Syringe and Needle Selection
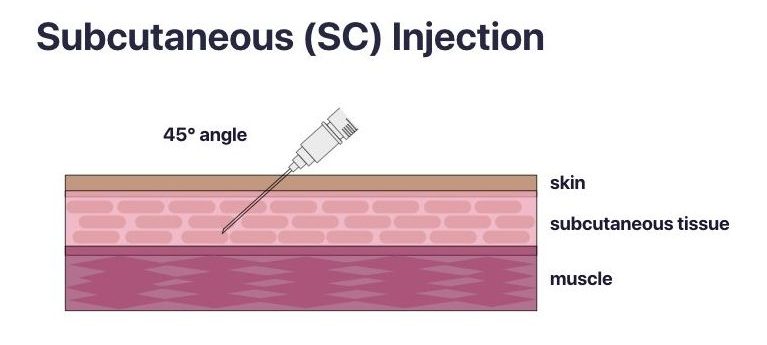
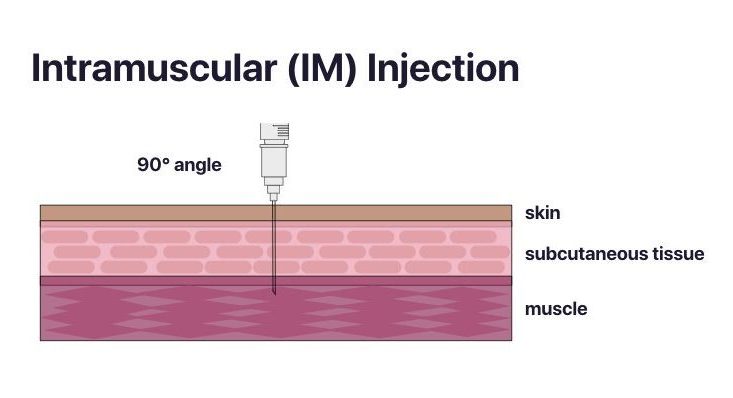
Depending on the vaccine dose, health professionals should use a 1 mL or 3 mL syringe. Depending on the site of administration, it is important to select the right needle size to optimize the immune response and reduce the risk of injection site reactions. For example, vaccines with adjuvants need to be injected into the muscle and not the subcutaneous tissue to prevent inflammation and formation of granulomas. Furthermore, vaccine absorption can be impaired if the vaccine is inadvertently injected into lymphatic circulation. When selecting a needle length for an intramuscular (IM) injection, consider a length that is long enough to reach deep tissue without involving underlying bone, nerves, or blood vessels. Longer needles often result in less redness and swelling when compared to shorter needles. The selection of the right needle should be determined by: 1) route of administration; 2) the client’s age and size of muscle mass; 3) viscosity of the vaccine or passive immunizing agent. Table 3.3 offers needle selection guidelines to inform clinical judgement, which are then visualized in Images 3.2 and 3.3. It is important to note that the needle size recommendations are based on the practice of having the skin stretched flat between thumb and forefinger at the time of administration.
Table 3.3: Needle Selection Guidelines
| Route of Administration | Needle Gauge | Age of vaccine recipient | Site of injection | Needle Length |
|
Intradermal (ID)
|
26-27
|
All ages
|
1.0 cm
|
|
|
Subcutaneous (SC) 45 degree angle
|
25
|
All ages
|
< 1 year: anterolateral thigh ≥ 1 year: upper triceps area or anterolateral thigh
|
1.6 cm
|
|
Intramuscular (IM) 90 degree angle
|
22-25
|
Newborn (>28 days) and preterm infants
|
Anterolateral thigh
|
1.6 cm
|
|
Infants (1 – 12 months)
|
Anterolateral thigh
|
2.2 – 2.5 cm
|
||
|
Young children (>12 months – 3 years)
|
Deltoid muscle
|
1.6 – 2.5 cm
|
||
|
Anterolateral thigh
|
2.5 – 3.5 cm
|
|||
|
Children (>3 – 12 years)
|
Deltoid muscle
|
1.6 – 2.5 cm
|
||
|
Anterolateral thigh
|
2.5 – 3.5 cm
|
|||
|
Adolescents (>12 years – 18 years)
|
Deltoid muscle
|
Consult weight-based recommendations
|
||
|
Anterolateral thigh
|
2.5 – 3.2 cm
|
|||
|
Deltoid muscle
|
For those weighing <130 lbs (<60 kg): 1.6 cm – 2.5 cm (⅝ inch – 1 inch)
Males weighing 130 – 260 lbs (60 – 118 kg) and females weighing 130 – 200 lbs (60 – 90 kg): 2.5 cm (1 inch)
Males weighing >260 lbs (118 kg) and females weighing >200 lbs (90 kg): 3.8 cm (1½ inch)
|
Points of Consideration
Despite popular belief, there is no evidence to support avoiding injection through a tattoo or superficial birthmark.
Content in the Table 3.3 was adapted, with editorial changes, from: Page 8: Canadian Immunization Guide: Part 1 – Key Immunization Information by the Government of Canada and is reproduced under non-commercial conditions.

