Part 3 – Absorption Refrigeration Systems
Ammonia Absorption Systems
-
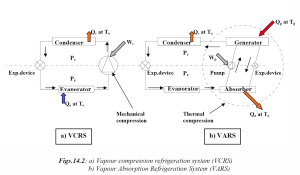
- Condenser and evaporator perform the same functions as they did in the ammonia compression system.
- Compressor is replaced by a generator or re-boiler
- Temperature and pressure of the ammonia is raised while it is absorbed in water.
- An absorber, and a pump for handling the mixture of water and ammonia (known as aqua) are also required.
- Compressor is replaced by a generator or re-boiler
- Condenser and evaporator perform the same functions as they did in the ammonia compression system.
Activity: Absorption Refrigeration Systems
Click through the images to view different diagrams of Absorption Refrigeration Systems.
Parts of an Ammonia Absorption System

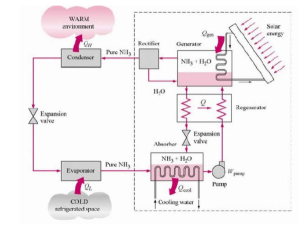
The Analyzer
The Analyzer is a distillation column that is located at the top of the generator.
- Consists of number of plates positioned horizontally.
- When the ammonia refrigerant along with the water vapor particles enters the analyzer, the solution is cooled.
- Water vapor gets condensed into the water particles that drip down into the generator.
- The ammonia refrigerant in the gaseous state continues to rise up and it moves to the rectifier
Rectifier (Reflux Condenser)
Rectifier (Reflux Condenser) is a heat exchanger cooled by the water
- Ammonia vapour from the generator to the rectifier
- Remaining water vapor mixed with the ammonia refrigerant gets condensed along with some particles of ammonia.
- This weak solution of water and ammonia drains down to the analyzer and then to the generator.
Domestic Absorption Refrigerator

Solar Absorption Refrigeration System
Operation of Absorption Systems
Operation of the ammonia absorption system of refrigeration depends upon the affinity of water and ammonia for each other, and fractional distillation. Fractional distillation is the application of heat to a mixture of water and ammonia (aqua ammonia) drives off the ammonia as a gas leaving the water behind. Ammonia evaporates at a much lower temperature than water. Water has the capacity for dissolving from 500 to 1200 times its own volume of ammonia gas. It does depend upon temperature and pressure. Increasing pressure or decreasing temperature increases the quantity of ammonia gas that the water can absorb.
Cycle of Operation
An exchange of heat is made by water circulating through pipes.
-
-
- Raising the temperature of the strong aqua before it enters the generator
- Reducing the temperature of the weak aqua before it enters the weak aqua cooler and passes to the absorber.
-