6.2 The Roles of Mission, Vision, and Values
Learning Objectives
- Define mission and vision.
- Outline how values are important for mission and vision.
Mission, Vision, and Values

Mission and vision both relate to an organization’s purpose and are typically communicated in some written form. Mission and vision are statements from the organization that answer questions about who we are, what we value, and where we’re going. A study by the consulting firm Bain and Company reports that 90% of the 500 firms surveyed issue some form of mission and vision statements (Bart & Baetz, 1998). Moreover, firms with clearly communicated, widely understood, and collectively shared mission and vision have been shown to perform better than those without them, with the caveat that they related to effectiveness only when strategy and goals and objectives were aligned with them as well (Bart, et. al., 2001).
A mission statement communicates the organization’s reason for being, and how it aims to serve its key stakeholders. Customers, employees, and investors are the stakeholders most often emphasized, but other stakeholders like government or communities (i.e., in the form of social or environmental impact) can also be discussed. Mission statements are often longer than vision statements. Sometimes mission statements also include a summation of the firm’s values. Values are the beliefs of an individual or group, and in this case the organization, in which they are emotionally invested.
A vision statement, in contrast, is a future-oriented declaration of the organization’s purpose and aspirations. In many ways, you can say that the mission statement lays out the organization’s ‘purpose for being’, and the vision statement then says, ‘based on that purpose, this is what we want to become’. The strategy should flow directly from the vision, since the strategy is intended to achieve the vision and thus satisfy the organization’s mission. Typically, vision statements are relatively brief.
Any casual tour of business or organization Web sites will expose you to the range of forms that mission and vision statements can take. To reiterate, mission statements are longer than vision statements, often because they convey the organizations core values. Mission statements answer the questions of “Who are we?” and “What does our organization value?” Vision statements typically take the form of relatively brief, future-oriented statements—vision statements answer the question “Where is this organization going?” Increasingly, organizations also add a values statement which either reaffirms or states outright the organization’s values that might not be evident in the mission or vision statements.
Roles Played by Mission and Vision
Mission and vision statements play three critical roles: (1) communicate the purpose of the organization to stakeholders, (2) inform strategy development, and (3) develop the measurable goals and objectives by which to gauge the success of the organization’s strategy. These interdependent, cascading roles, and the relationships among them, are summarized in the figure.
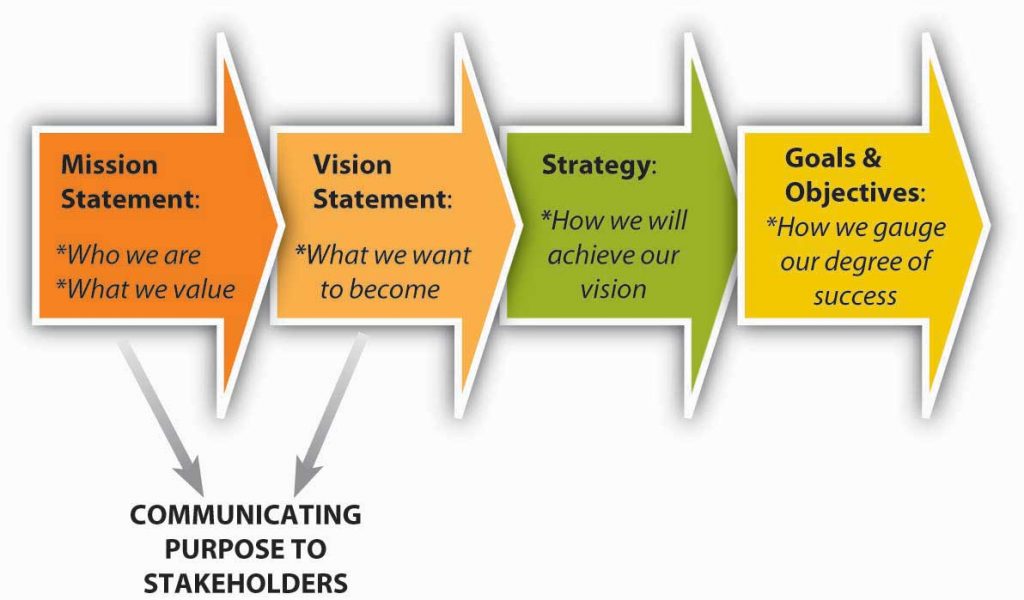
First, mission and vision provide a vehicle for communicating an organization’s purpose and values to all key stakeholders. Stakeholders are those key parties who have some influence over the organization or stake in its future. You will learn more about stakeholders and stakeholder analysis later in this chapter; however, for now, suffice it to say that some key stakeholders are employees, customers, investors, suppliers, and institutions such as governments. Typically, these statements would be widely circulated and discussed often so that their meaning is widely understood, shared, and internalized. The better employees understand an organization’s purpose, through its mission and vision, the better able they will be to understand the strategy and its implementation, and the better decisions they will make.
Second, mission and vision create a target for strategy development. That is, one criterion of a good strategy is how well it helps the firm achieve its mission and vision. To better understand the relationship among mission, vision, and strategy, it is sometimes helpful to visualize them collectively as a funnel. At the broadest part of the funnel, you find the inputs into the mission statement. Toward the narrower part of the funnel, you find the vision statement, which has distilled down the mission in a way that it can guide the development of the strategy. In the narrowest part of the funnel you find the strategy—it is clear and explicit about what the firm will do, and not do, to achieve the vision. Vision statements also provide a bridge between the mission and the strategy. In that sense the best vision statements create a tension and restlessness with regard to the status quo—that is, they should foster a spirit of continuous innovation and improvement. London Business School professors Gary Hamel and C. K. Prahalad describe this tense relationship between vision and strategy as stretch and ambition. Indeed, in a study of such able competitors as CNN, British Airways, and Sony, they found that these firms displaced competitors with stronger reputations and deeper pockets through their ambition to stretch their organizations in more innovative ways (Hamel & Prahalad, 1993).
Third, mission and vision provide a high-level guide, and the strategy provides a specific guide, to the goals and objectives showing success or failure of the strategy and satisfaction of the larger set of objectives stated in the mission.
Exercises
- What is a mission statement?
- What is a vision statement?
- How are values important to the content of mission and vision statements?
- Where does the purpose of mission and vision overlap?
- How do mission and vision relate to a firm’s strategy?
- Why are mission and vision important for organizational goals and objectives?
Key Takeaways
“The Roles of Mission, Vision and Values” in Principles of Management by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

