1.2 Factor Trinomials
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Factor trinomials of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex]
- Factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using trial and error
- Factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using the ‘[latex]ac[/latex]’ method
- Factor using substitution
Try It
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz:
1) Find all the factors of [latex]72[/latex].
2) Find the product: [latex]\left(3y+4\right)\left(2y+5\right)[/latex].
3) Simplify: [latex]-9\left(6\right)[/latex] and [latex]-9\left(-6\right)[/latex].
Factor Trinomials of the Form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex]
You have already learned how to multiply binomials using FOIL. Now you’ll need to “undo” this multiplication. To factor the trinomial means to start with the product, and end with the factors.
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}&{\color{blue}{\overrightarrow{{\color{red}{\textbf{MULTIPLY}}}}}}{}&\\\begin{array}{c}{\color{blue}{\underbrace{{\color{black}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}}}}}\\{\color{blue}{\text{factors}}}\end{array}&&\begin{array}{c}\underbrace{{\color{black}{x^2+5x+6}}}\\{\color{blue}{\text{product}}}\end{array}\\&{\color{blue}{\overleftarrow{{\color{red}{\textbf{FACTOR}}}}}}&\end{array}[/latex]
HOW TO
Factor a Trinomial of the Form [latex]x^2+bx+c[/latex]
To figure out how we would factor a trinomial of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex], such as [latex]{x}^{2}+5x+6[/latex] and factor it to [latex]\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)[/latex], let’s start with two general binomials of the form [latex]\left(x+m\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(x+n\right)[/latex].
| [latex](x+m)(x+n)[/latex] | |
| Foil to find the product. | [latex]x^2+mx+nx+mn[/latex] |
| Factor the GCF from the middle terms. | [latex]x^2+(m+n)x+mn[/latex] |
| Our trinomial is of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex]. | [latex]\overset{\color{Red} x^2\;+\;bx\;+\;c}{\overbrace{x^2+(m+n)x+mn}}[/latex] |
This tells us that to factor a trinomial of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex], we need two factors [latex]\left(x+m\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(x+n\right)[/latex] where the two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] multiply to [latex]c[/latex] and add to [latex]b[/latex].
Example 1.2.1
How to Factor a Trinomial of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex]
Factor: [latex]{x}^{2}+11x+24[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Write the factors as two binomials with first terms [latex]x[/latex].
Write two sets of parentheses and put [latex]x[/latex] as the first term.
[latex](x^2+11x+24)[/latex]
[latex](x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)(x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)[/latex]
Step 2: Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that multiply to [latex]c[/latex], [latex]m\cdot n=c[/latex] and add to [latex]b[/latex], [latex]m+n=b[/latex].
Find two numbers that multiply to [latex]24[/latex] and add to [latex]11[/latex].
| Factors of [latex]24[/latex] | Sum of Factors |
| [latex]1,\;24[/latex] | [latex]1+24=25[/latex] |
| [latex]2,\;12[/latex] | [latex]2+12=14[/latex] |
| [latex]3,\;8[/latex] | [latex]3+8=11^*[/latex] |
| [latex]4,\;6[/latex] | [latex]4+6=10[/latex] |
Step 3: Use [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] as the last terms of the factors.
Use [latex]3[/latex] and [latex]8[/latex] as the last terms of the binomials.
[latex](x+3)(x+8)[/latex]
Step 4: Check by multiplying the factors.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(x+3)(x+8)\\&=&x^2+8x+3x+24\\&=&x^2+11x+24\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
4) Factor: [latex]{q}^{2}+10q+24[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(q+4\right)\left(q+6\right)[/latex]
Try It
5) Factor: [latex]{t}^{2}+14t+24[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(t+2\right)\left(t+12\right)[/latex]
Let’s summarize the steps we used to find the factors.
HOW TO
Factor trinomials of the form [latex]x^2+bx+c[/latex].
- Write the factors as two binomials with first terms [latex]x[/latex]. [latex]\begin{array}{c}x^2+bx+c\hfill \\ (x\;\;\;\;\;)(x\;\;\;\;\;)\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
- Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that
- multiply to [latex]c,\;m\cdot n=c[/latex]
- add to [latex]b,\;m+n=b[/latex]
- Use [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] as the last terms of the factors. [latex](x+m)(x+n)[/latex]
- Check by multiplying the factors.
In the first example, all terms in the trinomial were positive. What happens when there are negative terms? Well, it depends which term is negative. Let’s look first at trinomials with only the middle term negative.
How do you get a positive product and a negative sum? We use two negative numbers.
Example 1.2.2
Again, with the positive last term, [latex]28[/latex], and the negative middle term, [latex]-11y[/latex], we need two negative factors. Find two numbers that multiply [latex]28[/latex] and add to [latex]-11[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Write the factors as two binomials with first terms [latex]y[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{c}y^2-11y+28\\(y\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)(y\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)\end{array}[/latex]
Step 2: Find two numbers that multiply to [latex]28[/latex] and add to [latex]-11[/latex].
| Factors of [latex]28[/latex] | Sum of factors |
|---|---|
| [latex]-1,\;-28[/latex] [latex]-2,\;-14[/latex] [latex]-4,\;-7[/latex] |
[latex]-1+\left(-28\right)=-29[/latex] [latex]-2+\left(-14\right)=-16[/latex] [latex]-4+\left(-7\right)={-11}^{*}[/latex] |
Step 3: Use [latex]-4,\;-7[/latex] as the last terms of the binomials.
[latex](y-4)(y-7)[/latex]
Step 4: Check.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(y-4)(y-7)\\&=&y^2-7y-4y+28\\&=&y^2-11y+28\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
6) Factor: [latex]{u}^{2}-9u+18[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(u-3\right)\left(u-6\right)[/latex]
Try It
7) Factor: [latex]{y}^{2}-16y+63[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(y-7\right)\left(y-9\right)[/latex]
Now, what if the last term in the trinomial is negative? Think about FOIL. The last term is the product of the last terms in the two binomials. A negative product results from multiplying two numbers with opposite signs. You have to be very careful to choose factors to make sure you get the correct sign for the middle term, too.
How do you get a negative product and a positive sum? We use one positive and one negative number.
When we factor trinomials, we must have the terms written in descending order—in order from highest degree to lowest degree.
Example 1.2.3
Factor: [latex]2x+x^2-48[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: First we put the terms in decreasing order.
[latex]{x}^{2}+2x-48[/latex]
Step 2: Factors will be two binomials with first terms [latex]x[/latex].
[latex](x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)(x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;)[/latex]
| Factors of [latex]-48[/latex] | Sum of factors |
|---|---|
| [latex]-1,\;48[/latex] [latex]-2,\;24[/latex] [latex]-3,\;16[/latex] [latex]-4,\;12[/latex] [latex]-6,\;8[/latex] |
[latex]-1+48=47[/latex] [latex]-2+24=22[/latex] [latex]-3+16=13[/latex] [latex]-4+12=8[/latex] [latex]-6+8={2}^{*}[/latex] |
Step 3: Use [latex]-6,\;-8[/latex] as the last terms of the binomials.
[latex](x-6)(x+8)[/latex]
Step 4: Check.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(x-6)(x+8)\\&=&x^2-6x+8x-48\\&=&x^2+2x-48\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
8) Factor: [latex]9m+{m}^{2}+18[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(m+3\right)\left(m+6\right)[/latex]
Try It
9) Factor: [latex]-7n+12+{n}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(n-3\right)\left(n-4\right)[/latex]
Sometimes you’ll need to factor trinomials of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bxy+c{y}^{2}[/latex] with two variables, such as [latex]{x}^{2}+12xy+36{y}^{2}[/latex]. The first term, [latex]{x}^{2}[/latex], is the product of the first terms of the binomial factors, [latex]x\cdot x[/latex]. The [latex]{y}^{2}[/latex] in the last term means that the second terms of the binomial factors must each contain [latex]y[/latex]. To get the coefficients [latex]b[/latex] and [latex]c[/latex], you use the same process summarized in How To Factor trinomials.
Example 1.2.4
We need [latex]r[/latex] in the first term of each binomial and [latex]s[/latex] in the second term. The last term of the trinomial is negative, so the factors must have opposite signs.
Factor: [latex]{r}^{2}-8rs-9{s}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Note that the first terms are [latex]r[/latex], and last terms contain [latex]s[/latex].
[latex](r\;\;\;\;\;\;s)(r\;\;\;\;\;\;s)[/latex]
Step 2: Find the numbers that multiply to [latex]-9[/latex] and add to [latex]-8[/latex].
| Factors of [latex]-9[/latex] | Sum of factors |
| [latex]1,\;-9[/latex] | [latex]-1+9=8[/latex] |
| [latex]-1,\;9[/latex] | [latex]1+\left(-9\right)=-{8}^{*}[/latex] |
| [latex]3,\;-3[/latex] | [latex]3+\left(-3\right)=0[/latex] |
Step 3: Use [latex]1,\;-9[/latex] as coefficients of the last terms.
[latex](r+s)(r-9s)[/latex]
Step 4: Check.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(r-9s)(r+s)\\&=&r^2+rs-9rs-9s^2\\&=&r^2-8rs-9s^2\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
10) Factor: [latex]{a}^{2}-11ab+10{b}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(a-b\right)\left(a-10b\right)[/latex]
Try It
11) Factor: [latex]{m}^{2}-13mn+12{n}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(m-n\right)\left(m-12n\right)[/latex]
Some trinomials are prime. The only way to be certain a trinomial is prime is to list all the possibilities and show that none of them work.
Example 1.2.5
We need [latex]u[/latex] in the first term of each binomial and [latex]v[/latex] in the second term. The last term of the trinomial is negative, so the factors must have opposite signs.
Factor: [latex]u^2-9uv-12v^2[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Note that the first terms are [latex]u[/latex], and last terms contain [latex]v[/latex].
[latex](u\;\;\;\;\;\;v)(u\;\;\;\;\;\;v)[/latex]
Step 2: Find the numbers that multiply to [latex]-12[/latex] and add to [latex]-9[/latex].
| Factors of [latex]-12[/latex] | Sum of factors |
|---|---|
| [latex]1,\;-12[/latex] [latex]-1,\;12[/latex] [latex]2,\;-6[/latex] [latex]-2,\;6[/latex] [latex]3,\;-4[/latex] [latex]-3,\;4[/latex] |
[latex]1+\left(-12\right)=-11[/latex] [latex]-1+12=11[/latex] [latex]2+\left(-6\right)=-4[/latex] [latex]-2+6=4[/latex] [latex]3+\left(-4\right)=-1[/latex] [latex]-3+4=1[/latex] |
Step 3: Note there are no factor pairs that give us [latex]-9[/latex] as a sum.
The trinomial is prime.
Try It
12) Factor: [latex]{x}^{2}-7xy-10{y}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
Prime
Try It
13) Factor: [latex]{p}^{2}+15pq+20{q}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
Prime
Let’s summarize the method we just developed to factor trinomials of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex].
Strategy for Factoring Trinomials of the Form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex]
When we factor a trinomial, we look at the signs of its terms first to determine the signs of the binomial factors.
[latex]x^2+bx+c[/latex]
[latex](x+m)(x+n)[/latex]
When [latex]c[/latex] is positive, [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have the same sign.
| [latex]b\text{ positive}[/latex] | [latex]b\text{ negative}[/latex] |
| [latex]m,\;n\text{ positive}[/latex] | [latex]m,\;n\text{ negative}[/latex] |
| [latex]x^2+5x+6[/latex] | [latex]x^2-6x+8[/latex] |
| [latex](x+2)(x+3)[/latex] | [latex](x-4)(x-2)[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{same signs}[/latex] | [latex]\text{same signs}[/latex] |
When [latex]c[/latex] is negative, [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have the opposite sign.
| [latex]x^2+x-12[/latex] | [latex]x^2-2x-15[/latex] |
| [latex](x+4)(x-3)[/latex] | [latex](x-5)(x+3)[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{opposite signs}[/latex] | [latex]\text{opposite signs}[/latex] |
Notice that, in the case when [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have opposite signs, the sign of the one with the larger absolute value matches the sign of [latex]b[/latex].
Factor Trinomials of the form [latex]ax^2+bx+c[/latex] using Trial and Error
Our next step is to factor trinomials whose leading coefficient is not 1, trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex].
Remember to always check for a GCF first! Sometimes, after you factor the GCF, the leading coefficient of the trinomial becomes 1 and you can factor it by the methods we’ve used so far. Let’s do an example to see how this works.
Example 1.2.6
Factor: [latex]4x^3+16x^2-20x[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Is there a greatest common factor?
Yes, [latex]\mathrm{GCF}=4x[/latex]. Factor it.
[latex]4x\left({x}^{2}+4x-5\right)[/latex]
Step 2: Is it a binomial, trinomial, or more than three terms?
It is a trinomial. So “undo FOIL.”
[latex]4x(x\;\;\;\;\;\;)(x\;\;\;\;\;\;)[/latex]
Step 3: Use a table like the one shown to find two numbers that multiply to [latex]-5[/latex] and add to [latex]4[/latex].
| Factors of [latex]-5[/latex] | Sum of factors |
| [latex]-1,\;5[/latex] [latex]1,\;-5[/latex] |
[latex]-1+5={4}^{*}[/latex] [latex]1+\left(-5\right)=-4[/latex] |
Step 4: Check.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&4x(x-1)(x+5)\\&=&4x(x^2+5x-x-5)\\&=&4x(x^2+4x-5)\\&=&4x^3+16x^2-20x\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
14) Factor completely: [latex]5{x}^{3}+15{x}^{2}-20x[/latex].
Solution
[latex]5x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+4\right)[/latex]
Try It
15) Factor completely: [latex]6{y}^{3}+18{y}^{2}-60y[/latex].
Solution
[latex]6y\left(y-2\right)\left(y+5\right)[/latex]
What happens when the leading coefficient is not 1 and there is no GCF? There are several methods that can be used to factor these trinomials. First we will use the Trial and Error method.
Let’s factor the trinomial [latex]3{x}^{2}+5x+2[/latex].
From our earlier work, we expect this will factor into two binomials.
We know the first terms of the binomial factors will multiply to give us [latex]3{x}^{2}[/latex]. The only factors of [latex]3{x}^{2}[/latex] are [latex]1x,\;3x[/latex]. We can place them in the binomials.
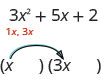
Check: Does [latex]1x\cdot 3x=3{x}^{2}[/latex]?
We know the last terms of the binomials will multiply to [latex]2[/latex]. Since this trinomial has all positive terms, we only need to consider positive factors. The only factors of [latex]2[/latex] are [latex]1,\;2[/latex]. But we now have two cases to consider as it will make a difference if we write [latex]1,\;2[/latex] or [latex]2,\;1[/latex].

Which factors are correct? To decide that, we multiply the inner and outer terms.
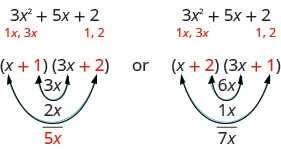
Since the middle term of the trinomial is [latex]5x[/latex], the factors in the first case will work. Let’s use FOIL to check.
Our result of the factoring is:
Example 1.2.7
How to Factor a Trinomial Using Trial and Error
Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]3{y}^{2}+22y+7[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Write the trinomial in descending order.
The trinomial is already in descending order.
[latex]3y^2+22y+7[/latex]
Step 2: Factor any GCF.
There is no GCF.
Step 3: Find all the factor pairs of the first term.
The only of [latex]3y^2[/latex] are [latex]1y,\;3y[/latex].
[latex]\underset{\color{Red} 1y,\;3y}{3y^2}+22y+7[/latex]
Since there is only one pair, we can put them in the parentheses.
[latex](y\;\;\;\;\;\;)(3y\;\;\;\;\;)[/latex]
Step 4: Find all the factor pairs of the third term.
The only factors of 7 are [latex]1,\;7[/latex].
[latex]\underset{\color{Red} 1y,\;3y}{3y^2}+22y+\underset{\color{Red} 1,\;7}{7}[/latex]
[latex](y\;\;\;\;\;\;)(3y\;\;\;\;\;)[/latex]
Step 5: Test all the possible combinations of the factors until the correct product is found.
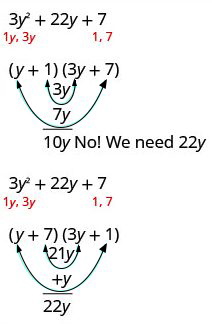
| [latex]3y^2+22y+7[/latex] | |
| Possible Factors | Product |
| [latex](y+1)(3y+7)[/latex] | [latex]3y^2+10y+7[/latex] |
| [latex](y+7)(3y+1)[/latex] | [latex]3y^2+22y+7[/latex] |
Step 6: Check by multiplying.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(y+7)(3y+1)\\&=&3y^2+22y+7\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
16) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]2{a}^{2}+5a+3[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(a+1\right)\left(2a+3\right)[/latex]
Try It
17) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]4{b}^{2}+5b+1[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(b+1\right)\left(4b+1\right)[/latex]
HOW TO
Factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using trial and error.
- Write the trinomial in descending order of degrees as needed.
- Factor any GCF.
- Find all the factor pairs of the first term.
- Find all the factor pairs of the third term.
- Test all the possible combinations of the factors until the correct product is found.
- Check by multiplying.
Remember, when the middle term is negative and the last term is positive, the signs in the binomials must both be negative.
Example 1.2.8
Solution
Step 1: The trinomial is already in descending order.
[latex]6b^2-13b+5[/latex]
Step 2: Find the factors of the first term.
[latex]\underset{{\color{red}{1}}{\color{red}{b}}{\color{red}{\cdot}}{\color{red}{6}}{\color{red}{b}}\\{\color{red}{2}}{\color{red}{b}}{\color{red}{\cdot}}{\color{red}{3}}{\color{red}{b}}}{6b^2}\;-\;13b\;+\;5[/latex]
Step 3: Find the factors of the last term.
Consider the signs. Since the last term, 5, is positive its factors must both be positive or both be negative. The coefficient of the middle term is negative, so we use the negative factors.
[latex]\underset{{\color{red}{1}}{\color{red}{b}}{\color{red}{\cdot}}{\color{red}{6}}{\color{red}{b}}\\{\color{red}{2}}{\color{red}{b}}{\color{red}{\cdot}}{\color{red}{3}}{\color{red}{b}}}{6b^2}\;-\;13b\;+\;\underset{{\color{red}{-}}{\color{red}{1}}{\color{red}{,}}{\color{red}{\;}}{\color{red}{-}}{\color{red}{5}}}5[/latex]
Step 4: Consider all the combinations of factors.
| [latex]6{b}^{2}-13b+5[/latex] | |
| Possible factors | Product |
|---|---|
| [latex]\left(b-1\right)\left(6b-5\right)[/latex] | [latex]6{b}^{2}-11b+5[/latex] |
| [latex]\left(b-5\right)\left(6b-1\right)[/latex] | [latex]6{b}^{2}-31b+5[/latex] |
| [latex]\left(2b-1\right)\left(3b-5\right)[/latex] | [latex]6{b}^{2}-13b+{5}^{*}[/latex] |
| [latex]\left(2b-5\right)\left(3b-1\right)[/latex] | [latex]6{b}^{2}-17b+5[/latex] |
The correct factors are those whose product is the original trinomial.
[latex](2b-1)(3b-5)[/latex]
Step 6: Check by multiplying.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(2b-1)(3b-5)\\&=&6b^2-10b-3b+5\\&=&6b^2-13b+5\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
18) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]8{x}^{2}-13x+3[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(2x-3\right)\left(4x-1\right)[/latex]
Try It
19) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]10{y}^{2}-37y+7[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(2y-7\right)\left(5y-1\right)[/latex]
When we factor an expression, we always look for a greatest common factor first. If the expression does not have a greatest common factor, there cannot be one in its factors either. This may help us eliminate some of the possible factor combinations.
Example 1.2.9
Factor: [latex]18x^2-37xy+15y^2[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: The trinomial is already in descending order.
[latex]18x^2-37xy+15y^2[/latex]
Step 2: Find the factors of the first term.
[latex]\underset{\color{red}{\begin{array}{c}1x\cdot18x\\2x\cdot9x\\3x\cdot6x\end{array}}}{18x^2}-37xy+15y^2[/latex]
Step 3: Find the factors of the last term.
Consider the signs. Since 15 is positive and the coefficient of the middle term is negative, we use the negative factors.
[latex]\underset{\color{red}{\begin{array}{c}1x\cdot18x\\2x\cdot9x\\3x\cdot6x\end{array}}}{18x^2}-37xy+\underset{\color{red}{\begin{array}{c}-1,\;-15\\-3,\;-5\end{array}}}{15y^2}[/latex]
Step 4: Consider all the combinations of factors.
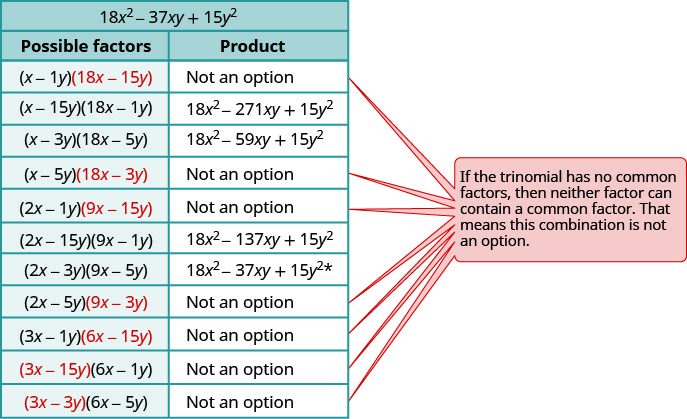
The correct factors are those whose product is the original trinomial.
[latex](2x-3y)(9x-5y)[/latex]
Step 6: Check by multiplying.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(2x-3y)(9x-5y)\\&=&18x^2-10xy-27xy+15y^2\\&=&18x^2-37xy+15y^2\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
20) Factor completely using trial and error [latex]18{x}^{2}-3xy-10{y}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(3x+2y\right)\left(6x-5y\right)[/latex]
Try It
21) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]30{x}^{2}-53xy-21{y}^{2}[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(3x+y\right)\left(10x-21y\right)[/latex]
Don’t forget to look for a GCF first and remember if the leading coefficient is negative, so is the GCF.
Example 1.2.10
Factor: [latex]-10y^4-55y^3-60y^2[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Notice the greatest common factor, so factor it first.
[latex]-5y^2\left(2y^2+11y+12\right)[/latex]
Step 2: Factor the trinomial.
[latex]-5y^2(\underset{\color{red}{y\cdot2y}}{2y^2}+11y+\underset{\color{Red}{\begin{array}{c}1\cdot12\\2\cdot6\\3\cdot4\end{array}}}{12})[/latex]
Step 3: Consider all the combinations.
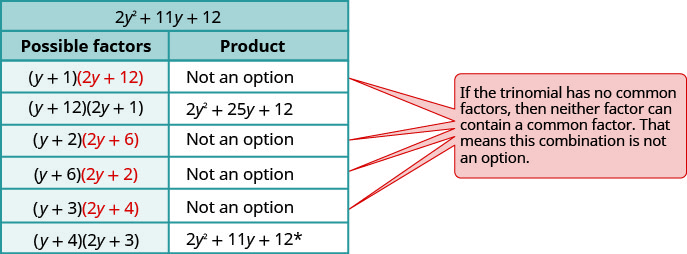
The correct factors are those whose product is the original trinomial. Remember to include the factor [latex]-5y^2[/latex].
[latex]-5y^2(y+4)(2y+3)[/latex]
Step 4: Check by multiplying.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&-5y^2(y+4)(2y+3)\\&=&-5y^2(2y^2+8y+3y+12)\\&=&-10y^4-55y^3-60y^2\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
22) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]15{n}^{3}-85{n}^{2}+100n[/latex].
Solution
[latex]5n\left(n-4\right)\left(3n-5\right)[/latex]
Try It
23) Factor completely using trial and error: [latex]56{q}^{3}+320{q}^{2}-96q[/latex].
Solution
[latex]8q\left(q+6\right)\left(7q-2\right)[/latex]
Factor Trinomials of the Form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using the “ac” Method
Another way to factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] is the “ac” method. (The “[latex]ac[/latex]” method is sometimes called the grouping method.) The “[latex]ac[/latex]” method is actually an extension of the methods you used in the last section to factor trinomials with leading coefficient one. This method is very structured (that is step-by-step), and it always works!
Example 1.2.11
How to Factor Trinomials using the “[latex]ac[/latex]” Method
Factor using the '[latex]ac[/latex]' method: [latex]6{x}^{2}+7x+2[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Factor any GCF.
Is there a greatest common factor? No!
[latex]6x^2+7x+2[/latex]
Step 2: Find the product [latex]ac[/latex].
[latex]a\cdot c[/latex]
[latex]6\cdot2[/latex]
[latex]12[/latex]
[latex]\overset{\color{Red} ax^2\;+\;bx\;+\;c}{6x^2+7x+2}[/latex]
Step 3: Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that:
Multiply to [latex]ac[/latex]. [latex]m\cdot n=a\cdot c[/latex]
Add to [latex]b[/latex]. [latex]m+n=b[/latex]
Find two numbers that multiply to 12 and add to 7. Both factors must be positive.
| [latex]3\cdot4=12[/latex] | [latex]3+4=7[/latex] |
Step 4: Split the middle term using [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex].
[latex]ax^2+bx+c[/latex]
[latex]ax^2+\overset{bx}{\overbrace{mx+nx}}+c[/latex]
Rewrite [latex]7x[/latex] as [latex]3x+4x[/latex]. It would also give the same result if we used [latex]4x+3x[/latex].
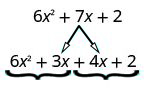
Notice that [latex]6x^2+3x+4x+2[/latex] is equal to [latex]6x^2+7x+2[/latex]. We just split the middle term to get a more useful form.
Step 5: Factor by grouping.
[latex]3x(2x+1)+2(2x+1)[/latex]
[latex](2x+1)(3x+2)[/latex]
Step 6: Check by multiplying the factors.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(2x+1)(3x+2)\\&=&6x^2+4x+3x+2\\&=&6x^2+7x+2\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
24) Factor using the ‘[latex]ac[/latex]’ method: [latex]6{x}^{2}+13x+2[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(x+2\right)\left(6x+1\right)[/latex]
Try It
25) Factor using the ‘[latex]ac[/latex]’ method: [latex]4{y}^{2}+8y+3[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(2y+1\right)\left(2y+3\right)[/latex]
HOW TO
Factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using the “[latex]ac[/latex]” method.
The “[latex]ac[/latex]” method is summarized here.
- Factor any GCF.
- Find the product [latex]ac[/latex].
- Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that:
[latex]\begin{array}{cccccc}\text{Multiply to }ac\hfill & & & & & m\cdot n=a\cdot c\hfill \\ \text{Add to }b\hfill & & & & & m+n=b\hfill \\ & & & & & a{x}^{2}+bx+c\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
- Split the middle term using [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex]. [latex]a{x}^{2}+mx+nx+c[/latex]
- Factor by grouping.
- Check by multiplying the factors.
Don’t forget to look for a common factor!
Example 1.2.12
Factor: [latex]10y^2-55y+70[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Is there a greatest common factor?
Yes. The GCF is [latex]5[/latex].
Step 2: Factor it.
[latex]5(2y^2-11y+14)[/latex]
The trinomial inside the parentheses has a leading coefficient that is not [latex]1[/latex].
[latex]5(\overset{\color{Red} ax^2\;+\;bx\;+\;c}{2y^2-11y+14})[/latex]
Step 3: Find the product [latex]ac[/latex].
[latex]ac=28[/latex]
Step 4: Find two numbers that multiply to [latex]ac[/latex] and add to [latex]b[/latex].
| [latex](-4)(-7)=28[/latex] | [latex]-4+(-7)=-11[/latex] |
Step 5: Split the middle term.
[latex]5(2y^2-\underbrace{11y}+14)[/latex]
[latex]5(\underbrace{2y^2-7y}-\underbrace{4y+14})[/latex]
Step 6: Factor the trinomial by grouping.
[latex]5(y(2y-7)-2(y-7))[/latex]
Step 7: Check by multiplying all three factors.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&5(y-2)(2y-7)\\&=&5(2y^2-7y-4y+14)\\&=&5(2y^2-11y+14)\\&=&10y^2-55y+70\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
26) Factor using the ‘[latex]ac[/latex]’ method: [latex]16{x}^{2}-32x+12[/latex].
Solution
[latex]4\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)[/latex]
Try It
27) Factor using the ‘[latex]ac[/latex]’ method: [latex]18{w}^{2}-39w+18[/latex].
Solution
[latex]3\left(3w-2\right)\left(2w-3\right)[/latex]
Factor Using Substitution
Sometimes a trinomial does not appear to be in the [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] form. However, we can often make a thoughtful substitution that will allow us to make it fit the [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] form. This is called factoring by substitution. It is standard to use [latex]u[/latex] for the substitution.
In the [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex], the middle term has a variable, [latex]x[/latex], and its square, [latex]{x}^{2}[/latex], is the variable part of the first term. Look for this relationship as you try to find a substitution.
Example 1.2.13
Factor: [latex]x^4-4x^2-5[/latex].
Solution
Step 1: Rewrite the trinomial to prepare for the substitution.
[latex]({\color{Red} x^2})^2-4({\color{Red} x^2})-5[/latex]
Step 2: Let [latex]u=x^2[/latex] and substitute.
[latex]{\color{Red} u}^2-4{\color{Red} u}-5[/latex]
Step 3: Factor the trinomial.
[latex](u+1)(u-5)[/latex]
Step 4: Replace [latex]u[/latex] with [latex]x^2[/latex].
[latex]({\color{Red} x^2}+1)({\color{Red} x^2}-5)[/latex]
Step 5: Check.
[latex]\begin{array}{rcl}&=&(x^2+1)(x^2-5)\\&=&x^4-5x^2+x^2-5\\&=&x^4-4x^2-5\;\checkmark\end{array}[/latex]
Try It
28) Factor by substitution: [latex]{h}^{4}+4{h}^{2}-12[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left({h}^{2}-2\right)\left({h}^{2}+6\right)[/latex]
Try It
29) Factor by substitution: [latex]{y}^{4}-{y}^{2}-20[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left({y}^{2}+4\right)\left({y}^{2}-5\right)[/latex]
Sometimes the expression to be substituted is not a monomial.
Example 1.2.14
Factor: [latex](x-2)^2+7(x-2)+12[/latex].
Solution
The binomial in the middle term, [latex]\left(x-2\right)[/latex] is squared in the first term. If we let [latex]u=x-2[/latex] and substitute, our trinomial will be in [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] form.
Step 1: Rewrite the trinomial to prepare for the substitution.
[latex]{\color{Red} (x-2)}^2+7{\color{Red} (x-2)}+12[/latex]
Step 2: Let [latex]u=x-2[/latex] and substitute.
[latex]{\color{Red} u}^2+7{\color{Red} u}+12[/latex]
Step 3: Factor the trinomial.
[latex](u+3)(u+4)[/latex]
Step 4: Replace [latex]u[/latex] with [latex]x-2[/latex].
[latex]({\color{Red} (x-2)}+3)({\color{Red} (x-2)}+4)[/latex]
Step 5: Simplify inside the parentheses.
[latex](x+1)(x+2)[/latex]
This could also be factored by first multiplying out the [latex](x-2)^2[/latex] and the [latex]7(x-2)[/latex] and then combining like terms and then factoring. Most students prefer the substitution method.
Try It
30) Factor by substitution: [latex]{\left(x-5\right)}^{2}+6\left(x-5\right)+8[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)[/latex]
Try It
31) Factor by substitution: [latex]{\left(y-4\right)}^{2}+8\left(y-4\right)+15[/latex].
Solution
[latex]\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)[/latex]
Access this online resource for additional instruction and practice with factoring.
Key Concepts
- How to factor trinomials of the form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex].
- Write the factors as two binomials with first terms [latex]x[/latex]. [latex]\begin{array}{c}x^2+bx+c\hfill \\ (x\;\;\;\;\;)(x\;\;\;\;\;)\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
- Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that
- multiply to [latex]c,\;m\cdot n=c[/latex]
- add to [latex]b,\;m+n=b[/latex]
- Use [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] as the last terms of the factors. [latex](x+m)(x+n)[/latex]
- Check by multiplying the factors.
- Strategy for Factoring Trinomials of the Form [latex]{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex].
When we factor a trinomial, we look at the signs of its terms first to determine the signs of the binomial factors.
[latex]x^2+bx+c[/latex]
[latex](x+m)(x+n)[/latex]When [latex]c[/latex] is positive, [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have the same sign.
[latex]b\text{ positive}[/latex] [latex]b\text{ negative}[/latex] [latex]m,\;n\text{ positive}[/latex] [latex]m,\;n\text{ negative}[/latex] [latex]x^2+5x+6[/latex] [latex]x^2-6x+8[/latex] [latex](x+2)(x+3)[/latex] [latex](x-4)(x-2)[/latex] [latex]\text{same signs}[/latex] [latex]\text{same signs}[/latex] When [latex]c[/latex] is negative, [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have the opposite sign.
[latex]x^2+x-12[/latex] [latex]x^2-2x-15[/latex] [latex](x+4)(x-3)[/latex] [latex](x-5)(x+3)[/latex] [latex]\text{opposite signs}[/latex] [latex]\text{opposite signs}[/latex] Notice that, in the case when [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] have opposite signs, the sign of the one with the larger absolute value matches the sign of [latex]b[/latex].
- How to factor trinomials of the form [latex]a{x}^{2}+bx+c[/latex] using trial and error.
- Write the trinomial in descending order of degrees as needed.
- Factor any GCF.
- Find all the factor pairs of the first term.
- Find all the factor pairs of the third term.
- Test all the possible combinations of the factors until the correct product is found.
- Check by multiplying.
- How to factor trinomials of the form [latex]ax^2+bx+c[/latex] using the “[latex]ac[/latex]” method.
- Factor any GCF.
- Find the product [latex]ac[/latex].
- Find two numbers [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex] that:
[latex]\begin{array}{cccccc}\text{Multiply to }ac.\hfill & & & & & m\cdot n=a\cdot c\hfill \\ \text{Add to }b.\hfill & & & & & m+n=b\hfill \\ & & & & & a{x}^{2}+bx+c\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
- Split the middle term using [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]n[/latex]. [latex]a{x}^{2}+mx+nx+c[/latex]
- Factor by grouping.
- Check by multiplying the factors.
Self Check
a) After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.
b) After reviewing this checklist, what will you do to become confident for all objectives?

