Part 3 – Resistive Curve
Voltage/Current/Power In Purely Resistive Circuits
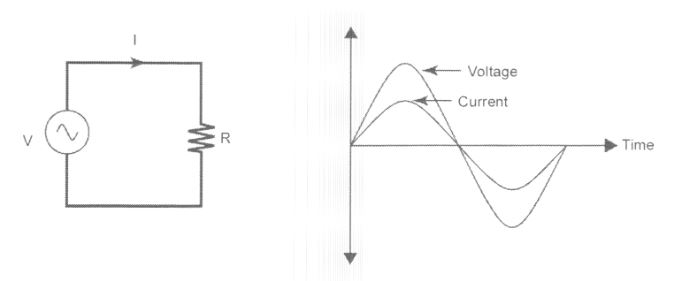
Voltage and current are in phase, meaning that when the voltage reaches its peak value or is zero, the current also simultaneously reaches its peak value or becomes zero.
Using Ohm’s law, if the resistance is 12 ohms and the rms voltage is 120 volts, the rms current would be:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \Large \[ I = \frac{E}{R} = \frac{120}{12} = 10 \text{ amps} \]](https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/app/uploads/quicklatex/quicklatex.com-bfdf35d226dc63f800fed66a67b1d75b_l3.png)
Power P can be expressed by the formulas:
- P (watts) = E (volts) x I (amps)
- P = (IR) x I = I2R
- P = E x (E/R) = E2/R
Activity: Resistive AC Circuit
Click the tick marks on the slider to learn more about resistive AC circuits.
