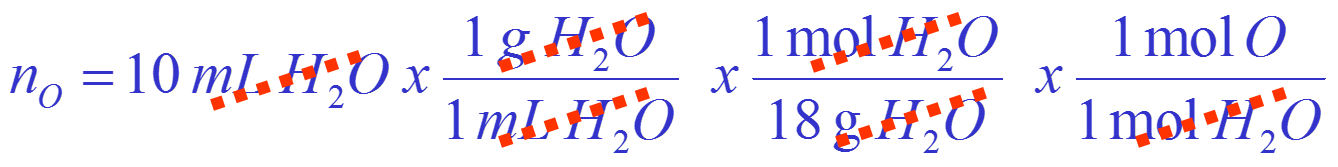4 Summary
Take the Test
Review Module 1 Material
Scientific Measurement
Accuracy: |
How close a measured value is to the accepted or real value. |
Precision: |
The degree of reproducibility of a measured quantity; how close a series of measurements of the same quantity are to one other. |
Volume: |
Volume is a measure of space. It is a unit of length raised to the third power. The SI unit of length is the meter. One meter cubed is equivalent to 1000 L. Litres, which are a convenient unit for scientific measurements, are a more common measurement unit than meters cubed.
|
Density: |
A ratio of mass (m) to volume (V) of a substance.
|
SI Base Units
Click on the following units of measurement to reveal their definition.
Note: Precise definitions of the SI units are not necessary to memorize. Rather, the relationships between the units and how to use them are the important parts to know.
SI Prefixes: Units of Measure for All Sizes
Multipliers that change unit values by multiples of ten.
Presenting Chemical Data
Significant Figures
An accepted method for preserving the precision of a measurement when recording data or doing calculations.
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. |
| Non-zero digits are significant. | Exact numbers are significant. | Contained zeros are significant. | Leading zeros are not significant. |
| 5. | ||
| Trailing zeros have significance as follows: | ||
| a. | b. | c. |
| After a decimal point, significant | After a non-zero number and before a decimal point, significant | After a non-zero number that in not a decimal number, generally a place holder |
For an even more detailed breakdown on significant figures click the link below to view.
Scientific Notation
A notation for expressing large and small numbers as a small decimal between one and ten multiplied by a power of ten.
How to write using scientific notation:
|
1. |
2. |
2a. |
2a. |
| Move the decimal point to the left or right to reach a decimal number between one and ten. | Write the number obtained in step 1 multiplied by 10 raised to the number of places the decimal point was moved. |
If the decimal is moved to the left, the power is positive. Example: |
If the decimal is moved to the right, the power is negative. Example: |
Chemical Problem Solving Strategies
Unit Analysis and Problem Solving
A ‘book-keeping’ method for units in a calculation |
Over all method of “unit analysis”: |
| Indicates errors in a multi-step calculation
Provides the units for the final answer |
1) Write the units with every number you include in a series of calculations 2) String your calculations together as a series of multiplications or divisions before doing any math 3) Cancel your units to see the calculation evolve |
Calculations: Converting from One Unit to Another |
|
Unit analysis: |
Conversion factor: |
|
A method that uses a conversion factor to convert a quantity expressed in one unit to an equivalent quantity in a different unit. |
States the relationship between two different units. |
original quantity x conversion factor = equivalent quantity
For example converting between length units
Given that 1 meter = 39.37 inches
Conversion factors ![]() or
or ![]()
The same relationship, just invert as necessary to give you the units you need!
Problem Solving Examples
How many moles of oxygen atoms are there in a 10 mL volume of water?
What is being asked? |
What data is provided? |
What do I need to know? |
How do I need to state the answer? |
| Given a volume can you calculate a number of atoms? | Data: 10 mL of water | Need to know: water is |
Answer in moles of oxygen O |
Convert volume of water to moles of oxygen:
Calculation is: Volume of ![]() mass of
mass of ![]() mols of
mols of ![]() mols of
mols of ![]()
= There are 0.55 moles of oxygen atoms.
Always Check Units!