Part 1 – Compressor Applications
Compressors
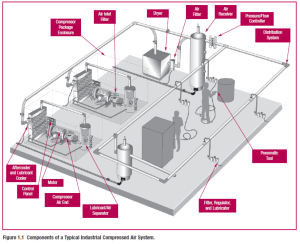
Increase the pressure of a compressible fluid (gas).
Applications:
-
-
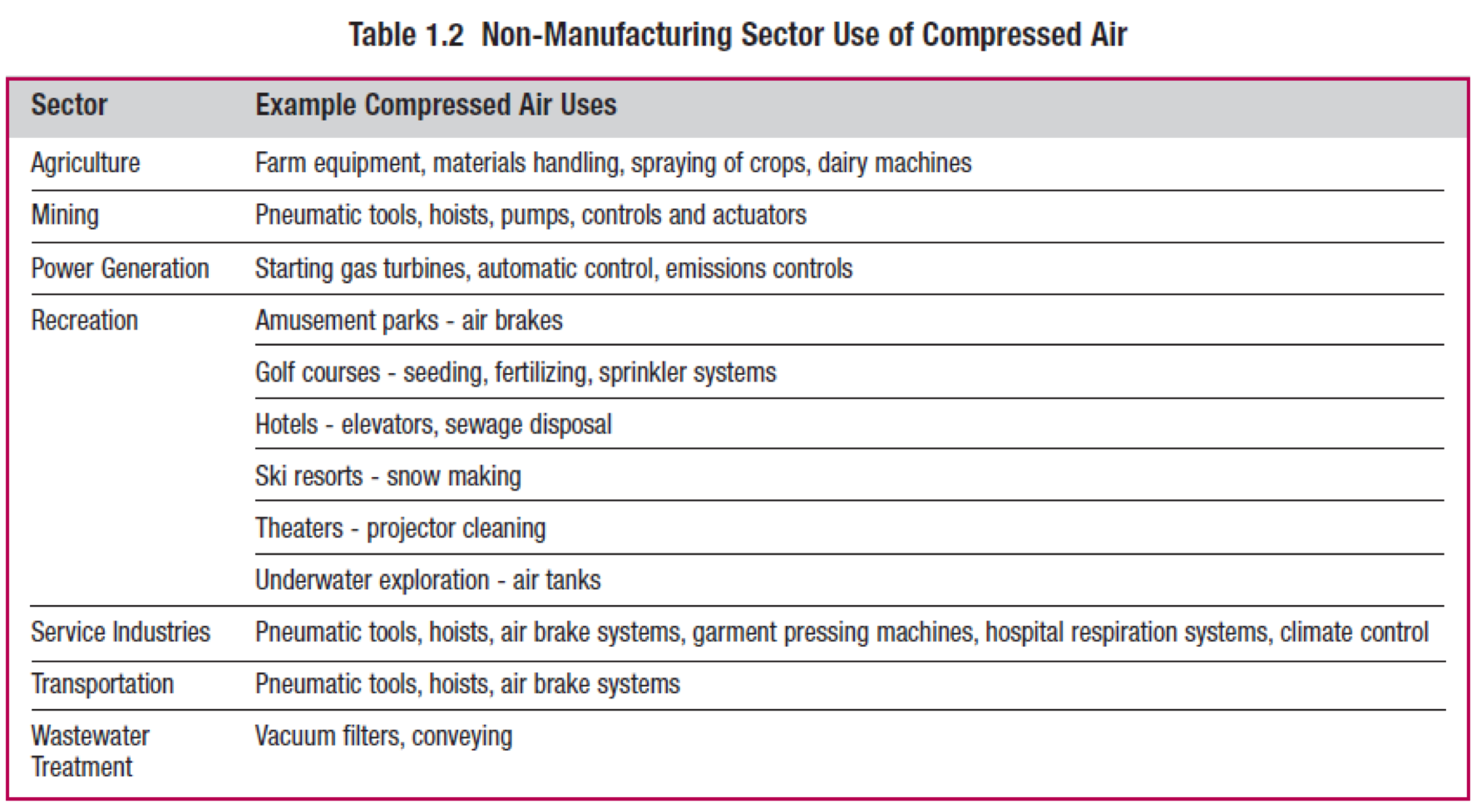
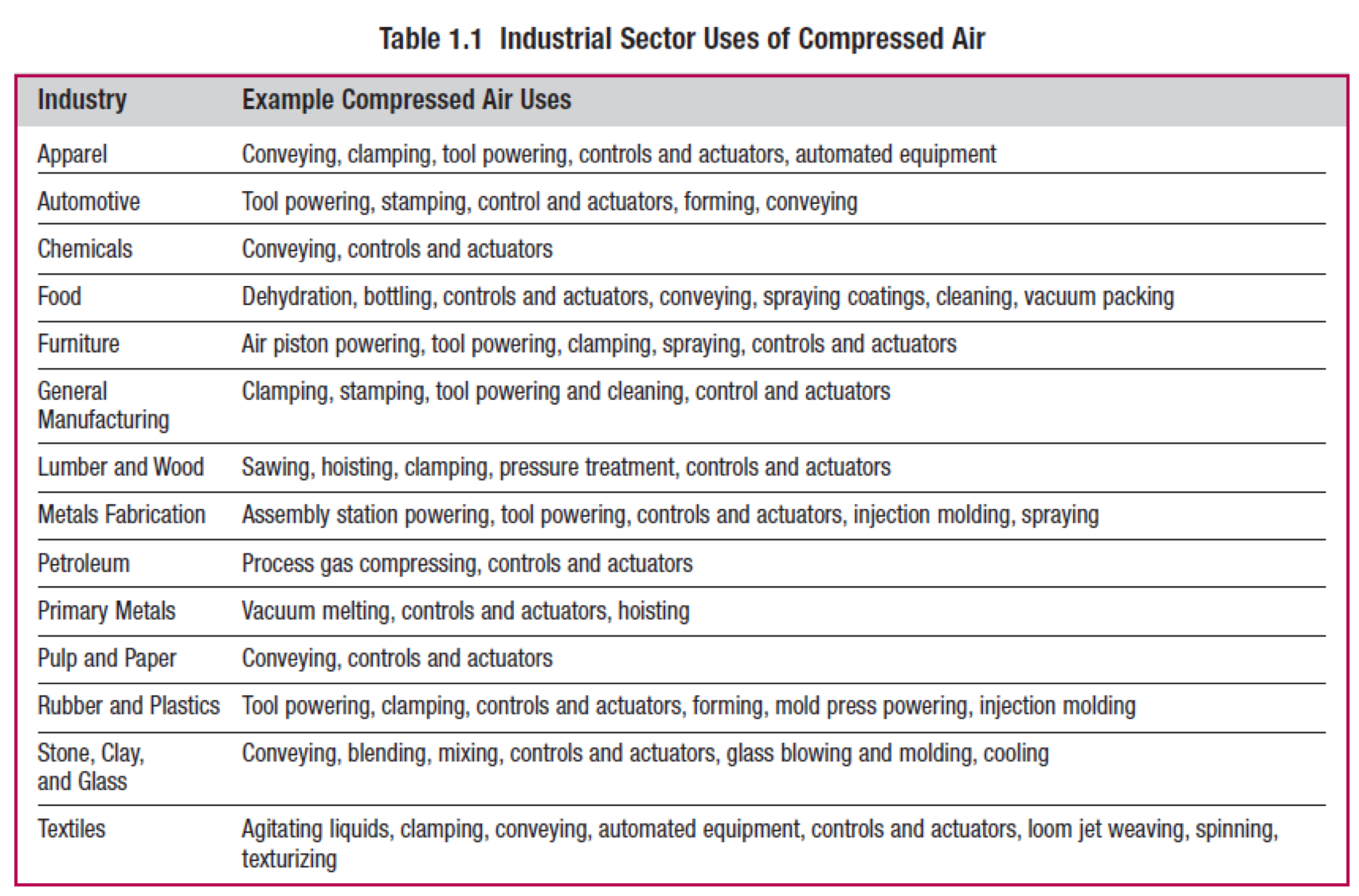
- Compressed air systems to supply compressed air to instruments and for power tools.
- Integral component of air conditioning and refrigeration systems
- Used for engine starters, turbochargers and superchargers.
- Used in medical systems, industrial systems and chemical processes.
-
Air Compression
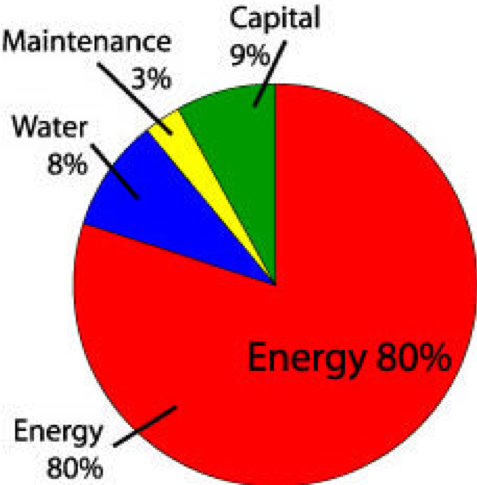
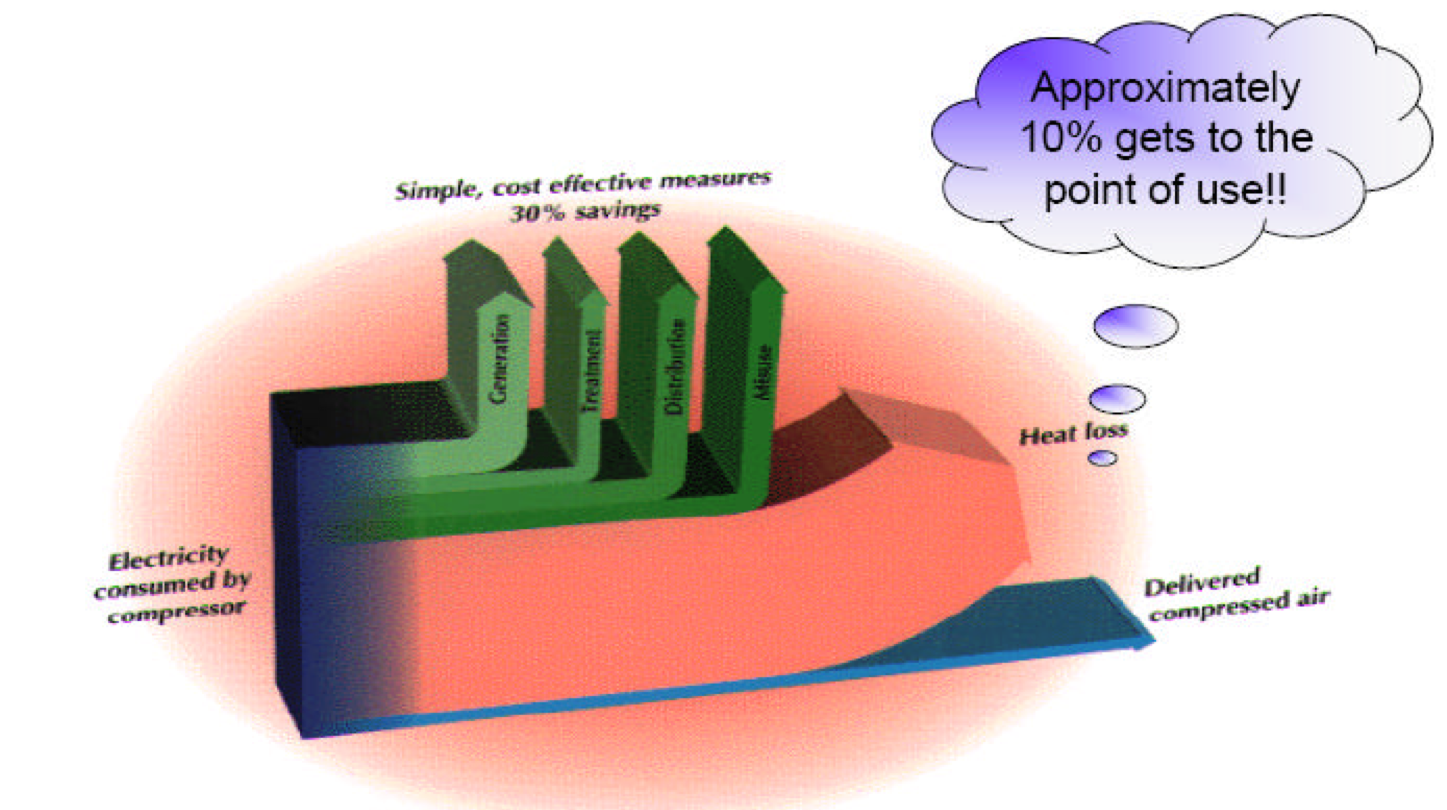
Used widely in industry. Air compression is considered the “fourth utility” at many facilities. Plant air compressor systems vary in size from a small unit of 5 horsepower (hp) to huge systems with more than 50,000 hp. Use more electricity than any other type of equipment and therefore inefficiencies in compressed air systems can be significant. Energy savings from system improvements can range from 20 to 50 percent or more of electricity consumption
High volume applications:
- Construction industry- Uses air compressors to provide power for tools
- Mining- Air for hoists
- Automotive
- Painting
- Food processing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Natural gas transportation- Uses largest compressors
Air Measurement
SCFM – Standard Cubic Feet per Minute
Many definitions of SCFM – one of most common used is with “sea-level” properties:
- 101.3 kPa
- 14.696 psia
- 15oC
- 60 oF
- 0% Relative Humidity (RH).
ACFM – Actual Cubic Feet per Minute
Actual air volume flow is often termed ACFM – Actual Cubic Feet per Minute.
Actual Cubic Feet per Minute – ACFM, depends on the following: pressure, temperature, and humidity of the actual air.
The conversion from SCFM to ACFM can be expressed as:
ACFM = SCFM [Pstd / (Pact – Psat Φ)](Tact / Tstd)
Where:
-
- ACFM = Actual Cubic Feet per Minute
- SCFM = Standard Cubic Feet per Minute
- Pstd = Standard absolute air pressure (psia)
- Pact = Absolute pressure at the actual level (psia)
- Psat = Saturation pressure at the actual temperature (psi)
- Φ = Actual relative humidity
- Tact = Actual ambient air temperature (oR)
Tstd = Standard temperature (oR)
ICFM – Inlet Cubic Feet per Minute
ICFM, is used by compressor vendors to establish conditions in front of additional equipment like inlet filter, blower or booster.
Compressor Drivers
Prime movers can develop the required power at a constant speed provide power at a range of speeds.The drivers energy source may be either electrical or mechanical.
Types of prime movers for compressors:
Gas turbines- Used in axial and centrifugal flow compressors
Steam turbines or water turbines- Used in large compressors
Electric motors- Small motors suitable for domestic electrical supplies use single phase alternating current. Larger motors can only be used where an industrial electrical three phase alternating current supply is available.
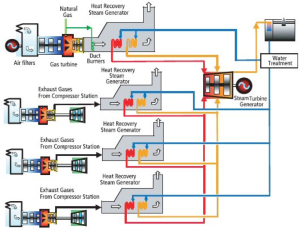
Types of prime movers for compressors- Diesel or natural gas engines are common compressor power sources in the oil and gas industries.
Considerations such as convenience, cost and availability of liquid fuel and natural gas must be considered.
Some common combinations are:
-
- A reciprocating engine driving a reciprocating compressor
- An electric motor driving a reciprocating compressor
- An electric motor driving a screw compressor
- A gas turbine driving a centrifugal compressor
- A steam turbine driving a centrifugal compressor
- An electric motor driving a centrifugal compressor
- A steam turbine driving an axial compressor
Chart: A High-level comparison of Important Compressor Types -Sustainable Energy Development Office, 2022.
| Item | Reciprocating | Rotary Value | Rotary Screw | Centrifugal |
| Efficiency at full load | High | Medium-High | High | High |
| Efficiency at part load | High due to staging | Poor: below 60% of full load | Poor, below 60% of full load | Poor: below 60% of full load |
| Efficiency at no load (power as % of full load) | High (10%-25%) | Medium (30%- 40 %) | High-Poor (25%-60%) | High-Medium (20%-30%) |
| Noise Level | Large | Quiet | Quiet0if enclosed | Quiet |
| Size | Moderate | Compact | Compact | Compact |
| Oil Carry Over | High | Low-Medium | Low | Low |
| Vibration | High | Almost none | Almost none | Almost-none |
| Maintenance | Many wearing-parts | Few Wearing Parts | Very few wearing parts | Sensitive to dust in air |
| Capacity | Low-high | Low-Medium | Low-high | Medium-high |
| Pressure | Medium=very high | Low-Medium | Medium-high | Medium-high |
Gas turbines and Steam turbines are used for the largest power requirements because their power to weight ratio is the highest. Steam turbines are best where steam is readily available. Gas turbines are used where a hydrocarbon fuel is accessible.Electric motors are used for reciprocating engines. They are best for low to medium power requirements.
Electric Motors – Synchronous or induction AC motors are common drivers of compressors and are available in all sizes. Oversized motors may be purchased because the actual load conditions are not fully known or because of anticipated load increases. If the compressor should not be brought up to speed quickly, a variable speed (variable frequency) electric drive may be used. this allows the speed of the motor to be varied.
Steam Turbines– Used to power centrifugal compressors in processing plants that have a steam supply. Variable speed of the turbine is an advantage when running a compressor. The steam turbine and compressor often come as a package with a common lubricating oil system.
Gas Turbines– Option when no electricity or steam is available, such as on gas pipeline compressor stations. More often used to drive centrifugal compressors. May also used to drive axial and large screw compressors.