11.7 Sales Promotions
Learning Objectives
- Learn about different types of sales promotions companies use to get customers to buy their products.
- Understand the different types of sales promotions companies use with their business customers.
- Understand why sales promotions have become such an integral part of an organization’s promotion mix.
- Differentiate between push and pull strategies.
Sales promotions are activities that supplement a company’s advertising, public relations, and professional selling efforts. They create incentives for customers to buy products more quickly and make larger purchases. Sales promotions are often temporary, but when the economy is weak, sales promotions become even more popular for consumers and are used more frequently by organizations.
Consumer Sales Promotions
Samples, coupons, premiums, contests, and rebates are examples of consumer sales promotions. Do you like free samples? Most people do. A free sample allows consumers to try a small amount of a product so that hopefully they will purchase it. The strategy encourages trial and builds awareness. You have probably purchased a product that included a small free sample with it—for example, a small amount of conditioner packaged with your shampoo. Have you ever gone to a store that provided free samples of different food items? Although sampling is an expensive strategy, it is usually very effective for food products. People try the product, and the person providing the sample tells them about the product and mentions any special prices for it.
In many retail grocery stores, coupons are given to consumers with the samples. Coupons provide an immediate price reduction off an item. The amount of the coupon is later reimbursed to the retailer by the manufacturer. The retailer gets a handling fee for accepting coupons. When the economy is weak, more consumers cut out coupons and look for special bargains such as double coupons and buy-one-get-one-free (BOGO) coupons. They may also buy more store brands.

“Coupon Pile Stock Pile” by Carol Pyles, CC BY 2.0.
While many consumers cut coupons from the inserts in Sunday newspapers, other consumers find coupons online or on their cell phones. Point-of-purchase displays, including coupon machines placed next to products in stores, encourage consumers to buy a brand or product immediately. When a consumer sees a special display or can get a coupon instantly, manufacturers hope the sales promotion increases sales. Stores may also provide coupons for customers with loyalty cards to encourage them to select particular brands and products.
Mobile marketing and the Internet provide consumers in international markets access to coupons and other promotions. In India, the majority of coupons used are digital, while paper coupons have the largest share in the United States. Over 80 percent of diapers are purchased with coupons; imagine how much easier and less wasteful digital coupons scanned from a mobile phone are for both organizations and consumers.
Other sales promotions may be conducted online and include incentives such as free items, free shipping, coupons, and sweepstakes. For example, many online merchants such as Shoe Station and Zappos offer free shipping and free return shipping to encourage consumers to shop online. Some firms have found that the response they get to their online sales promotions is better than response they get to traditional sales promotions.
Another very popular sales promotion for consumers is a premium. A premium is something you get either for free or for a small shipping and handling charge with your proof of purchase (sales receipt or part of package). Remember wanting your favourite cereal because there was a toy in the box? The toy is an example of a premium. Sometimes you might have to mail in a certain number of proofs of purchase to get a premium. The purpose of a premium is to motivate you to buy a product multiple times. What many people don’t realize is that when they pay the shipping and handling charges, they may also be paying for the premium.
Contests or sweepstakes also attract a lot of people. Contests are sales promotions people enter or participate in to have a chance to win a prize. The Publisher’s Clearing House Sweepstakes and the Monopoly Game at McDonald’s are both examples. The organization that conducts the sweepstakes or contest hopes you will not only enter its contest but buy some magazines (or more food) when you do.
Loyalty programs are sales promotions designed to get repeat business. Loyalty programs include things such as frequent flier programs, hotel programs, and shopping cards for grocery stores, drugstores, and restaurants. Sometimes point systems are used in conjunction with loyalty programs. After you accumulate so many miles or points, an organization might provide you with a special incentive such as a free flight, free hotel room, or free sandwich. Many loyalty programs, especially hotels and airlines, have partners to give consumers more ways to accumulate and use miles and points.
Rebates are popular with both consumers and the manufacturers that provide them. When you get a rebate, you are refunded part (or all) of the purchase price of a product back after completing a form and sending it to the manufacturer with your proof of purchase. The trick is completing the paperwork on time. Although different types of sales promotions work best for different organizations, rebates are very profitable for companies because many consumers forget or wait too long to send in their rebate forms. Consequently, they do not get any money back. Rebates sound great to consumers until they forget to send it back.
Trade Promotions
In business-to-business (B2B) marketing, sales promotions are typically called trade promotions because they are targeted to channel members who conduct business or “trade” with consumers. Trade promotions include trade shows, conventions, event marketing, trade allowances, training, and special incentives given to retailers to market particular products and services, such as extra money, in-store displays, and prizes.
Trade shows are one of the most common types of sales promotions in B2B markets. A trade show is an event in which firms in a particular industry display and demonstrate their offerings to other organizations they hope will buy them. There are typically many different trade shows in which one organization can participate. Using displays, brochures, and other materials, representatives at trade shows can identify potential customers (prospects), inform customers about new and existing products, and show them products and materials. Representatives can also get feedback from prospects about their company’s products and materials and perhaps about competitors.
Companies also gather competitive information at trade shows because they can see the products other firms are exhibiting and how they are selling them. While approximately 75 percent of representatives attending trade shows actually buy the product(s) they see, 93 percent of attendees are influenced by what they see at the trade shows. However, only 20 percent of organizations follow up on leads obtained at trade shows and only 17 percent of buyers are called upon after they express interest in a particular company’s products.[1] Figure 11.11 is an example of a booth display at a trade show showcasing the Korean electronics firm Samsung. Trade shows can be very successful, although the companies that participate in them need to follow-up on the leads generated at the shows. With changing technology, Webinars are being used to reach businesses that may not be able to attend trade shows. Follow-up after a webinar is also essential.

Photo by LGEPR, CC BY 2.0.
Conventions, or meetings, with groups of professionals also provide a way for sellers to show potential customers different products. For example, a medical convention might be a good opportunity to display a new type of medical device. Sales representatives and managers often attend conventions to market their products.
“Da Vinci robot” by Docor Comunicacion, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Sales contests, which are often held by manufacturers or vendors, provide incentives for salespeople to increase their sales. Often, the contests focus on selling higher-profit or slow-moving products. The sales representative with the most sales of the product wins a prize such as a free vacation, company recognition, or cash.
Trade allowances give channel partners—for example, a manufacturer’s wholesalers, distributors, retailers, and so forth—different incentives to push a product. One type of trade allowance is an advertising allowance (money) to advertise a seller’s products in local newspapers. An advertising allowance benefits both the manufacturer and the retailer. Typically, the retailer can get a lower rate than manufacturers on advertising in local outlets, saving the manufacturer money. The retailer benefits by getting an allowance from the manufacturer.
Another sales promotion that manufacturers, such as those in the tool or high tech industries, offer businesses is training to help their salespeople understand how the manufacturers’ products work and how consumers can be enticed to buy them. Many manufacturers also provide in-store product demonstrations to show a channel partner’s customers how products work and answer any questions they might have. Demonstrations of new video game systems and computers are extremely popular and successful in generating sales.
Free merchandise, such as a tool, television, or other product produced by the manufacturer, can also be used to get retailers to sell products to consumers. In other words, a manufacturer of televisions might offer the manager of a retail electronics store a television to push its products. If a certain number of televisions are sold, the manager gets the television. Have you ever been to an electronics store or a furniture store and felt like the salesperson was pushing one particular television or one particular mattress? Perhaps the salesperson was getting push money, or a cash incentive from the manufacturer to push a particular item. The push to sell the item might be because there is a large amount of inventory of it, it is being replaced by a new model, or the product is not selling well. Table 11.1 “Examples of Sales Promotions” recaps the different types of sales promotions designed for both consumers and businesses.
| Consumer Sales Promotions | Business-to-Business Sales Promotions |
|---|---|
| Coupons | Trade shows and conventions |
| Sweepstakes or contests | Sales contests |
| Premiums | Trade and advertising allowances |
| Rebates | Product demonstrations |
| Samples | Training |
| Loyalty programs | Free merchandise |
| Point-of-purchase displays | Push money |
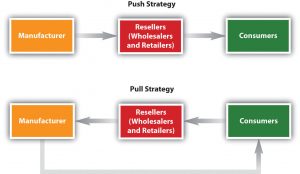
Push versus Pull Strategy
Businesses must also decide whether to use a push strategy, a pull strategy, or both push and pull strategies. A push strategy involves promoting a product to businesses (middlemen), such as wholesalers and retailers, who then push the product through the channel promoting it to final consumers. Manufacturers may set up displays in retail outlets for new products or provide incentives such as price discounts to the retailer so the retailer can promote or push the product to consumers.
Companies use a pull strategy when they target final consumers with promotions. In other words, a company promotes it products and services to final consumers to pull consumers into the stores or get the consumers asking for the product. If a company sends coupons to the consumers, hopefully the consumers will take the coupons (sales promotion) to the store and buy the product. A manufacturer promotes its new product on television to consumers and places coupons in the newspaper inserts, hoping consumers will demand the product. Their pull causes wholesalers and retailers to buy the product to try to meet the demand.
Many manufacturers use both a push strategy and a pull strategy, promoting their products and services to both final consumers and their trade partners (e.g., retailers and wholesalers). Figure 11.13 “A Push versus a Pull Strategy” shows how push strategy differs from a pull strategy.
Let’s go and hunt for some sales promotion examples … both for consumers and for businesses!
Key Takeaways
Companies use sales promotions to get customers to take action (make purchases) quickly. Sales promotions increase the awareness of products, help introduce new products, and often create interest in the organizations that run the promotions. Coupons, contests, samples, and premiums are among the types of sales promotions aimed at consumers. Trade promotions, or promotions aimed at businesses, include trade shows, sales contests, trade allowances, and push money.
Review Questions
- What are the objectives of sales promotions?
- What is a trade promotion?
- Identify and provide an example of three sales promotion tools targeted at consumers.
- Identify and provide an example of three sales promotion tools targeted at businesses.
- Explain the difference between a push strategy and a pull strategy.
- Tanner, J. F. Jr., and Dennis Pitta, “Identifying and Creating Customer Value” (special session presentation, Summer Educators’ Conference, Chicago, 2009). ↵

