Chapter 5: Audience & Purpose of Writing
Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content
Identifying Common Academic Purposes
The purpose is simply the reason you are writing a particular document. Basically, the purpose of a piece of writing answers the question “why?” For example, why write a play? To entertain a packed theatre. Why write instructions to the babysitter? To inform them of your schedule and rules. Why write a letter to your Member of Parliament? To persuade them to address your community’s needs.
In academic settings, the reasons for writing typically fulfill four main purposes: to summarize, to analyze, to synthesize, and to evaluate. You will encounter these four purposes not only as you read for your classes but also as you read for work or pleasure. Because reading and writing work together, your writing skills will improve as you read.
Eventually, your instructors will ask you to complete assignments specifically designed to meet one of the four purposes. As you will see, the purpose for writing will guide you through each part of the paper, helping you make decisions about content and style. For now, identifying these purposes by reading paragraphs will prepare you to write individual paragraphs and to build longer assignments.
Summary Paragraphs
Summary paragraphs are designed to give the reader a quick overview of a subject or topic of often addresses the 5 W’s (who, what, where, when, why). This type of paragraph is often found towards the end of an essay or chapter. You may also encounter these types of paragraphs as abstracts or executive summaries.
Analysis Paragraphs
An analysis separates complex materials into their different parts and studies how the parts relate to one another. The analysis of simple table salt, for example, would require a deconstruction of its parts—the elements sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Then, scientists would study how the two elements interact to create the compound NaCl, or sodium chloride, which is also called simple table salt.
Analysis is not limited to the sciences, of course. An analysis paragraph in academic writing fulfills the same purpose. Instead of deconstructing chemical compounds, academic analysis paragraphs typically deconstruct documents. An analysis takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point. It communicates the main points of the document by examining individual points and identifying how they relate to one another. Take a look at a student’s analysis of the journal report.
Notice how the analysis does not simply repeat information from the original report, but considers how the points within the report relate to one another? By doing this, the student uncovers a discrepancy between the points that are backed up by statistics and those that require additional information. Analyzing a document involves a close examination of each of the individual parts and how they work together.
Synthesis Paragraphs
A synthesis combines two or more items to create an entirely new item. Consider the electronic musical instrument aptly named the synthesizer. It looks like a simple keyboard but displays a dashboard of switches, buttons, and levers. With the flip of a few switches, a musician may combine the distinct sounds of a piano, a flute, or a guitar—or any other combination of instruments—to create a new sound. The purpose of the synthesizer is to blend together the notes from individual instruments to form new, unique notes.
The purpose of an academic synthesis is to blend individual documents into a new document. An academic synthesis paragraph considers the main points from one or more pieces of writing and links the main points together to create a new point, one not replicated in either document.
Take a look at a student’s synthesis of several sources about underage drinking.

Notice how the synthesis paragraphs consider each source and use information from each to create a new thesis. A good synthesis does not repeat information; the writer uses a variety of sources to create a new idea.
Evaluation Paragraphs
An evaluation judges the value of something and determines its worth. Evaluations in everyday experiences are often not only dictated by set standards but are also influenced by opinion and prior knowledge. For example, at work, a supervisor may complete an employee evaluation by judging his subordinate’s performance based on the company’s goals. If the company focuses on improving communication, the supervisor will rate the employee’s customer service according to a standard scale. However, the evaluation still depends on the supervisor’s opinion and prior experience with the employee. The purpose of the evaluation is to determine how well the employee performs on the job.

An academic evaluation communicates your opinion, and its justifications, about a document or a topic of discussion. Evaluations are influenced by your reading of the document, your prior knowledge, and your prior experience with the topic or issue. Because an evaluation incorporates your point of view and the reasons for your point of view, it typically requires more critical thinking and a combination of summary, analysis, and synthesis skills. Thus evaluation paragraphs often follow summary, analysis, and synthesis paragraphs. Read a student’s evaluation paragraph.
Notice how the paragraph incorporates the student’s personal judgment within the evaluation. Evaluating a document requires prior knowledge that is often based on additional research.
Self-Practice Exercise
Read the following paragraphs about four films and then identify the purpose of each paragraph.
This film could easily have been cut down to less than two hours. By the final scene, I noticed that most of my fellow moviegoers were snoozing in their seats and were barely paying attention to what was happening on screen. Although the director sticks diligently to the book, he tries too hard to cram in all the action, which is just too ambitious for such a detail-oriented story. If you want my advice, read the book and give the movie a miss.
During the opening scene, we learn that the character Laura is adopted and that she has spent the past three years desperately trying to track down her real parents. Having exhausted all the usual options—adoption agencies, online searches, family trees, and so on—she is on the verge of giving up when she meets a stranger on a bus. The chance encounter leads to a complicated chain of events that ultimately result in Laura getting her lifelong wish. But is it really what she wants? Throughout the rest of the film, Laura discovers that sometimes the past is best left where it belongs.
To create the feeling of being gripped in a vise, the director, May Lee, uses a variety of elements to gradually increase the tension. The creepy, haunting melody that subtly enhances the earlier scenes becomes ever more insistent, rising to a disturbing crescendo toward the end of the movie. The desperation of the actors, combined with the claustrophobic atmosphere and tight camera angles create a realistic firestorm, from which there is little hope of escape. Walking out of the theatre at the end feels like staggering out of a Roman dungeon.
The scene in which Campbell and his fellow prisoners assist the guards in shutting down the riot immediately strikes the viewer as unrealistic. Based on the recent reports on prison riots in both Detroit and California, it seems highly unlikely that a posse of hardened criminals would intentionally help their captors at the risk of inciting future revenge from other inmates. Instead, both news reports and psychological studies indicate that prisoners who do not actively participate in a riot will go back to their cells and avoid conflict altogether. Examples of this lack of attention to detail occur throughout the film, making it almost unbearable to watch.
Collaboration: Share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Writing at Work
Thinking about the purpose of writing a report in the workplace can help focus and structure the document. A summary should provide colleagues with a factual overview of your findings without going into too much detail. In contrast, an evaluation should include your personal opinion, along with supporting evidence, research, or examples to back it up. Listen for words such as summarize, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate when your boss asks you to complete a report to help determine a purpose for writing.
Self-Practice Exercise
Consider the expository essay you will soon have to write. Identify the most effective academic purpose for the assignment.
My assignment: ____________________________________________
My purpose: ________________________________________________
Identifying the Audience
Imagine you must give a presentation to a group of executives in an office. Weeks before the big day, you spend time creating and rehearsing the presentation. You must make important, careful decisions not only about the content but also about your delivery. Will the presentation require technology to project figures and charts? Should the presentation define important words, or will the executives already know the terms? Should you wear your suit and dress shirt? The answers to these questions will help you develop an appropriate relationship with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Now imagine you must explain the same business concepts from your presentation to a group of high school students. Those important questions you previously answered may now require different answers. The figures and charts may be too sophisticated, and the terms will certainly require definitions. You may even reconsider your outfit and sport a more casual look. Because the audience has shifted, your presentation and delivery will shift as well to create a new relationship with the new audience.
In these two situations, the audience—the individuals who will watch and listen to the presentation—plays a role in the development of presentation. As you prepare the presentation, you visualize the audience to anticipate their expectations and reactions. What you imagine affects the information you choose to present and how you will present it. Then, during the presentation, you meet the audience in person and discover immediately how well you perform.
Although the audience for writing assignments—your readers—may not appear in person, they play an equally vital role. Even in everyday writing activities, you identify your readers’ characteristics, interests, and expectations before making decisions about what you write. In fact, thinking about audience has become so common that you may not even detect the audience driven decisions.
For example, you update your status on a social networking site with the awareness of who will digitally follow the post. If you want to brag about a good grade, you may write the post to please family members. If you want to describe a funny moment, you may write with your friends’ sense of humour in mind. Even at work, you send emails with an awareness of an unintended receiver who could intercept the message.
In other words, being aware of “invisible” readers is a skill you most likely already possess and one you rely on every day. Consider the following paragraphs. Which one would the author send to her parents? Which one would she send to her best friend?
Example A
Last Saturday, I volunteered at a local hospital. The visit was fun and rewarding. I even learned how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR. Unfortunately, I think caught a cold from one of the patients. This week, I will rest in bed and drink plenty of clear fluids. I hope I am well by next Saturday to volunteer again.
Example B
Most likely, you matched each paragraph to its intended audience with little hesitation. Because each paragraph reveals the author’s relationship with her intended readers, you can identify the audience fairly quickly. When writing your own paragraphs, you must engage with your audience to build an appropriate relationship given your subject. Imagining your readers during each stage of the writing process will help you make decisions about your writing. Ultimately, the people you visualize will affect what and how you write.
PRO TIP: While giving a speech, you may articulate an inspiring or critical message, but if you left your hair a mess and laced up mismatched shoes, your audience would not take you seriously. They may be too distracted by your appearance to listen to your words.
Similarly, grammar and sentence structure serve as the appearance of a piece of writing. Polishing your work using correct grammar will impress your readers and allow them to focus on what you have to say.
Because focusing on audience will enhance your writing, your process, and your finished product, you must consider the specific traits of your audience members. Use your imagination to anticipate the readers’ demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations.
- Demographics: These measure important data about a group of people, such as their age range, ethnicity, religious beliefs, or gender. Certain topics and assignments will require you to consider these factors as they relate to your audience. For other topics and assignments, these measurements may not influence your writing. Regardless, it is important to consider demographics when you begin to think about your purpose for writing.
- Education: Education considers the audience’s level of schooling. If audience members have earned a doctorate degree, for example, you may need to elevate your style and use more formal language. Or, if audience members are still in college, you could write in a more relaxed style. An audience member’s major or emphasis may also dictate your writing.
- Prior knowledge: Prior knowledge is what the audience already knows about your topic. If your readers have studied certain topics, they may already know some terms and concepts related to the topic. You may decide whether to define terms and explain concepts based on your audience’s prior knowledge. Although you cannot peer inside the brains of your readers to discover their knowledge, you can make reasonable assumptions. For instance, a nursing major would presumably know more about health-related topics than a business major would.
- Expectations: These indicate what readers will look for while reading your assignment. Readers may expect consistencies in the assignment’s appearance, such as correct grammar and traditional formatting like double-spaced lines and a legible font. Readers may also have content-based expectations given the assignment’s purpose and organization. In an essay titled “The Economics of Enlightenment: The Effects of Rising Tuition,” for example, audience members may expect to read about the economic repercussions of post-secondary tuition costs.
Self-Practice Exercise
On a sheet of paper, generate a list of characteristics under each category for each audience. This list will help you later when you read about tone and content.
Your classmates:
Demographics ____________________________________________
Education ____________________________________________
Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
Expectations ____________________________________________
Demographics ____________________________________________
Education ____________________________________________
Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
Expectations ____________________________________________
The head of your academic department
Demographics ____________________________________________
Education ____________________________________________
Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
Expectations ____________________________________________
Now think about your next writing assignment. Identify the purpose (you may use the same purpose listed in Self–Practice Exercise 1.6b and then identify the audience. Create a list of characteristics under each category.
My assignment:____________________________________________
My purpose: ____________________________________________
My audience: ____________________________________________
Demographics ____________________________________________
Education ____________________________________________
Prior knowledge ____________________________________________
Expectations ____________________________________________
Collaboration: please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Keep in mind that as your topic shifts in the writing process, your audience may also shift. Also, remember that decisions about style depend on audience, purpose, and content. Identifying your audience’s demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations will affect how you write, but purpose and content play an equally important role. The next subsection covers how to select an appropriate tone to match the audience and purpose.
Selecting an Appropriate Tone
Tone identifies a speaker’s attitude toward a subject or another person. You may pick up a person’s tone of voice fairly easily in conversation. A friend who tells you about her weekend may speak excitedly about a fun skiing trip. An instructor who means business may speak in a low, slow voice to emphasize her serious mood. Or, a co-worker who needs to let off some steam after a long meeting may crack a sarcastic joke. Tone is important because the way you might speak to your friends (“oh shut up, it’s fine…”) would definitely not be appropriate when speaking to your boss or your professor.
Just as speakers transmit emotion through voice, writers can transmit through writing a range of attitudes, from excited and humorous to somber and critical. These emotions create connections among the audience, the author, and the subject, ultimately building a relationship between the audience and the text. To stimulate these connections, writers intimate their attitudes and feelings with useful devices, such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language. Keep in mind that the writer’s attitude should always appropriately match the audience and the purpose, which means that you need to choose appropriate language and sentence structure that will convey your ideas with your intent.
Read the following paragraph and consider the writer’s tone. How would you describe the writer’s attitude toward wildlife conservation?
Self-Practice Exercise
Think about the assignment and purpose you selected in Self–Practice Exercise 1.6b and the audience you selected in Self–Practice Exercise 1.6c. Now, identify the tone you would use in the assignment.
My assignment: ____________________________________________
My purpose: ____________________________________________
My audience: ____________________________________________
My tone: ____________________________________________
Choosing Appropriate, Interesting Content
Content refers to all the written substance in a document. After selecting an audience and a purpose, you must choose what information will make it to the page. Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations, but no matter the type, the information must be appropriate and interesting for the audience and purpose. An essay written for grade 3 students that summarizes the legislative process, for example, would have to contain succinct and simple content.
Content is also shaped by tone. When the tone matches the content, the audience will be more engaged, and you will build a stronger relationship with your readers. Consider that audience of grade 3 students. You would choose simple content that the audience will easily understand, and you would express that content through an enthusiastic tone. The same considerations apply to all audiences and purposes.
Self-Practice Exercise
Using the assignment, purpose, audience, and tone fromSelf–Practice Exercise 1.6d, generate a list of content ideas. Remember that content consists of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations.
My assignment: ____________________________________________
My purpose: ____________________________________________
My audience: ____________________________________________
My tone: ____________________________________________
My content ideas: ____________________________________________
Common Writing Assignments
Writing assignments at the post-secondary level serve a different purpose than the typical writing assignments you completed in high school. In high school, teachers generally focus on teaching you to write in a variety of modes and formats, including personal writing, expository writing, research papers, creative writing, and writing short answers and essays for exams. Over time, these assignments help you build a foundation of writing skills.
Now, however, your instructors will expect you to already have that foundation. Your composition courses will focus on helping you make the transition to higher-level writing assignments. However, in most of your other courses, writing assignments serve a different purpose. In those courses, you may use writing as one tool among many for learning how to think about a particular academic discipline.
Additionally, certain assignments teach you how to meet the expectations for professional writing in a given field. Depending on the class, you might be asked to write a lab report, a case study, a literary analysis, a business plan, or an account of a personal interview. You will need to learn and follow the standard conventions for those types of written products.
Finally, personal and creative writing assignments are less common at the post-secondary level than in high school. College and university courses emphasize expository writing—writing that explains or informs. Often expository writing assignments will incorporate outside research, too. Some classes will also require persuasive writing assignments in which you state and support your position on an issue. Your instructors will hold you to a higher standard when it comes to supporting your ideas with reasons and evidence.
Common Types of Writing Assignments
|
Assignment Type |
Description |
Example |
| Personal response paper | Expresses and explains your response to a reading assignment, a provocative quote, or a specific issue; may be very brief (sometimes a page or less) or more in depth | For a labour management course, students watch and write about videos of ineffective management/staff interactions. |
| Summary | Restates the main points of a longer passage objectively and in your own words | For a psychology course, students write a one-page summary of an article about a man suffering from short-term memory loss. |
| Persuasive/
position paper |
States and defends your position on an issue (often a controversial issue) | For a criminal justice course, students state their positions on capital punishment using research to support their argument. |
| Problem-solution paper | Presents a problem, explains its causes, and proposes and explains a solution | For an emergency management course, a student presents a plan for implementing a crisis communications strategy. |
| Critique/
literary analysis |
States a thesis about a particular literary work and develops the thesis with evidence from the work and, sometimes, from additional sources | For a literature course, a student analyzes a short story by Ian Rankin and how it relates to the field of criminology OR compares multiple works by analyzing commonalities and differences. |
| Research/ literature review |
Sums up available research findings on a particular topic | For a course in criminology, a student reviews the past 20 years of research on whether violence in television and movies is correlated with violent behaviour. |
| Case study or case analysis | Investigates a particular person, group, or event in depth for the purpose of drawing a larger conclusion from the analysis | For a health science course, a student writes a case study demonstrating the successful treatment of a patient experiencing congestive heart failure. |
| Laboratory report | Presents a laboratory experiment, including the hypothesis, methods of data collection, results, and conclusions | For a psychology course, a group of students presents the results of an experiment in which they explored whether sleep deprivation produced memory deficits in lab rats. |
| Research journal | Records a student’s ideas and findings during the course of a long-term research project | For a capstone project, a student maintains a journal throughout a semester-long research project within the local fire department. |
| Research paper | Presents a thesis and supports it with original research and/or other researchers’ findings on the topic; can take several different formats depending on the subject area | For a criminology course, a student chooses a topic/thesis on de-escalation techniques and conducts background research on existing evidence then creates his or her own research tool to measure the effectiveness of such techniques. |
Writing at Work
Part of managing your education is communicating well with others at your institution. For instance, you might need to email your instructor to request an office appointment or explain why you will need to miss a class. You might need to contact administrators with questions about your tuition or financial aid. Later, you might ask instructors to write recommendations on your behalf.
Treat these documents as professional communications. Address the recipient politely; state your question, problem, or request clearly; and use a formal, respectful tone. Doing so helps you make a positive impression and get a quicker response.
Using the Writing Process
To complete a writing project successfully, good writers use some variation of the following process.
The Writing Process
- Prewriting. The writer generates ideas to write about and begins developing these ideas.
- Outlining a structure of ideas.The writer determines the overall organizational structure of the writing and creates an outline to organize ideas. Usually this step involves some additional fleshing out of the ideas generated in the first step.
- Writing a rough draft.The writer uses the work completed in prewriting to develop a first draft. The draft covers the ideas the writer brainstormed and follows the organizational plan that was laid out in the first step.
- Revising.The writer revisits the draft to review and, if necessary, reshape its content. This stage involves moderate and sometimes major changes: adding or deleting a paragraph, phrasing the main point differently, expanding on an important idea, reorganizing content, and so forth.
- Editing. The writer reviews the draft to make additional changes. Editing involves making changes to improve style and adherence to standard writing conventions—for instance, replacing a vague word with a more precise one or fixing errors in grammar and spelling. Once this stage is complete, the work is a finished piece and ready to share with others.
Chances are you have already used this process as a writer. You may also have used it for other types of creative projects, such as developing a sketch into a finished painting or composing a song. The steps listed above apply broadly to any project that involves creative thinking. You come up with ideas (often vague at first), you work to give them some structure, you make a first attempt, you figure out what needs improving, and then you refine it until you are satisfied.
Most people have used this creative process in one way or another, but many people have misconceptions about how to use it to write. Here are a few of the most common misconceptions students have about the writing process:
- “I do not have to waste time on prewriting if I understand the assignment.” Even if the task is straightforward and you feel ready to start writing, take some time to develop ideas before you plunge into your draft. Freewriting—writing about the topic without stopping for a set period of time—is one prewriting technique you might try in that situation.
- “It is important to complete a formal, numbered outline for every writing assignment.” For some assignments, such as lengthy research papers, proceeding without a formal outline can be very difficult. However, for other assignments, a structured set of notes or a detailed graphic organizer may suffice. The important thing is to have a solid plan for organizing ideas and details.
- “My draft will be better if I write it when I am feeling inspired.” By all means, take advantage of those moments of inspiration. However, understand that sometimes you will have to write when you are not in the mood. Sit down and start your draft even if you do not feel like it. If necessary, force yourself to write for just one hour. By the end of the hour, you may be far more engaged and motivated to continue. If not, at least you will have accomplished part of the task.
- “My instructor will tell me everything I need to revise.” If your instructor chooses to review drafts, the feedback can help you improve. However, it is still your job, not your instructor’s, to transform the draft to a final, polished piece. That task will be much easier if you give your best effort to the draft before submitting it. During revision, do not just go through and implement your instructor’s corrections. Take time to determine what you can change to make the work the best it can be.
- “I am a good writer, so I do not need to revise or edit.” Even talented writers still need to revise and edit their work. At the very least, doing so will help you catch an embarrassing typo or two. Revising and editing are the steps that make good writers into great writers.
Managing Your Time
When your instructor gives you a writing assignment, write the due date on your calendar. Then work backward from the due date to set aside blocks of time when you will work on the assignment. Always plan at least two sessions of writing time per assignment, so that you are not trying to move from step 1 to step 5 in one evening. Trying to work that fast is stressful, and it does not yield great results. You will plan better, think better, and write better if you space out the steps.
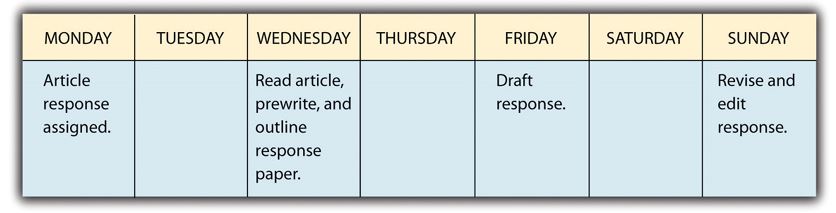
Ideally, you should set aside at least three separate blocks of time to work on a writing assignment: one for prewriting and outlining, one for drafting, and one for revising and editing. Sometimes those steps may be compressed into just a few days. If you have a couple of weeks to work on a paper, space out the five steps over multiple sessions. Long-term projects, such as research papers, require more time for each step:
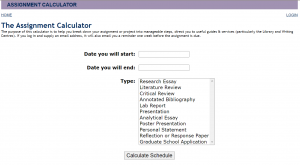
Again, an assignment calculator is an incredibly useful tool for helping with this process: