19 Main Ideas
Week 5
Gravity
Concept Map of the Week
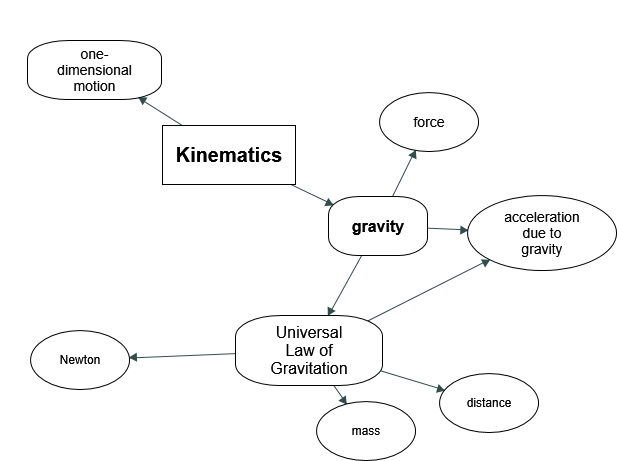
Note: image by Chudaeva, E. (2022).
Concept Trailer
Gravitation
Watch this video.
Then watch the video again and answer the following questions:
- Is there a place in the universe where gravity is zero?
- Who discovered the Universal Law of Gravitation?
- What this law is about?
- The form of the Universal Law of Gravitation is valid for what objects/bodies/masses?
- What is the shape of the trajectory of the Moon around the Earth?
- What is the shape of the path of the Earth around the Sun?
Key Terms
Review the following key terms (Glossary chapter 2 and 6):
acceleration
the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over a period of time
acceleration due to gravity
acceleration of an object as a result of gravity
average acceleration
the change in velocity divided by the time over which it changes
average speed
distance traveled divided by time during which motion occurs
average velocity
displacement divided by time over which displacement occurs
distance
the magnitude of displacement between two positions
free-fall
the state of movement that results from gravitational force only
gravitational constant, G
a proportionality factor used in the equation for Newton’s universal law of gravitation; it is a universal constant—that is, it is thought to be the same everywhere in the universe
position
the location of an object at a particular time
scalar
a quantity that is described by magnitude, but not direction
time
change, or the interval over which change occurs
vector
a quantity that is described by both magnitude and direction
More terms can be found in the textbook Glossary.

