Hugh’s Health: Hypertension
Hugh was diagnosed with hypertension in 1990.
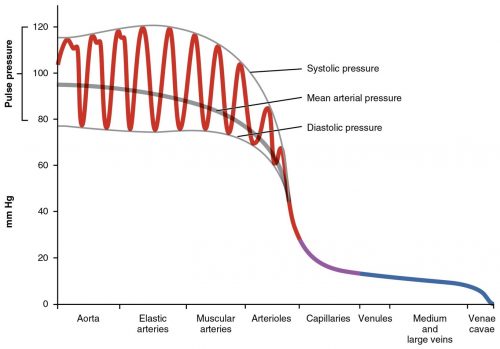
Components of Arterial Blood Pressure
The systolic pressure is the higher value and reflects the arterial pressure resulting from the ejection of blood during ventricular contraction, or systole.
The diastolic pressure is the lower value and represents the arterial pressure of blood during ventricular relaxation, or diastole.
Hypertension Medications
| Systolic | Diastolic | |
| Normal | 90 – 129 | 60 – 79 |
| Stage 1 | 130 – 139 | 80 – 89 |
| Stage 2 | 140 – 179 | 90 – 109 |
| Critical | Over 180 | Over 110 |
- Diuretics: get rid of excess sodium and water, often used with additional prescription therapies
- Thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, combination diuretics
- Beta-blockers: reduce heart rate, workload, and output
- ACE inhibitors: help to produce less angiotensin, blood vessels relax and open up
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers: block the receptors so angiotensin fails to constrict blood vessels
- Calcium channel blockers: prevents calcium from entering the smooth muscle cells of the heart & arteries and open up narrowed blood vessels
- Alpha blockers: reduce artery resistance, relaxing the muscle tone of the vascular wall
- Alpha-2 receptor agonists: decreasing the activity of the sympathetic portion of the involuntary NS
- Combined alpha and beta-blockers: used IV for hypertensive crisis
- Central agonists: decrease blood vessels’ ability to tense up or contract (different nerve pathway than α & β-blockers)
- Peripheral adrenergic inhibitors: blocks neurotransmitters in the brain for smooth muscle contraction
- Vasodilators: muscle in the blood vessel walls to relax → vessel dilation
Hugh’s Blood Pressure Medications
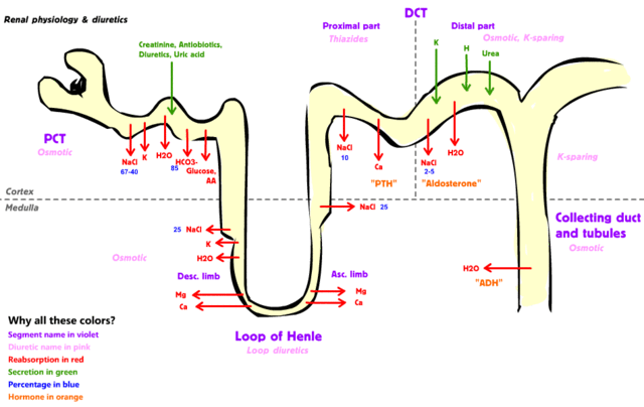
Furosemide (Lasix)-loop diuretic
- Inhibits the NKCC2 cotransporter.
- Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium.
- The interstitium will lose its tonicity.
- Affecting how much water is reabsorbed by the Loop of Henle and collecting ducts.
- More water leaves via the filtrate rather than go back into the blood.
Ramipril (Altace)-ACE inhibitor
- Reduce the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme.
- ACE is responsible for hormones that help control BP.
- Narrowing effect on blood vessels that ↑BP.
- ACE inhibitors limit this enzyme, making the blood vessels relax and widen.
- Lowering BP and improving blood flow to the heart muscle.
Managing Hypertension
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Decrease the salt in your diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Managing your stress
- Limit alcohol
- Don’t smoke