42 Drivers of Success and Failure When Competing in International Markets
Learning Objectives
- Explain the elements of the “diamond model.”
- Understand how the model helps to explain success and failure in international markets.
The title of a book written by newspaper columnist Thomas Friedman attracted a great deal of attention when the book was released in 2005. In The World Is Flat: A Brief History of the 21st Century, Friedman argued that the Internet coupled with globalization and increased liberalization of trade is leveling the competitive playing field between developed and emerging countries. This means that companies exist in a “flat world” because economies across the globe are converging on a single integrated global system (Friedman, 2005). For executives, a key implication is that a firm’s being based in a particular country is ceasing to be an advantage or disadvantage, except for industries where transportation is a key aspect of the product.
While Friedman’s notion of business becoming a flat world is flashy and attention grabbing, it does not match reality. Research studies conducted since 2005 have found that some firms enjoy advantages based on their country of origin while others suffer disadvantages. A powerful framework for understanding how likely it is that firms based in a particular country will be successful when competing in international markets was provided by Professor Michael Porter of the Harvard Business School (Porter, 1990). The framework is formally known as “the determinants of national advantage,” but it is often referred to more simply as “the diamond model” because of its shape (Figure 7.14 “Diamond Model of National Advantage”).

According to the model, the ability of the firms in an industry whose origin is in a particular country (e.g., South Korean automakers or Italian shoemakers) to be successful in the international arena is shaped by four factors: (1) their home country’s demand conditions, (2) their home country’s factor conditions, (3) related and supporting industries within their home country, and (4) strategy, structure, and rivalry among their domestic competitors.
Demand Conditions
Within the diamond model, demand conditions[1] refer to the nature and volume of domestic customers (Figure 7.15 “Demand Conditions”). It is tempting to believe that firms benefit when their domestic customers are perfectly willing to purchase inferior products. This would be a faulty belief! Instead, firms benefit when their domestic customers have high expectations.
Japanese consumers are known for insisting on very high levels of quality, aesthetics, and reliability. Japanese automakers such as Honda, Toyota, and Nissan reap rewards from this situation. These firms have to work hard to satisfy their domestic buyers. Living up to lofty quality standards at home prepares these firms to offer high-quality products when competing in international markets. In contrast, French car buyers do not stand out as particularly fussy. It is probably not a coincidence that French automakers Renault and Peugeot have struggled to gain traction within the global auto industry.

Demand conditions also help to explain why German automakers such as Porsche, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW create excellent luxury and high-performance vehicles. German consumers value superb engineering. While a car is simply a means of transportation in some cultures, Germans place value on the concept of fahrvergnügen, which means “driving pleasure.” Meanwhile, demand for fast cars is high in Germany because the country has built nearly 8,000 miles of superhighways known as autobahns. No speed limits for cars are enforced on more than half of the 8,000 miles. Many Germans enjoy driving at 150 miles per hour or more, and German automakers must build cars capable of safely reaching and maintaining such speeds. When these companies compete in the international arena, the engineering and performance of their vehicles stand out.

Factor Conditions
Factor conditions[2] refer to the nature of raw material and other inputs, including qualified labor, that firms need to create goods and services (Figure 7.17 “Factor Conditions”). Examples include land, labor, capital markets, and infrastructure. Firms benefit when they have good access to factor conditions and face challenges when they do not. Companies based in Canada and the United States, for example, are able to draw on plentiful natural resources, a skilled labor force, highly developed transportation systems, and sophisticated capital markets to be successful. The dramatic growth of Chinese manufacturers in recent years has been fueled in part by the availability of cheap labor and access to cheap capital.
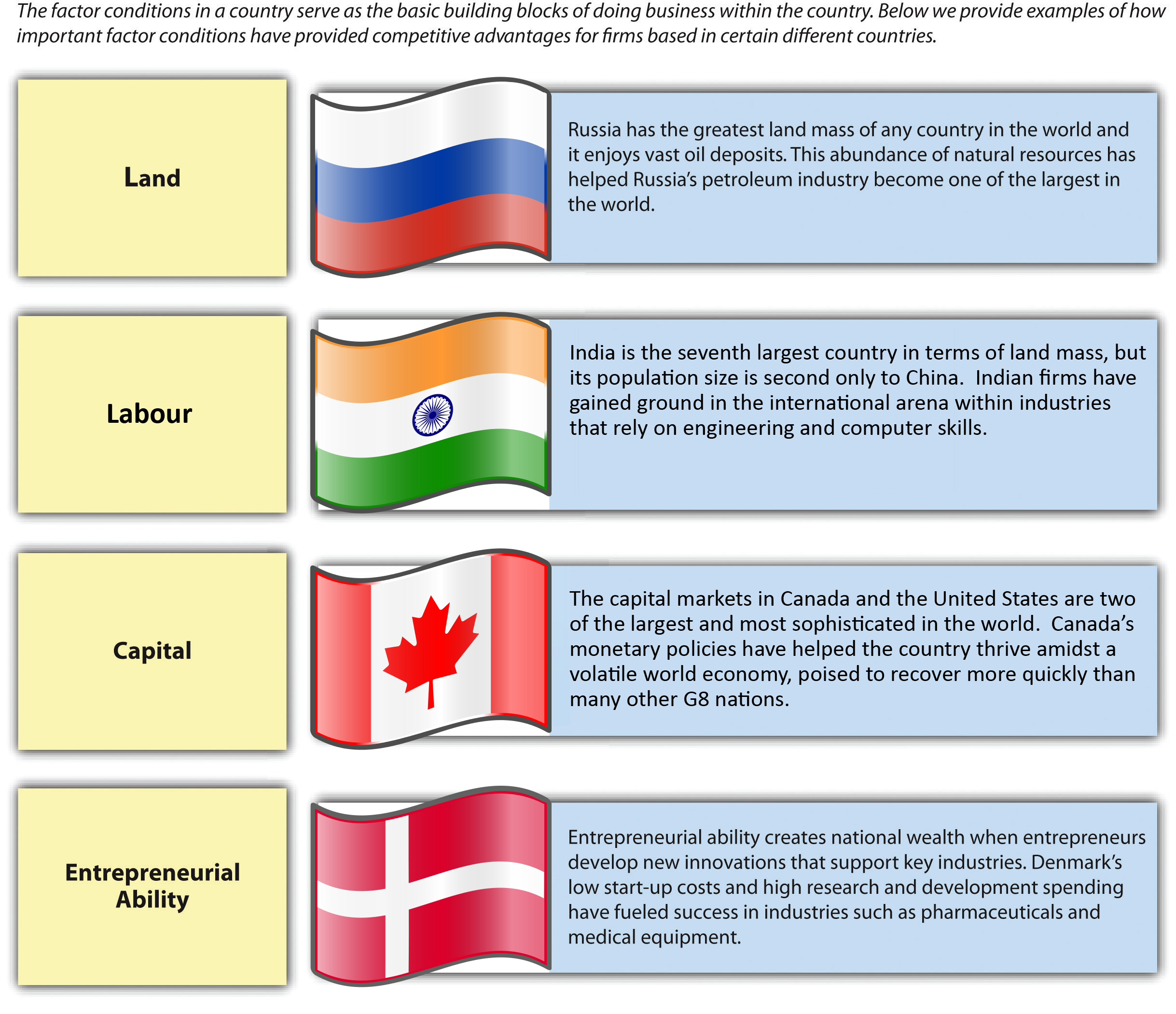
In some cases, overcoming disadvantages in factor conditions leads companies to develop unique skills. Japan is a relatively small island nation with little room to spare. This situation has led Japanese firms to be pioneers in the efficient use of warehouse space through systems such as just-in-time inventory management (JIT).[3] Rather than storing large amounts of parts and material, JIT management conserves space—and lowers costs—by requiring inputs to a production process to arrive at the moment they are needed. Their use of JIT management has given Japanese manufacturers an advantage when they compete in international markets.

Related and Supporting Industries
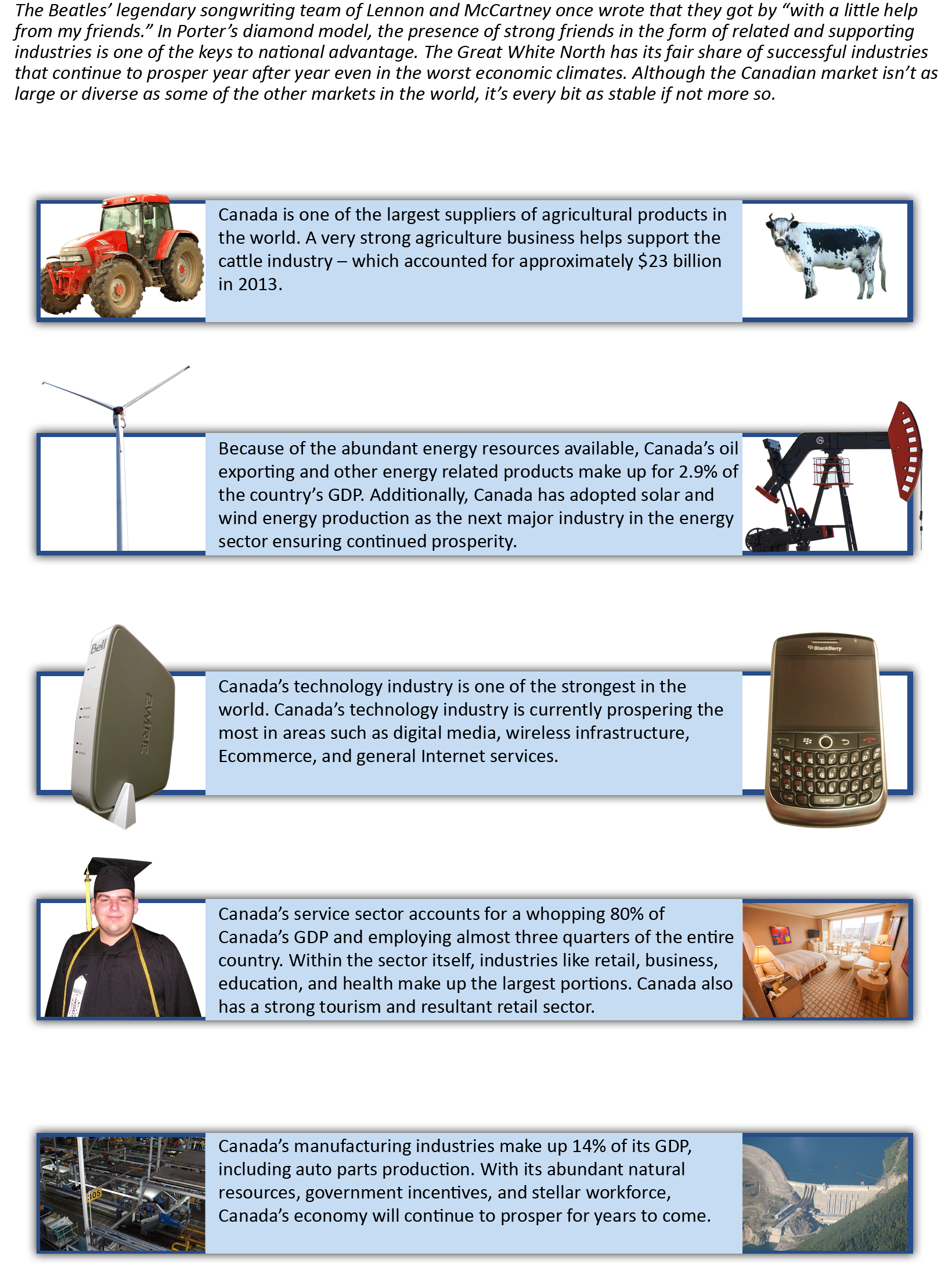
Could Italian shoemakers create some of the world’s best shoes if Italian leather tanners were not among the world’s best? Possibly, but it would be much more difficult. The concept of related and supporting industries[4] refers to the extent to which firms’ domestic suppliers and other complementary industries are developed and helpful (Figure 7.19 “Related and Supporting Industries”). Italian shoemakers such as Salvatore Ferragamo, Prada, Gucci, and Versace benefit from the availability of top-quality leather within their home country. If these shoemakers needed to rely on imported leather, they would lose some of their flexibility and speed.

The auto industry is a setting where related and supporting industries are very important. Electronics are key components of modern vehicles. South Korean automakers Kia and Hyundai can leverage the excellent electronics provided by South Korean firms Samsung and LG. Similarly, Honda, Nissan, and Toyota are able to draw on the skills of Sony and other Japanese electronics firms. Unfortunately, for French automakers Renault and Peugeot, no French electronics firms are standouts in the international arena. This situation makes it difficult for Renault and Peugeot to integrate electronics into their vehicles as effectively as their South Korean and Japanese rivals.
The development of the international Detroit(U.S.)/Windsor (Canada) car manufacturing hub saw many component manufacturing companies set up shop in the region to be near the Big Three auto manufacturing plants. This initiative was accelerated with just-in-time supply chain management. The relatively close location of these manufacturing and design firms continues to attract a strong labor force of engineers and designers of car components and parts, resulting in many new ideas for car manufacturing.
In extreme cases, the poor condition of related and supporting industries can undermine an operation. Kaufman Footwear, formerly the Kaufman Rubber Company, was a shoe manufacturing company in Kitchener, Ontario, that produced well-known brands such as Sorel winter boots, Kingtread work boots, Foamtread slippers, and Black Diamond industrial footwear. The company had sales warehouses across Canada. The Kaufman plant opened in 1908 with 350 employees, and produced rubber footwear for both domestic and foreign markets. By the 1950s, the Canadian rubber footwear industry was feeling the impact of competing imported products, so Kaufman Rubber began manufacturing footwear made from synthetic materials. In 1982, Canada removed import quotas from leather shoe imports, which eventually snowballed into the demise of much of its national shoe industry. Kaufman declared bankruptcy in 2000, one of the many Canadian shoe manufacturers unable to compete in the face of increased global competition. The Sorel trademark was bought by Columbia Sportswear and continues the brand name today. Canada still has several highly specialized footwear manufacturers, including Boulet Boots, Blondo, La Canadienne, Cougar, Dayton Boots, John Fleuvog, Kamik, Pajar, Roots, and Sorel Footwear.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
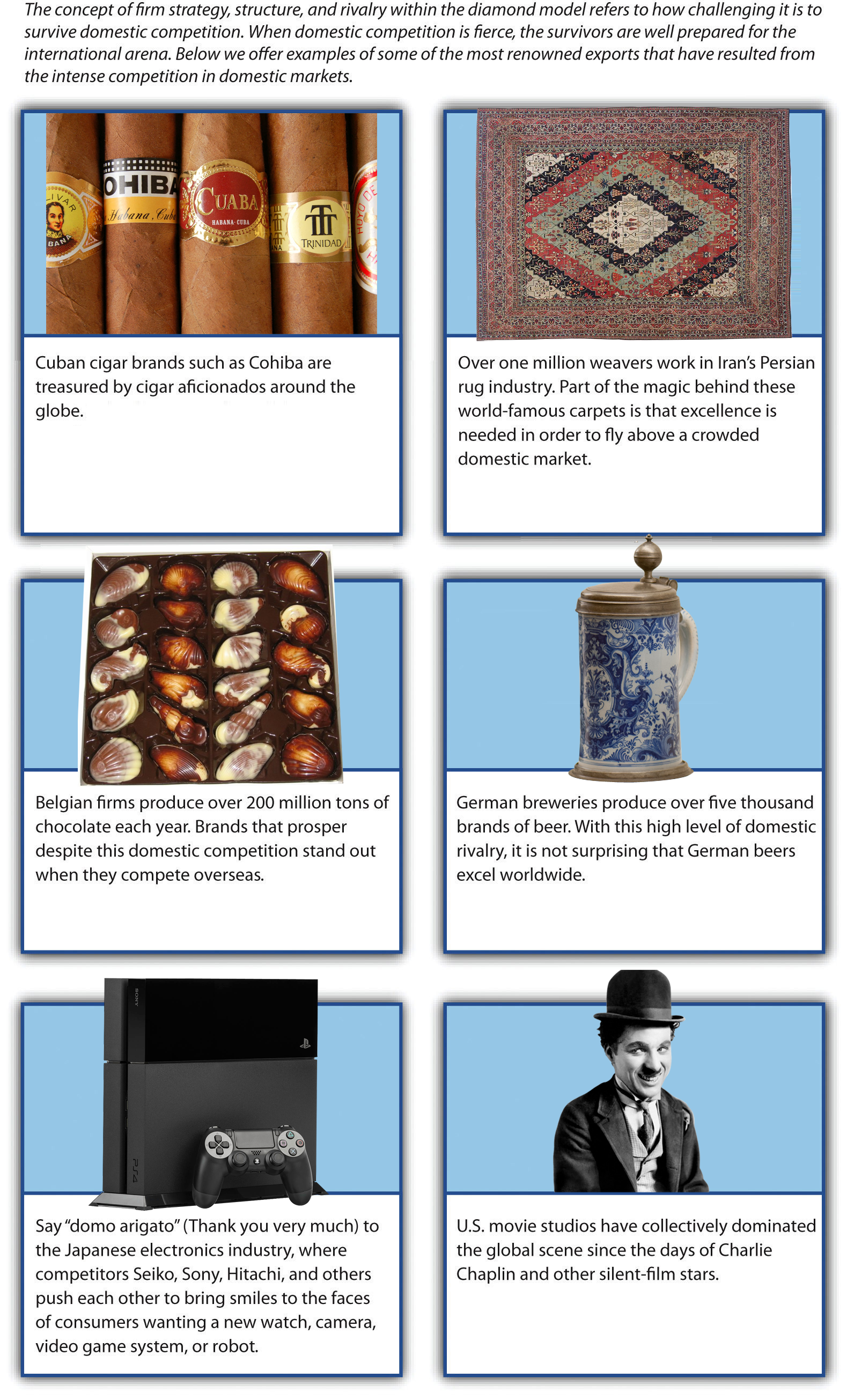
The concept of firm strategy, structure, and rivalry[5] refers to how challenging it is to survive domestic competition (Figure 7.21 “Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry”). The Olympics offer a good analogy for illustrating the positive aspects of very challenging domestic situations. If the competition to make a national team in gymnastics is fierce, the gymnasts who make the team will have been pushed to stretch their abilities and performance. In contrast, gymnasts who faced few contenders in their quest to make a national team will not have been tested with the same level of intensity. When the two types meet at the Olympics, the gymnasts who overcame huge hurdles to make their national teams are likely to have an edge over athletes from countries with few skilled gymnasts.
Companies that have survived intense rivalry within their home markets are likely to have developed strategies and structures that will facilitate their success when they compete in international markets. Hyundai and Kia had to keep pace with each other within the South Korean market before expanding overseas. The leading Japanese automakers—Honda, Nissan, and Toyota—have had to compete not only with one another but also with smaller yet still potent domestic firms such as Isuzu, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Subaru, and Suzuki. In both examples, the need to navigate potent domestic rivals has helped firms later become fearsome international players.

If, in contrast, domestic competition is fairly light, a company may enjoy admirable profits within its home market. However, the lack of being pushed by rivals will likely mean that the firm struggles to reach its full potential in creativity and innovation. This undermines the firm’s ability to compete overseas and even makes it vulnerable to foreign entry into its home market. Because neither Renault nor Peugeot has been a remarkable innovator historically, these French automakers have enjoyed fairly gentle domestic competition. Once the auto industry became a more global marketplace and competition, however, these firms found themselves trailing their Asian rivals.
Key Takeaway
- The likelihood that a firm will succeed when it competes in international markets is shaped by four aspects of its domestic market: (1) demand conditions; (2) factor conditions; (3) related and supporting industries; and (4) strategy, structure, and rivalry among its domestic competitors.
Exercises
- Which of the four elements of the diamond model do you believe has the strongest influence on a firm’s fate when it competes in international markets?
- Automakers in China and India have yet to compete on the world stage. Based on the diamond model, would these firms be likely to succeed or fail within the global auto industry?
References
Aeppel, T. (2008, March 3). US shoe factory finds supplies are Achilles’ heel. Wall Street Journal. Retrieved from http://online.wsj.com/article/SB120450124543206313.html
Friedman, T. L. (2005). The world is flat: A brief history of the 21st century. New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Porter, M. E. (1990). The competitive advantage of nations. New York, NY: Free Press.
- Demand conditions: The nature of domestic customers, especially whether they have high expectations of the goods and services that they buy. ↵
- Factor conditions: The nature of raw material and other inputs that firms need to create goods and services. ↵
- Just-in-time inventory management (JIT): A production system that conserves space and lowers costs by requiring inputs to arrive at the moment they are needed. ↵
- Related and supporting industries: The extent to which firms’ domestic suppliers and other complementary industries are developed and helpful. ↵
- Firm strategy, structure, and rivalry: How challenging it is for firms to survive domestic competition. ↵

