21 Your Presentation Style
Learning Objectives
Upon completing this chapter, you should be able to
- recognize the value of self-awareness in the delivery of effective presentations,
- describe the function of active listening and feedback in verbal communication,
- describe verbal techniques used to support professional presentations, and
- describe non-verbal techniques used to support professional presentations.
This chapter is all about getting to know yourself as a presenter. Many people have very limiting beliefs about presentations and their own abilities to give one. Examining your skills, fears, and preferences is your first step in opening yourself up to reaching your full potential as a presenter.
We begin this “self”-focused chapter by considering what you think makes a successful speech or presentation. Here we look at who you might consider to be great and/or successful speakers while examining the role of the audience in making a good speech happen.
From there we delve more deeply into the dimensions of self such as self-awareness around your values, perceptions, and presentation strengths and weaknesses.
Your voice is a powerful communication tool, and how you use it can make or break your presentation. You will learn about how you use verbal elements of presentation by examining techniques like pitch, volume, and pronunciation among others.
Your non-verbal cues like gestures, facial expressions, and posture can punctuate and strengthen your message or do the opposite. You will learn about these non-verbal elements and have a chance to see how you use them in conjunction with your verbal cues by recording and examining a pre-selected speech or presentation.
After combining all of these elements, you will have a better understanding of who you are as a presenter and what you can bring to the table to develop your presentation strategy in the next chapter.
What Makes a Successful Speech or Presentation?
When considering what makes a successful speech or presentation, it’s worth thinking about the speeches or presentations you’ve heard that resonated with you. (If you’re still scratching your head at this point, you can do a search in YouTube or check out some talks on ted.com.) What do you remember about it? How did it make you feel? Did you learn anything? Where were you when you heard it? How did other people around you (if there were any) react?
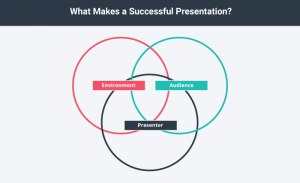
It’s important to remember that a successful speech or presentation depends on a number of factors. For our purposes we can boil them down to three main factors: the environment, the presenter, and the audience. Speeches and presentations usually take place in controlled environments, so this is often overlooked. But everything from a natural disaster to technology failure to a room being too hot or too cold can thwart a presentation’s success. The environment affects both the speaker and the audience. You can’t have a successful speech or presentation without a presenter or speaker, and you also can’t have it without an audience.
Figure 3.1.1 What Makes a Successful Pres
Figure 3.1.1 What Makes a Successful Presentation by Laura Underwood
A successful speech occurs when the speaker and the audience connect in a benign environment. In order to facilitate this, it helps to look at some things that typically make a successful speaker as well as the role of the audience in making a speech or presentation great.
What Makes a Successful Speaker?
According to longtime Toastmasters member Bob Kienzle, there are a few key elements that tend to make a successful speaker:
-
Voice—Can the person be easily understood?
-
Body Language—Does their body support what they’re saying? Are they confident?
-
Coherent Structure—Does what they’re presenting make sense? Is it logical?
-
Enthusiasm—Do they care about what they’re presenting?
-
Expertise—Do they know what they’re talking about? Are they credible?
-
Practice—If they haven’t practiced or sufficiently prepared, it will likely show up in one or more of the above.
A successful speaker can be inspired by other speeches or speakers but may fall flat if they try to copy someone else. Authenticity and passion can resonate so much with an audience that it can outweigh elements otherwise considered pitfalls. The techniques, tools, and best practices are a guideline, and it’s important to note there is no such thing as “perfection” in public speaking. “Failure” can happen in myriad ways, but it’s more helpful to see them as learning opportunities, or opportunities to make a stronger connection to your audience.
The biggest failure, according to Kienzle, is to pass up opportunities to practise your skills in presenting or public speaking.
Audience Role
One of the most anxiety-inducing areas of presenting or speech-making is being in front of the audience. Some people may feel more at ease with relatively small audiences of up to about 10 people. Others feel like 10 people is too “intimate” and actually feel more comfortable with the “impersonal” numbers in the hundreds or thousands.
People often think of hostile audiences throwing tomatoes and yelling boos if the presenter makes the slightest mistake or slip of the tongue. But the truth is most audiences desperately want you to succeed. They are overwhelmingly on your side. This means in most situations they are very forgiving; they know being up there can be tough. If you make a mistake, you can apologize or laugh it off and keep going.
The audience is at least as involved in your presentation as you are. Awareness of yourself and awareness of them is key. If you are so preoccupied with your fear of the audience that you bury your head in the podium while reading a boring list of facts your audience could read themselves, you will lose them. If you’re not interested, they’re not interested. If you are so frightened of your audience that you never look at them, you will not be able to get cues about their involvement in your presentation.
What you bring to the audience affects what they get from your presentation or speech. For that reason, it is tremendously important to develop enough self awareness so that you can be present for your audience and have the confidence to make adjustments to keep them on your side and involved in your presentation.
Self-Awareness
The connection between self-awareness and being a good presenter may not be immediately obvious. But a good presenter usually has a very good idea not just of the audience and the environment but also about themselves, their motivation, values, perception, and other elements. Without delving into a full-on psychological profile, taking some time getting to know more about you and what makes you tick is still extremely useful in the pre-strategizing stage of planning for your presentation. Oftentimes these things lie below the surface of our awareness. Imagine, for example, seeing only the tip of the iceberg, not knowing the even greater mass of ice that lies beneath the water’s surface.
We already know that your success as a presenter depends on the three factors of the presenter, the audience, and the environment. Doing a bit of self-analysis as a presenter, then, is just as important as doing an audience analysis or examining the environment. In order to become more self-aware, it’s important to first ponder a few concepts that may or may not be new to you. These include self concept, self-reflection, internal monologue, and dimensions of self. Later we’ll examine importance of knowing about your values and perceptions, active listening, as well as strengths and weaknesses.
Your self-concept is “what we perceive ourselves to be” (McLean, 2005) and involves aspects of image and esteem. How you feel about yourself influences how you communicate with others. What you are thinking now and the way you communicate influences how others treat you. For example, if you perceive yourself to be a horrible presenter, your behaviour will likely follow your thoughts. Your audience then encounters several cringeworthy moments mirroring your feelings of discomfort, and they wish you’d get off the stage as quickly as possible too! On the flipside, if you feel nervous about presenting but confident that you know your topic so well, you let your passion and expertise shine through, and your audience focuses on that and isn’t fazed by your sweaty palms or your occasional mispronunciations.
Self-reflection can be a useful tool in helping to improve or support your self-concept. Self-reflection is a trait that allows you to adapt and change to the context or environment, to accept or reject messages, to examine your concept of yourself, and to improve.
Your internal monologue is your mental self-talk. It can be a running monologue in your mind that is rational and reasonable, or disorganized and illogical. It can interfere with listening to others, impede your ability to focus, and become a barrier to effective communication. Self-reflection can be a useful tool here as well, allowing you to distinguish whether what you’re saying to yourself is constructive and honest or destructive and false.
Who are you? What are your dimensions of self? You are more than your actions and more than your communication, and the result may be greater than the sum of the parts, but how do you know yourself?
For many, answering these questions can prove challenging while trying to reconcile the self-concept you perceive with what you want others to perceive about you. Is it even possible to see yourself through interactions with others, and can you come to terms with the idea that we may not know everything there is to know about ourselves?
Joseph Luft and Harry Ingram gave considerable thought and attention to these dimensions of self, which are represented in the figure below known as the Johari Window (Luft & Ingram, 1955).
In the first quadrant of the figure, information is known to you and others, such as your height and colour. The second quadrant represents things others observe about us that we are unaware of, such as how many times we say “umm” in the space of five minutes. The third quadrant involves information that you know but do not reveal to others. It may involve actively hiding or withholding information, or may involve social tact, such as thanking your Aunt Martha for the large purple hat she’s given you that you know you will never wear. Finally, the fourth quadrant involves information that is unknown to you and to others, such as, for example, a childhood experience that has been long forgotten or repressed may still motivate you.

Figure 3.1.2 JOHARI Window by Laura Underwood Adapted from Luft & Ingram (1955)
These dimensions of self remind us that we are not fixed—that freedom to change combined with the ability to reflect, anticipate, plan, and predict allows us to improve, learn, and adapt to our surroundings.
In the context of business communication, the self plays a central role. How do you describe yourself? Do your career path, job responsibilities, goals, and aspirations align with your talents? How you represent “self” through your résumé, in your writing, in your articulation and presentation—these all play an important role as you negotiate the relationships and climate present in any organization.
Your Values and Perceptions
Another key element in becoming more self-aware involves understanding your values and perceptions. Your values are defined as “the principles or standards of behaviour; one’s judgement of what is important in life” (OxfordDictionaries.com, 2015). Your values are often so embedded in who you are that you probably don’t think twice about them. You could also be totally unaware of what they are if you take for granted that everyone shares your values. As a speaker it’s important for you to uncover what your values are to avoid glaring blind spots (visible to others but not to you) and know more about who you are.
Our values and life experience can also lead to our perception about ourselves and others. Perception is defined as “the way in which something is regarded, understood, or interpreted.” The problem is that our perception or interpretation of events can go unchallenged, and we can cling to perceptions whether they are accurate or inaccurate.
If you’ve never considered your values or perceptions before, it can be helpful to monitor what issues or concerns cause you to take the following behaviours:
Judging
Judging is defined as forming an opinion or conclusion about something (OxfordDictionaries.com, 2015). If you find yourself jumping to conclusions or nitpicking minor details to condemn someone or something, it may be because the issue or person has challenged your values. Judgement in the best sense of the term leads to useful and ethical decision making; in its negative sense it can lead to bias. Bias is the “inclination or prejudice for or against one person or group, especially in a way considered to be unfair” (OxfordDictionaries.com, 2015).
Anticipating
When you anticipate, you “regard [something] as probable” or “expect or predict [something]” (OxfordDictionaries.com, 2015). Anticipating can be a by-product of judging, when you have already decided what the other person is going to say. You might even start filling in their words for them. The point is, you have stopped listening to the other person. You may be polite in letting them finish, but your mind is already formulating witty comebacks to something they said that challenged your values or perceptions. At its best, anticipating can solidify that people are on the same wavelength, like an old married couple who know each other so well they really can fill in their words meaningfully. On the other end of the spectrum, anticipating leads to shutting down true communication, often followed by a fruitless power struggle over winning an argument that neither party is listening to or learning from.
Emotional Reaction or Response
To have an emotional reaction or response means “Arousing or (being) characterized by intense feeling.” These intense feelings can be a strong indicator that your values or perceptions are being challenged. Emotional reactions can be physiological; your heartbeat quickens, palms get sweaty, you feel your face heating from the neck up. In more severe reactions it can trigger mild or violent responses, anything from walking away to arguing to physical violence. You can also have an emotional reaction that no one else notices; you may even be vocal about how much you don’t care about a particular thing or person. But if you feel emotional discomfort, follow those feelings to examine what values or perceptions may lie below the surface; in this way, you will know yourself better and understand what triggers you.
To sum up, if you find yourself judging, jumping the gun by anticipating, or having a strong emotional response, some element of your deeply held values are likely at play or have been betrayed in some way. This is very important information that can help you understand yourself in terms of what you bring to the stage or podium as a presenter. This knowledge can be used to examine whether or not your perceptions are accurate or false, and lead to approaches to help you improve in areas such as (a) active listening and (b) knowing your strengths and weaknesses—both of which are examined next.
Active Listening
Listening vs. Hearing
Hearing is an accidental and automatic brain response to sound and requires no effort. We are surrounded by sounds most of the time. For example, we are accustomed to the sounds of airplanes, lawn mowers, furnace blowers, the rattling of pots and pans, and so on. We hear those incidental sounds and, unless we have a reason to do otherwise, we train ourselves to ignore them. We learn to filter out sounds that mean little to us, just as we choose to hear our ringing cell phones and other sounds that are more important to us.
| Hearing | Listening |
| Accidental | Focused |
| Involuntary | Voluntary |
| Effortless | Intentional |
Table 3.1.1 Active Listening
Listening, on the other hand, is purposeful and focused rather than accidental. As a result, it requires motivation and effort. Listening, at its best, is active, focused, concentrated attention for the purpose of understanding the meanings expressed by a speaker. We do not always listen at our best, however.
Effective listening is about self-awareness. You must pay attention to whether or not you are only hearing, passively listening, or actively engaging. Effective listening requires concentration and a focused effort that is known as active listening. Active listening can be broken down into three main elements: attention, attitude, and adjustment.
Attention
Hoppe (2006) advises that active listening is really a state of mind requiring us to choose to focus on the moment, being present and attentive while disregarding any of our anxieties of the day.
He suggests listeners prepare themselves for active attention by creating a listening reminder. This might be to write “Listen” at the top of a page in front of you in a meeting.
We know now that attention is the fundamental difference between hearing and listening. Paying attention to what a speaker is saying requires intentional effort on your part.
Nichols (1957), credited with first researching the field of listening, observed, “Listening is hard work. It is characterized by faster heart action, quicker circulation of the blood, a small rise in bodily temperature.”
Consider that we can process information four times faster than a person speaks. Yet, tests of listening comprehension show the average person listening at only 25 percent efficiency. A typical person can speak 125 words-per-minute, yet we can process up to three times faster, reaching as much as 500 words-per-minute. The poor listener grows impatient, while the effective listener uses the extra processing time to process the speaker’s words, distinguish key points, and mentally summarize them (Nichols, 1957).
While reading a book or having a discussion with an individual, you can go back and reread or ask a question to clarify a point. This is not always true when listening. Listening is of the moment, and we often only get to hear the speaker’s words once.
The key, then, is for the listener to quickly ascertain the speaker’s central premise or controlling idea. Once this is done, it becomes easier for the listener to discern what is most important. Of course, distinguishing the speaker’s primary goal, his main points, and the structure of the speech are all easier when the listener is able to listen with an open mind.
Attitude
Even if you are paying attention, you could be doing so with the wrong attitude. Telling yourself this is all a waste of time is not going to help you to listen effectively. You’ll be better off determining an internal motivation to be attentive to the person speaking.
Approaching the task of listening with a positive attitude and an open mind will make the act of listening much easier. As mentioned earlier, bad listeners make snap judgments that justify their decision to be inattentive. Yet, since you’re already there, why not listen to see what you can learn?
Kaponya (1991) warns against such psychological deaf spots, which impair our ability to perceive and understand things counter to our convictions. It can be as little as a word or phrase that might elicit “an emotional eruption,” causing communication efficiency to drop rapidly.
For instance, someone who resolutely supports military action as the best response to a terrorist action may be unable to listen objectively to a speaker endorsing negotiation as a better tool. Even if the speaker is effectively employing logic, drawing on credible sources, and appealing to emotion with a heartrending tale of the civilian casualties caused by bombings, this listener would be unable to keep an open mind. Failing to acknowledge your deaf spots will leave you at a deficit when listening.
You will always need to make up your own mind about where you stand—whether you agree or disagree with the speaker—but it is critical to do so after listening. Adler proposes having four questions in mind while listening: “What is the whole speech about?” “What are the main or pivotal ideas, conclusions, and arguments?” “Are the speaker’s conclusions sound or mistaken?” and “What of it?”
Once you have an overall idea of the speech, determine the key points, and gauge your agreement, you can decide why it matters, how it affects you, or what you might do as a result of what you have heard. Yet, he notes it is “impossible” to answer all these questions at the same time as you are listening. Instead, you have to be ready and willing to pay attention to the speaker’s point of view and changes in direction, patiently waiting to see where she is leading you.
Adjustment
The final element to consider is adjustment. Often when we hear someone speak, we don’t know in advance what the speaker will say. So, we need to be flexible, willing to follow a speaker along what seems like a verbal detour down a rabbit hole, until we are rewarded by the speaker reaching his final destination while his audience marvels at the creative means by which he reached his important point.
If the audience members are more intent on reacting to or anticipating what is said, they will be poor listeners indeed. Having an open attitude, paying attention, and being in the moment of the speech leads to the flexibility required to adjust to the situation.
Your Strengths and Weaknesses
Are you aware of what your strengths and weaknesses are as a presenter? You may have some ideas already. For example, if you are very soft spoken, you may consider that to be a weakness if you’re on stage, especially without a microphone. Soft-spoken people also sometimes keep low-key in other ways; maybe they’re more plain in the way they dress or have less expressive mannerisms. Many people think that to be effective on stage you must be a rip-roaring extrovert. This is not true. No matter who you are, if you are aware of the qualities that make you a unique individual and you spend time getting to know your audience, you can convert any perceived weaknesses into a potential strength. Conversely, if you are so overconfident about your abilities that it shows itself in poor preparation and lack of concern for your audience or environment, your strengths can quite quickly become weaknesses.
Your first step in helping define what makes you you is to look at what you’re good at and what you enjoy doing. At the same time, this helps you distinguish what you’re not so good at and what you don’t enjoy. Make a list as you go through the next sections on your verbal and non-verbal communication techniques to get a reasonable prediction about how to focus your strategy as a presenter.
What Are My Verbal Communication Techniques?
Pitch
Do you have a deep, low voice, or a high-pitched one? We all have a normal speaking pitch where we are most comfortable, but we can move our pitch up or down. Use pitch inflections to make your delivery more interesting and emphatic. If you don’t change pitch at all, your delivery will be monotone, which gets boring for the audience very quickly. Some people pitch their voices up at the end of sentences, making every statement sound like a question—avoid this common but distracting habit.
Volume
Do you speak softly or loudly? Adjust the volume of your voice to your environment and audience. If you’re in a large auditorium, speak up so that people in the back row can hear you. But if you’re in a small room with only a few people, you don’t want to alarm them by shouting! You may need to use volume to compensate for ambient noise like traffic or an air conditioner. You can use volume strategically to emphasize the most important points in your speech.
Emphasis
Stress certain words in your speech to add emphasis to them, that is, to indicate that they are particularly important. You may also use a visual aid to emphasize key points by using photographs or charts.
Pronunciation
Make sure that you know the appropriate pronunciation of the words you choose. If you mispronounce a word, it could hurt your credibility or confuse your audience. Websites such as Wiktionary contain audio files that you can play to hear standard pronunciation of many words. Your pronunciation is also influenced by your accent. If your accent is quite different from the accent you expect most members of your audience to have, practise your speech in front of someone with the same accent that your audience members will have, to ensure you are pronouncing words in a clear, understandable way.
Fillers
Avoid the use of “fillers” as placeholders for actual words (like, er, um, uh, etc.). You might get away with saying “um” two or three times in your speech before it becomes distracting, but the same cannot be said of “like”—a particularly troubling filler for many North American speakers. If you have a habit of using fillers, practise your speech thoroughly so that you remember what you want to say. This way, you are less likely to lose your place and let a filler word slip out.
Rate
Are you a fast or slow speaker? The pace that you speak at will influence how well the audience can understand you. Many people speak quickly when they are nervous. If this is a habit of yours, practice will help you here, too. Pause for breath naturally during your speech. Your speaking rate should be appropriate for your topic. A rapid, lively rate communicates enthusiasm, urgency, or humour. A slower, moderated rate conveys respect and seriousness. By varying your rate within a speech, you can emphasize your main points and keep your audience engaged.
What Non-Verbal Cues Do I Use?
Gestures
A gesture is “a movement of part of the body, especially a hand or the head, to express an idea or meaning” (OxfordDictionaries.com, 2015). You can use these to channel nervous energy into an enhancement of your speech, reinforcing important points, but they can be distracting if overused. If the audience is busy watching your hands fly around, they will not be able to concentrate on your words.
Take a look at this article, titled “What to Do with Your Hands When Speaking in Public” (The Washington Post, 2015) for do’s and don’ts of gesturing when you are speaking.
Facial Expression
You might be unaware of how much your facial expressions say when you are speaking. Facial expression comes so naturally that we are not always in control of the story our face is telling. Rehearse your speech in front of a mirror to see what facial expressions come across. You might find that your face is saying something entirely different about your topic than your words are! Practise using facial expressions consciously. If you are speaking about an upbeat topic, smile! Conversely, if your topic is serious or solemn, avoid facial expressions that are overtly cheerful, because the audience will be confused by the mixed message.
In North American culture, the most important facial expression you can use is eye contact. Briefly catch the eye of audience members as you move through your speech. If you can’t look your audience members in the eye, they may view you as untrustworthy. Remember, though, that eye contact is a culturally sensitive gesture. In some cultures, there are certain accepted behaviours for males looking females in the eye, and vice-versa. You’ll want to avoid holding eye contact for too long with any one person, as too much can be unnerving.
Posture
It’s easy to let your posture slip when you’ve been talking for a while, but try to stay conscious of this and stand up straight. This gives the audience the perception that you are authoritative and take your position seriously. If you are slouching, hunched over, or leaning on something, this gives the impression that you are anxious, lacking in credibility, or not serious about your message. Speakers often assume more casual posture as a presentation continues, but you only get one shot at making a first impression, so make sure you begin with a strong stance.
Silence
Silence is a powerful technique if used well, but it is often overlooked. Perhaps you had a teacher in high school who would stand sternly and silently at the front of the room, expectantly waiting for the chatter to die down. His silence and stance were unnerving, so students soon became quiet, didn’t they? And some of the best comedians use the well-timed pause for a powerful and hilarious—rather than serious—effect. Either way, pauses are useful for emphasis and dramatic effect when you are speaking.
Some speakers are reluctant to pause or use silence because they become uncomfortable with the dead air, but sometimes your audience needs a moment to process information and respond to you.
Movement
You can use your body movements to communicate positively with the audience. Leaning in or moving closer to the audience helps to bridge the space of separation. Moving from one side of the room to the other in a purposeful way that supports your content is a useful way to keep your audience engaged; their eyes will track your movements. Pacing rapidly with no purpose and no support to your message may quickly distract from your message, however. Standing still without movement when you are listening or responding to a question can show interest. However, standing still without any movement for the duration of your presentation could leave the audience bored. Balance is key, as is using your body as an extension of your content that suits the context of the environment and the audience.
Conclusion
This chapter helped you focus on getting to know your presentation style by understanding yourself better. You learned that elements of the environment, the audience, and the presenter had an impact on what makes for a good speech. You examined several issues related to self-awareness, including uncovering your values, understanding your perceptions, and dealing with strengths and weaknesses. Finally, you learned about verbal and non-verbal elements of your own presentation style, including how to work with your body as an extension of your presentation content. You should now be able to take what you have learned from this chapter into the next chapter as a foundation to build your presentation strategy.
Further Reading and Links
- Excerpts about the 10 greatest speeches of all time by women from Marie Claire magazine, UK.
- Talks on Technology, Education and Design from TED.
- Listening Effectively: Barriers to Effective Listening https://courses.candelalearning.com/publicspeaking1xmaster/chapter/chapter-4-barriers-to-effective-listening/
References
aniticipate. 2015. OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved December 17, 2015, from http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/anticipate
bias. 2015. OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved December 17, 2015, from http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/bias
gesture. 2015. OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved December 17, 2015, from http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/gesture
Hoppe, M. H. (2006). Active listening: Improve your ability to listen and lead [ebook]. Greensboro, NC: Center for Creative Leadership.
judging. 2015. OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved December 17, 2015, from http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/judge?q=judging#judge__9
Kaponya, P. J. (1991). The human resource professional: Tactics and strategies for career success. New York: Praeger Publishers.
Luft, J., & Ingram, H. (1955). The Johari Window: A graphic model for interpersonal relations. Los Angeles: University of California Western Training Lab.,Luft, J. (1970). Group processes: An introduction to group dynamics (2nd ed.). Palo Alto, CA: National Press Group.
McLean, S. (2005). The basics of interpersonal communication. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon
Nichols, R. G. (1957). Listening is a 10 part skill. Chicago, IL: Enterprise Publications. Retrieved from http://d1025403.site.myhosting.com/files.listen.org/NicholsTenPartSkill/Mr39Enf4.html
value. 2015. OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved December 17, 2015, from http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/value?q=values#value__4
The Washington Post. “What To Do With Your Hands When Speaking In Public”. 2015. Web. 18 Dec. 2015. Retrieved from https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/on-leadership/wp/2015/11/17/what-to-do-with-your-hands-when-speaking-in-public/
Attribution Statement (Your Presentation Style)
This chapter is a remix containing content from a variety of sources published under a variety of open licenses, including the following:
Chapter Content
-
- Original content contributed by the Olds College OER Development Team, of Olds College to Professional Communications Open Curriculum under a CC-BY 4.0 license
- Content created by Anonymous for Self-Concept and Dimensions of Self; in Communication for Business Success, published at http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/communication-for-business-success/s20-02-self-concept-and-dimensions-of.html under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license
- Listening vs. Hearing in Stand Up, Speak Out: The Practice and Ethics of Public Speaking adapted by The Saylor Foundation, previously shared at http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Stand-Up-Speak-Out-The-Practice-and-Ethics-of-Public-Speaking.pdf under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license
- Content created by Jenn Q. Goddu, for Three A’s of Active Listening from The Public Speaking Project, previously shared at http://publicspeakingproject.org/listening.html under a CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license
- Content adapted from Practicing for Successful Speech Delivery; in Public Speaking: Practice and Ethics, originally created by Anonymous, previously shared at http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/public-speaking-practice-and-ethics/s17-04-practicing-for-successful-spee.html under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license
- Content adapted from Movement and Gesture in Boundless Communication, previously shared at https://www.boundless.com/communications/textbooks/boundless-communications-textbook/delivering-the-speech-12/effective-visual-delivery-65/movement-and-gesture-261-10649/ under a http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
Check Your Understandings
- Original assessment items contributed by the Olds College OER Development Team, of Olds College to Professional Communications Open Curriculum under a CC-BY 4.0 license
- Assessment items in Stand Up, Speak Out – The Practice and Ethics of Public Speaking, Chapter 4 Exercises shared previously at http://www.saylor.org/books under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license