59 Understanding Thought Patterns: A Key to Corporate Leadership?
Learning Objectives
- Know the three major generational influences that make up the majority of the current workforce and their different perspectives and influences.
- Understand how decision biases may impede effective decision making.
Generational Influences on Work Behavior
Psychologist Kurt Lewin, known as the “founder of social psychology,” created a well-known formula B = ƒ(P,E) that states behavior is a function of the person and his or her environment. One powerful environmental influence that can be seen in organizations today is based on generational differences. Currently, four generations of workers (traditionalists, baby boomers, Generation X, Generation Y) coexist in many organizations. The different backgrounds and behaviors create challenges for leading these individuals that often have similar shared experiences within their generation but different sets of values, motivations, and preferences in contrast to other generations (Figure 10.12 “Managing Generational Differences”). Effective management of these four different generations involves a realization of their differences and preferred communication styles (Rathman, 2011).
The generation born between 1925 and 1946 that fought in World War II and lived through the Great Depression are referred to as traditionalists.[1] The perseverance of this generation has led journalist Tom Brokaw to dub this group “The Greatest Generation.” As a reflection of a generation that was molded by contributions to World War II, members of this generation value personal communication, loyalty, hierarchy, and are resistant to change. In 2012, as a result of various social changes and economic factors, the employment rate for traditionalists (then aged 65 and over) remained at 12 percent, with retirement slowly lowering the actual number in the workplace.

The generation known as baby boomers[2] was born between 1946 and 1964, corresponding with a population “boom” following the end of World War II. This group witnessed Beatlemania, the Quebec Revolution, and Canada’s new flag. College and university graduates should be aware that this group currently makes up the majority of the workforce and that boomer managers often view face time as an important contribution to a successful work environment (Fogg, 2008). In addition, a realization that this generation wants to be included in office activities and values recognition is important to achieving cohesiveness between generations. The oldest baby boomers, now 68 in 2014, are reaching traditional retirement age, and this trend will continue and accelerate over the the next decade.
Generation X,[3]born between 1965 and 1980, is marked by an X symbolizing their unknown nature. In contrast to the baby boomer’s value on office face time, Gen X members prize flexibility in their jobs and dislike the feeling that they are being micromanaged (Burk, Olsen, & Messerli, 2011). Because of the desire for independence as well as adaptability associated with this generation, you should try to answer the “What’s in it for me?” question to avoid the risk of Gen X members moving on to other employment opportunities.
The generation that followed Generation X, those born after 1980, is known as Generation Y[4] or millennials. This generation is highlighted by positive attributes such as the ability to embrace technology. More than previous generations, this group prizes job and life satisfaction highly, so making the workplace an enjoyable environment is key to managing Generation Y.

Wise members of this generation will also be aware of the negative attributes surrounding them. For example, millennials are associated with their “helicopter” parents who are often too comfortably involved in the lives of their children. For example, such parents have been known to show up to their children’s job orientations, often attempting to interfere with other workplace experiences such as pay and promotion discussions that may be unwelcome by older generations. In addition, this generation is viewed as needing more feedback than previous groups. Finally, the trend toward discouraging some competitive activities among individuals in this age group has led millennials to be dubbed “Trophy Kids” by more cynical writers.
Rational Decision Making
Understanding generational differences can provide valuable insight into the perspectives that shape the behaviors of individuals born at different periods of time. But such knowledge does not answer a more fundamental question of interest to students of strategic management, namely, why do CEOs make bad, unethical, or other questionable decisions with the potential to lead their firms to poor performance or firm failure? Part of the answer lies in the method by which CEOs and other individuals make decisions. Ideally, individuals would make rational decisions for important choices such as buying a car or house, or choosing a career or place to live. The process of rational decision making involves problem identification, establishment and weighing of decision criteria, generation and evaluation of alternatives, selection of the best alternative, decision implementation, and decision evaluation.
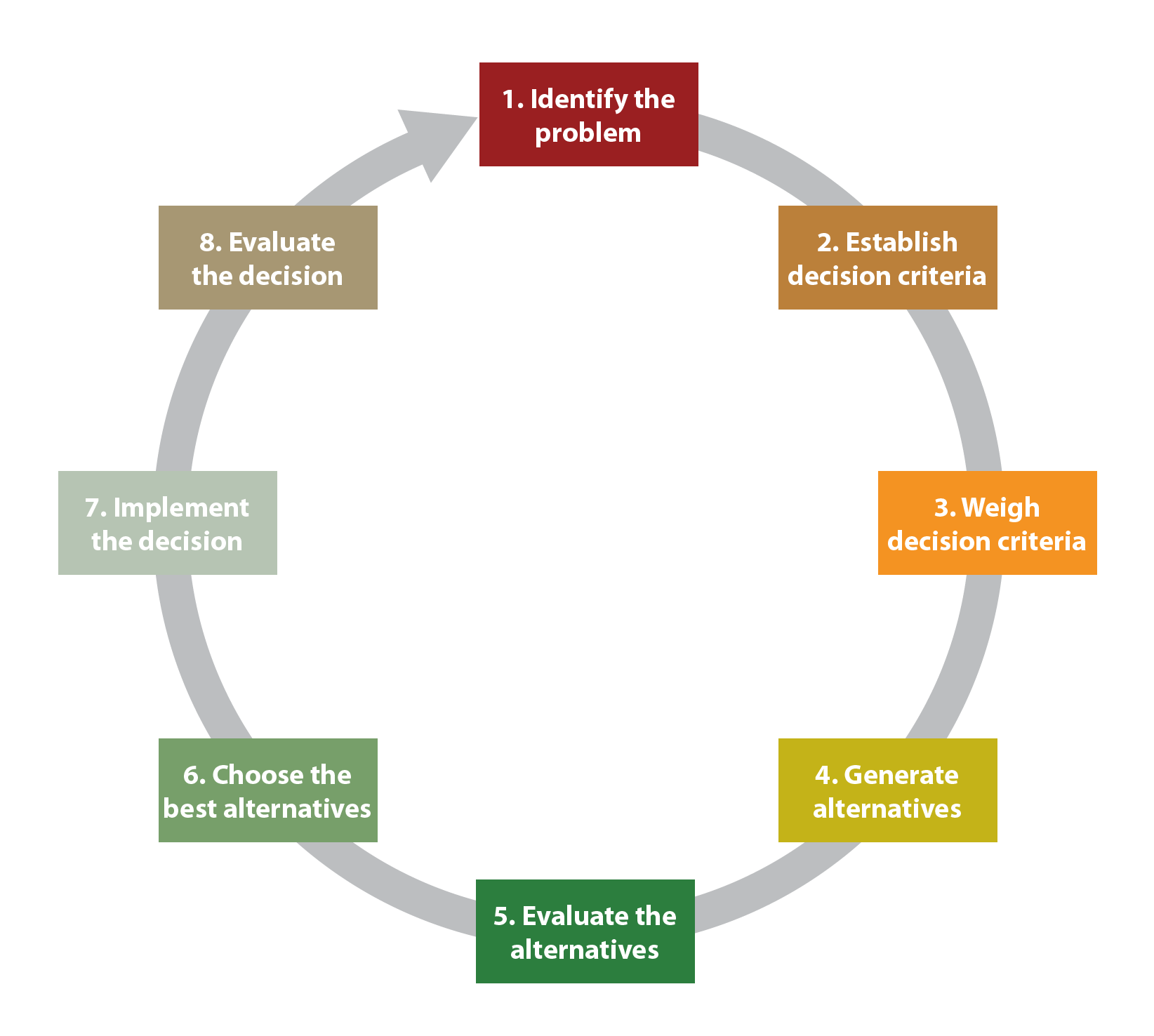
While this model provides valuable insights by providing an ideal approach by which to make decisions, there are several problems with this model when applied to many complex decisions. First, many strategic decisions are not presented in obvious ways, and many CEOs may not be aware their firms are having problems until it’s too late to create a viable solution. Second, rational decision making assumes that options are clear and that a single best solution exists. Third, rational decision making assumes no time or cost constraints. Fourth, rational decision making assumes accurate information is available. Because of these challenges, some have joked that marriage is one of the least rational decisions a person can make because no one can seek out and pursue every possible alternative—even with all the online dating and social networking services in the world.
Decision Biases
In reality, decision making is not rational because there are limits on our ability to collect and process information. Because of these limitations, Nobel Prize–winner Herbert Simon argued that we can learn more by examining scenarios where individuals deviate from the ideal. These decision biases provide clues to why individuals such as CEOs make decisions that in retrospect often seem very illogical—especially when they lead to actions that damage the firm and its performance. A number of the most common biases with the potential to affect business decision making are discussed next.
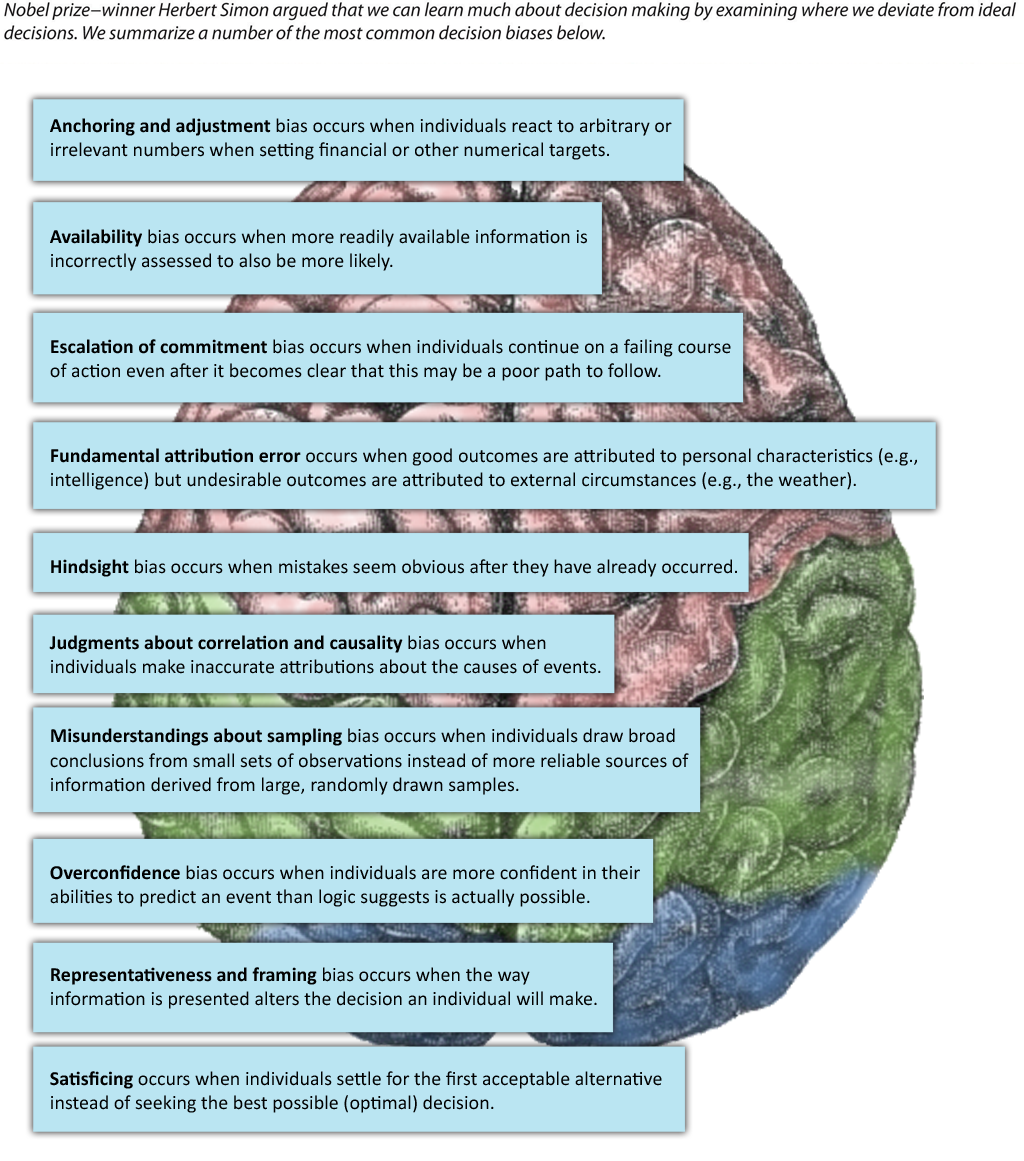
Anchoring and adjustment bias[5] occurs when individuals react to arbitrary or irrelevant numbers when setting financial or other numerical targets. For example, it is tempting for university and college graduates to compare their starting salaries at their first career job to the their wages earned at jobs used to fund school. Comparisons to siblings, friends, parents, and others with different majors are also very tempting while being generally irrelevant. Instead, research the average starting salary for your background, experience, and other relevant characteristics to get a true gauge of your current worth in the job market. At the firm performance level, this bias could undermine performance if executives make decisions about the potential value of a merger or acquisition by making comparisons to previous deals rather than based on a realistic and careful study of a move’s profit potential (Figure 10.14 “Decision Biases”).
The availability bias[6] occurs when more readily available information is incorrectly assessed to also be more likely. For example, research shows that most people think that auto accidents cause more deaths than stomach cancer because auto accidents are reported more in the media than deaths by stomach cancer at a rate of more than 100 to 1. This bias could cause trouble for executives if they focus on readily available information such as their own firm’s performance figures but fail to collect meaningful data on their competitors or industry trends that suggest the need for a potential change in strategic direction.
The idea of “throwing good money after bad” illustrates the bias of escalation of commitment,[7] when individuals continue on a failing course of action even after it becomes clear that this may be a poor path to follow. This can be regularly seen at Vegas casinos when individuals think the next coin is increasingly likely to hit the jackpot at the slots. The concept of escalation of commitment was chronicled in the 1990 book Barbarians at the Gate: The Rise and Fall of RJR Nabisco. The book follows the buyout of RJR Nabisco and the bidding war that took place between then CEO of RJR Nabisco F. Ross Johnson and leverage buyout pioneers Henry Kravis and George Roberts. The result of the bidding war was an extremely high sales price of the company that resulted in significant debt for the new owners.

Fundamental attribution error[8] occurs when good outcomes are attributed to personal characteristics but undesirable outcomes are attributed to external circumstances. Many professors lament a common scenario that, when a student does well on a test, it’s attributed to intelligence. But when a student performs poorly, the result is attributed to an unfair test or lack of adequate teaching based on the professor. In a similar vein, some CEOs are quick to take credit when their firm performs well, but often attribute poor performance to external factors such as the state of the economy.
Hindsight bias[9] occurs when mistakes seem obvious after they have already occurred. This bias is often seen when second-guessing failed plays on the football field and is so closely associated with watching football games on Sunday that the phrase Monday morning quarterback is a part of our business and sports vernacular. The decline of firms such as Kodak as victims to the increasing popularity of digital cameras may seem obvious in retrospect. It is easy to overlook the poor quality of early digital technology and to dismiss any notion that Kodak executives had good reason not to view this new technology as a significant competitive threat when digital cameras were first introduced to the market.
Judgments about correlation and causality[10] can lead to problems when individuals make inaccurate attributions about the causes of events. Three things are necessary to determine cause—or why one element affects another. For example, understanding how marketing spending affects firm performance involves (1) correlation (do sales increase when marketing increases), (2) temporal order (does marketing spending occur before sales increase), and (3) ruling out other potential causes (is something else causing sales to increase: better products, more employees, a recession, a competitor having gone bankrupt, etc.). The first two items can be tracked easily, but the third is almost impossible to fully isolate because there are always so many changing factors. In economics, the expression ceteris paribus (all things being equal or constant) is the basis of many economic models; unfortunately, the only constant in reality is change. Of course, just because determining causality is difficult and often inconclusive does not mean that firms should be slow to take strategic action. As the old business saying goes, “We know we always waste half of our marketing budget, we just don’t know which half.”
Misunderstandings about sampling[11] may occur when individuals draw broad conclusions from small sets of observations instead of more reliable sources of information derived from large, randomly drawn samples. Many CEOs have been known to make major financial decisions based on their own instincts rather than on careful number crunching.
Overconfidence bias[12] occurs when individuals are more confident in their abilities to predict an event than logic suggests is actually possible. For example, two-thirds of lawyers in civil cases believe their side will emerge victorious. But as the famed Yankees player/manager Yogi Berra once noted, “It’s hard to make predictions, especially about the future.” Such overconfidence is common in CEOs that have had success in the past and who often rely on their own intuition rather than on hard data and market research.
Representativeness[13] bias occurs when managers use stereotypes of similar occurrences when making judgments or decisions. In some cases, managers may draw from previous experiences to make good decisions when changes in the environment occur. In other cases, representativeness can lead to discriminatory behaviors that may be both unethical and illegal.
Framing[14] bias occurs when the way information is presented alters the decision an individual makes. Poor framing frequently occurs in companies because employees are often reluctant to bring bad news to CEOs. To avoid an unpleasant message, they might be tempted to frame information in a more positive light than reality, knowing that individuals react differently to news that a glass is half empty versus half full.
Satisficing[15] occurs when individuals settle for the first acceptable alternative instead of seeking the best possible (optimal) decision. While this bias might actually be desirable when others are waiting behind you at a vending machine, research shows that CEOs commonly satisfice with major decisions such as mergers and takeovers.
Key Takeaway
- Generational differences provide powerful influences on the mind-set of employees that should be carefully considered to effectively manage a diverse workforce. Wise managers will also be aware of the numerous decision biases that could impede effective decision making.
Exercises
- Explain how a specific decision bias mentioned in this chapter led to poor decision making by a firm.
- Are there negative generational tendencies in your age group that you have worked to overcome?
References
Burk, B., Olsen, H., & Messerli, E. 2011, May. Navigating the generation gap in the workplace from the perspective of Generation Y. Parks & Recreation, 35–36.
Employment and Social Development Canada. (2014). Indicators of Well-being in Canada. Retrieved from http://www4.hrsdc.gc.ca/.3ndic.1t.4r@-eng.jsp?iid=13
Fogg, P. 2008, July 18. When generations collide: Colleges try to prevent age-old culture clashes as four distinct groups meet in the workplace. Education Digest, 25–30.
Rathman, V. 2011. Four generations at work. Oil & Gas, 109, 10.
- Traditionalists: The generation born between 1925 and 1946 that fought in World War II and lived through the Great Depression. ↵
- Baby boomers: The generation born between 1946 and 1964, corresponding with a population “boom” following the end of World War II. ↵
- Generation X: The generation born between 1965 and 1980; the X symbolizes the unknown nature of this generation. ↵
- Generation Y: The generation following Generation X; this group is also known as millennials as well as “The Trophy Generation.” ↵
- Anchoring and adjustment bias: Individuals react to arbitrary or irrelevant numbers when setting financial or other numerical targets. ↵
- Availability bias: Readily available information is incorrectly assessed to also be more likely. ↵
- Bias of escalation of commitment: To continue on a failing course of action even after it becomes clear that this may be a poor path to follow. ↵
- Fundamental attribution error: When good outcomes are attributed to personal characteristics (e.g., intelligence), but undesirable outcomes are attributed to external circumstances (e.g., the weather). ↵
- Hindsight bias: Mistakes seem obvious after they have already occurred. ↵
- Judgments about correlation and causality: To make inaccurate attributions about the causes of events. ↵
- Misunderstandings about sampling: To draw broad conclusions from small sets of observations instead of more reliable sources of information derived from large, randomly drawn samples. ↵
- Overconfidence bias: To be more confident in your abilities to predict an event than logic suggests is actually possible. ↵
- Representativeness: Use of stereotypes of similar occurrences when making judgments or decisions. ↵
- Framing bias: The way information is presented alters the decision an individual makes. ↵
- Satisficing: To settle for the first acceptable alternative instead of seeking the best possible (optimal) decision. ↵

