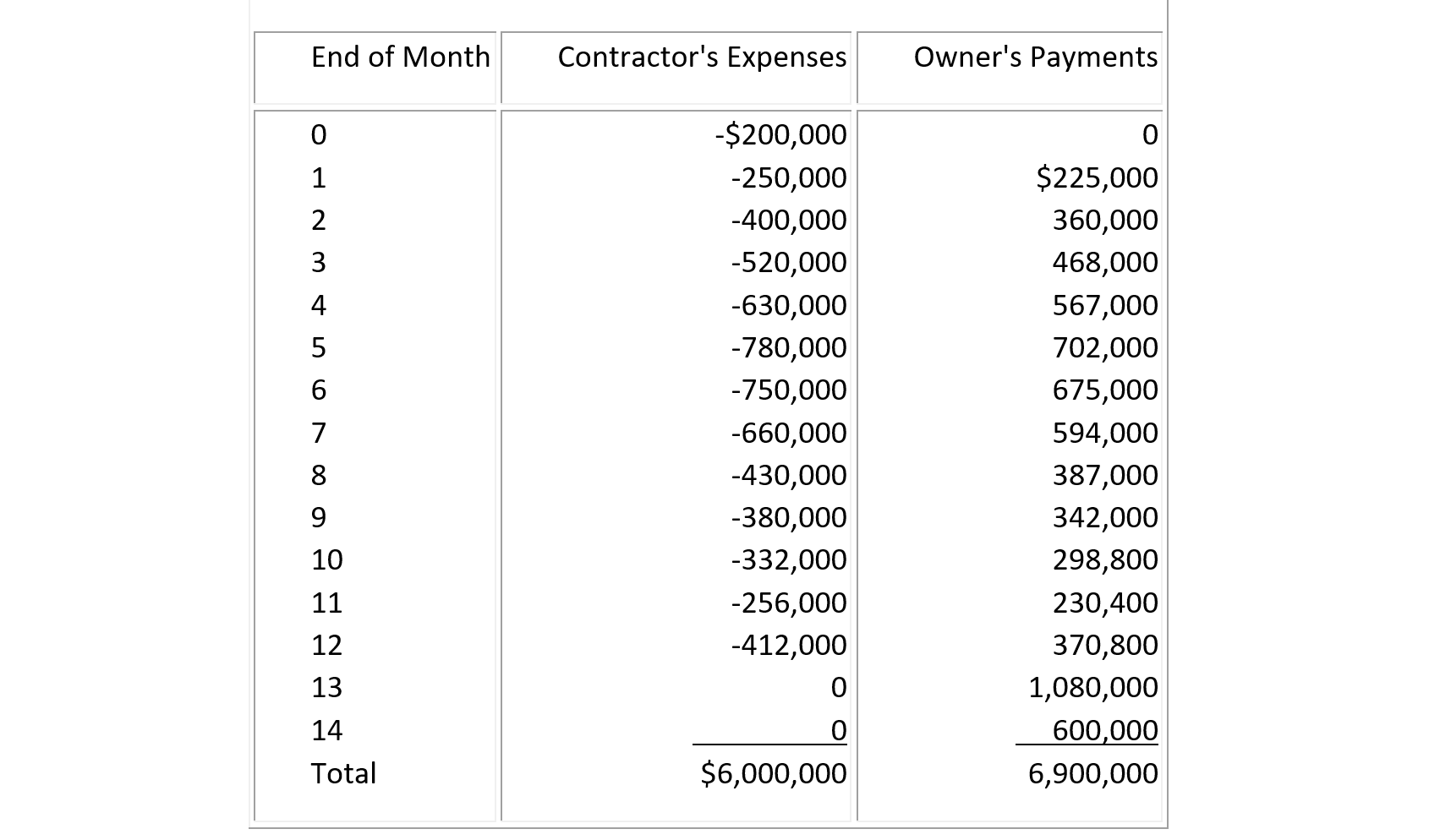
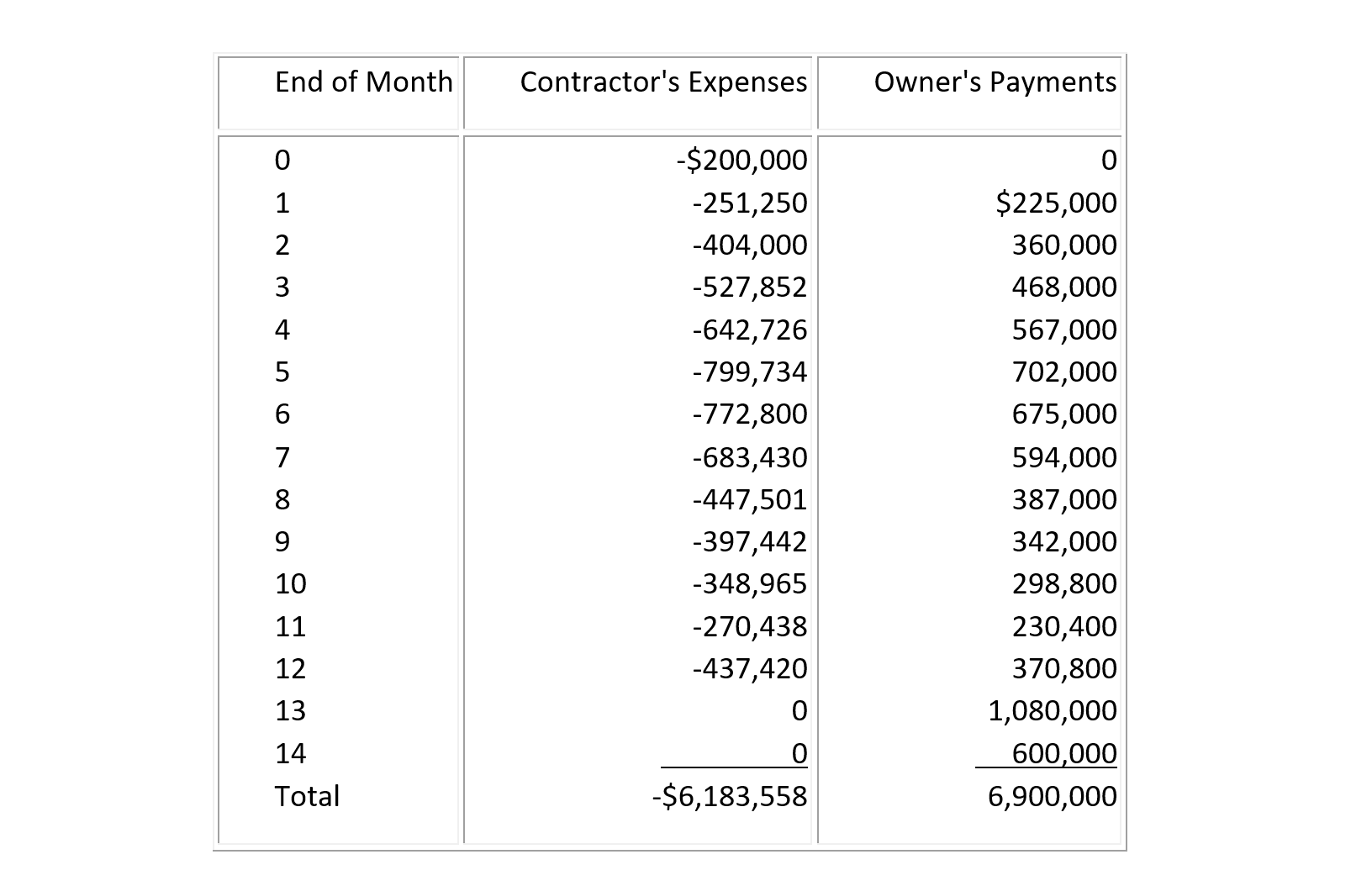
(11) Suppose that both contractor's expenses and owner's receipts for a construction project are expressed in then-current inflated dollars in Table 7-16. Suppose also that the monthly interest rate required by the bank is 1.5%. Suppose that the work is stopped for two months at the end of month 5 due to labor strike while the monthly inflation rate is 0.5%. Under the terms of the contract between the owner and the contractor, suppose that the owner's payments will be delayed but not adjusted for inflation. Find the cumulative net cash flow with interest due to overdrafting.
Table 7-16
(12) The contractor's construction expenses and the owner's payments for a construction project in then-current dollars as stipulated in the contract agreement are shown in Table 7-17. The contractor has established a line of credit from the bank at a monthly interest rate of 2% (based on then-current dollars), and the contractor is allowed to borrow the shortfalls between expense and receipt at the end of each month but must deposit any excess of net operating cash flow to reduce the loan amount. Determine the cumulative net cash flow including interest due to overdrafting. Also, find the contractor's gross profit.
Table 7-17
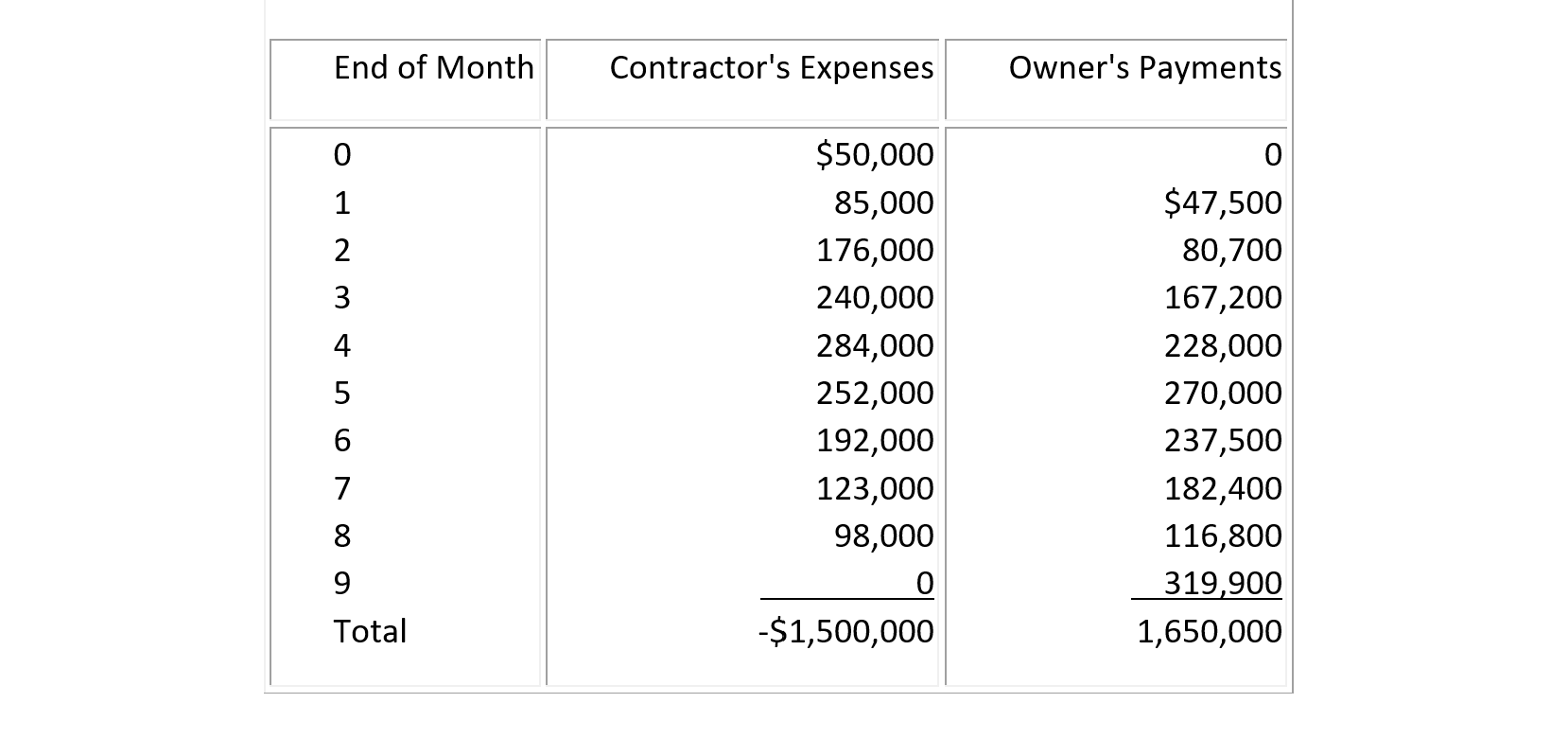
(13) Suppose that both the contractor's expenses and owner's payments for a construction project are expressed in then-current dollars in Table 7-17 (Problem 13). The monthly interest rate required by the bank is 2.5% based on then-current dollars. Suppose that the work is stopped for three months at the end of month 4 due to a labor strike while the monthly inflation rate is 0.5%. The owner's payments will be delayed but not adjusted for inflation. Find the cumulative net cash flow expressed in then-current dollars, with interest compounded and accumulated to the end of the project.
7.13 Footnotes
- This table is adapted from A.J. Henkel, "The Mechanics of a Revenue Bond Financing: An Overview," Infrastructure Financing, Kidder, Peabody & Co., New York, 1984. (Back)
- The calculations for this bond issue are adapted from a hypothetical example in F. H. Fuller, "Analyzing Cash Flows for Revenue Bond Financing," Infrastructure Financing, Kidder, Peabody & Co., Inc., New York, 1984, pp. 37-47. (Back)
- Maevis, Alfred C.,"Construction Cost Control by the Owner," ASCE Journal of the Construction Division, Vol. 106, No. 4, December, 1980, pg. 444. (Back)

