6.1 Mission and Strategy
What’s in It for Me?
Reading this chapter will help you do the following:
- Consider the roles of mission, strategy and decision making.
- Determine how creativity and passion are related to vision.
- Incorporate stakeholder interests into mission and vision.
- Develop statements that articulate organizational mission and vision.
- Apply mission, vision, and values to your personal goals and professional career.
- Analyze how strategies emerge.
- Interpret strategy as trade-offs, discipline, and focus.
- Conduct internal analysis to develop strategy.
- Conduct external analysis to develop strategy.
- Formulate organizational and personal strategy with the strategy diamond.
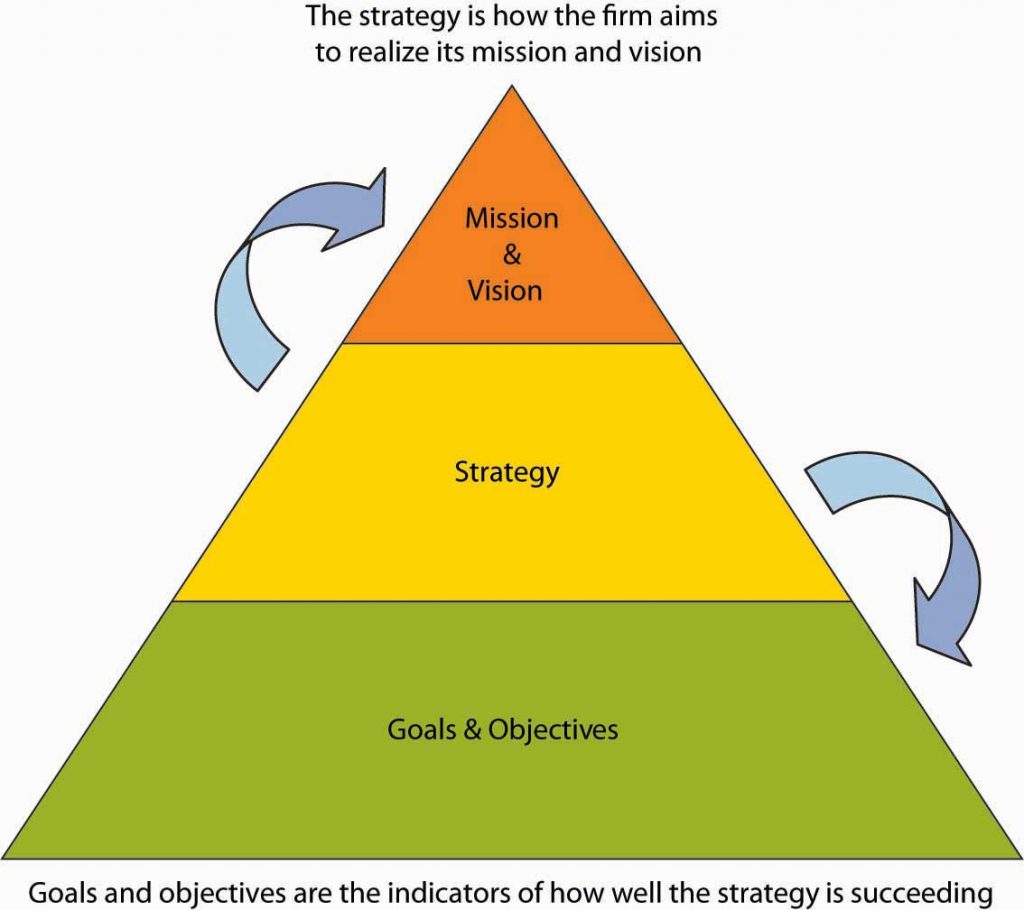
As we discussed in the last chapter, one of the roles of leadership is goal setting. Goal setting involves planning to achieve something—this something can be captured in the verbal and written statements of an organization’s mission and vision (its purpose, in addition to specific goals and objectives). With a mission and vision, you can craft a strategy for achieving them, and your benchmarks for judging your progress and success are clear goals and objectives. Mission and vision communicate the organization’s values and purpose, and help guide decision making.
Strategic management, strategizing for short, is essentially about choice—the decisions that will be made in order to achieve specific goals and objectives leading to the realization of the organization’s mission and vision. Strategy is also about making choices that provide an organization with some measure of competitive advantage or even a sustainable competitive advantage. For the most part, this chapter emphasizes strategy formulation (answers to the “What should our strategy be?” question) as opposed to strategy implementation (answers to questions about “How do we execute a chosen strategy?”). You will also learn how the concept of strategy can be applied to you personally, in addition to professionally.
Example: Xerox Motivates Employees for Success

Fortune Live Media – Fortune Most Powerful Women 2012 – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0; Fortune Live Media – Fortune Most Powerful Women – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
As of 2010, Xerox Corporation (NYSE: XRX) is a $22 billion, multinational company founded in 1906 and operating in 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut, and employs 130,000 people. How does a company of such size and magnitude effectively manage and motivate employees from diverse backgrounds and experiences? Such companies depend on the productivity and performance of their employees. The journey over the last 100 years has withstood many successes and failures. In 2000, Xerox was facing bankruptcy after years of mismanagement, piles of debt, and mounting questions about its accounting practices.
Anne Mulcahy turned Xerox around. Mulcahy joined Xerox as an employee in 1976 and moved up the corporate ladder, holding several management positions until she became CEO in 2001. In 2005, Mulcahy was named by Fortune magazine as the second most powerful woman in business. Based on a lifetime of experience with Xerox, she knew that the company had powerful employees who were not motivated when she took over. Mulcahy believed that among other key businesses changes, motivating employees at Xerox was a key strategy to pull the company back from the brink of failure. One of her guiding principles was a belief that in order to achieve customer satisfaction, employees must be treated as key stakeholders and become interested and motivated in their work. Mulcahy not only successfully saw the company through this difficult time but also was able to create a stronger and more focused company.
In 2009, Mulcahy became the chairman of Xerox’s board of directors and passed the torch to Ursula Burns, who became the new CEO of Xerox. Burns became not only the first African American woman CEO to head a Standard & Poor’s (S&P) company but also the first woman to succeed another woman as the head of an S&P 100 company. Burns is also a lifetime Xerox employee who has been with the company for over 30 years. She began as a graduate intern and was hired full time after graduation. Because of her tenure with Xerox, she has close relationships with many of the employees, which provides a level of comfort and teamwork. She describes Xerox as a nice family. She maintains that Mulcahy created a strong and successful business but encouraged individuals to speak their mind, to not worry about hurting one another’s feelings, and to be more critical.
Burns explains that she learned early on in her career, from her mentors at Xerox, the importance of managing individuals in different ways and not intentionally intimidating people but rather relating to them and their individual perspectives. As CEO, she wants to encourage people to get things done, take risks, and not be afraid of those risks. She motivates her teams by letting them know what her intentions and priorities are. The correlation between a manager’s leadership style and the productivity and motivation of employees is apparent at Xerox, where employees feel a sense of importance and a part of the process necessary to maintain a successful and profitable business. In 2010, Anne Mulcahy retired from her position on the board of directors to pursue new projects.
Exercises
- What values do the promotion and retention of Mulcahy and Burns suggest are important at Xerox? How might these values be reflected in its vision and mission statements?
- How do you think Xerox was able to motivate its employees through the crisis it faced in 2000?
- How do CEOs with large numbers of employees communicate priorities to a worldwide workforce?
- How might Ursula Burns motivate employees to take calculated risks?
- Both Anne Mulcahy and Ursula Burns were lifetime employees of Xerox. How does an organization attract and keep individuals for such a long period of time?
“Developing Mission, Vision and Values“, “Xerox Motivates Employees for Success“, and “Strategizing” in Principles of Management by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

