Building Healthy Eating Patterns
Helping People Make Healthy Choices
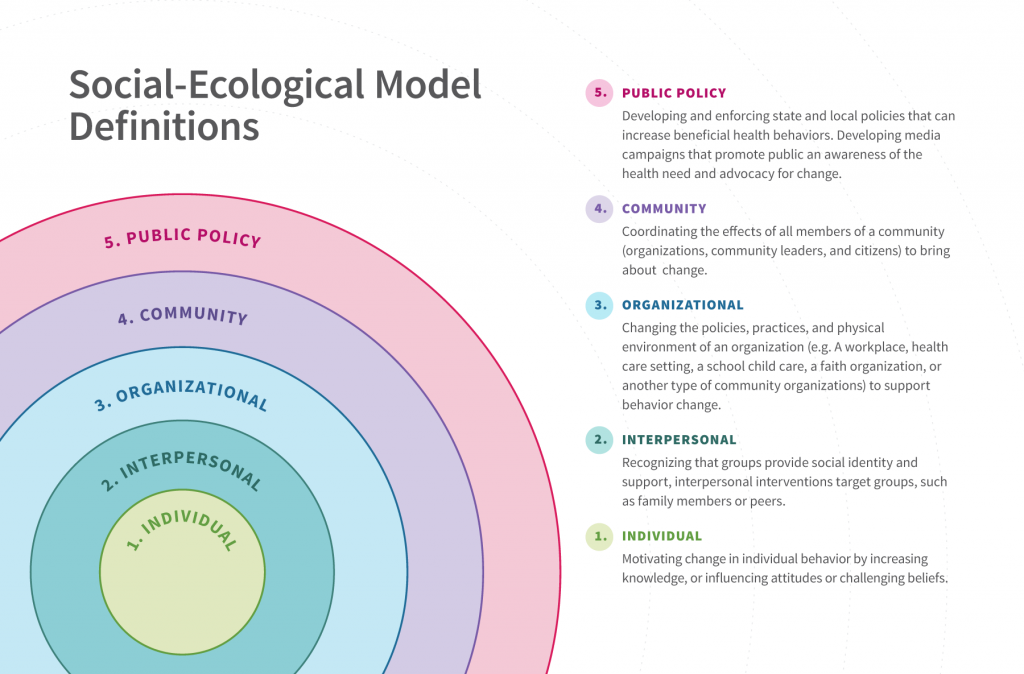
It is not just ourselves, the food industry, and federal government that shape our choices of food and physical activity, but also our sex, genetics, disabilities, income, religion, culture, education, lifestyle, age, and environment. All of these factors must be addressed by organizations and individuals that seek to make changes in dietary habits. The socioeconomic model incorporates all of these factors and is used by health-promoting organizations, such as the USDA and the HHS to determine multiple avenues through which to promote healthy eating patterns, to increase levels of physical activity, and to reduce the risk of chronic disease for all Americans. Lower economic prosperity influences diet specifically by lowering food quality, decreasing food choices, and decreasing access to enough food. The USDA reports that an estimated 12.3 percent or 15.6 million Americans were food insecure, meaning they had insufficient funds to feed all family members at least some time during the year in 2016[1].
Figure 12.7 Social-Ecological Model
Recommendations for Optimal Health
For many years, the US government has been encouraging Americans to develop healthful dietary habits. In 1992 the Food Pyramid was introduced, and in 2005 it was updated. This was the symbol of healthy eating patterns for all Americans. However, some felt it was difficult to understand, so in 2011, the pyramid was replaced with MyPlate.
The MyPlate program uses a tailored approach to give people the needed information to help design a healthy diet. The plate is divided according to the amount of food and nutrients you should consume for each meal. Each food group is identified with a different color, showing the food variety that all plates must have. Aside from educating people about the type of food that is best to support optimal health, the new food plan offers the advice that it is okay to enjoy food, just eat a diverse diet and in moderation[2].
Everyday Connections

Interested in another reliable source for nutrition and health information? The “Got Nutrients?” website highlights the importance of meeting essential nutrient needs in order to maintain optimum health. This website, geared for those interested in nutrition, fitness, and health, posts short daily nutrition and health messages. Each short “Daily Tip” includes links to both a popular article and to a related scientific resource. For more information about “Got Nutrients?” visit, http://www.gotnutrients.net. To receive the “Daily Tips” by email, visit http://www.gotnutrients.net/email_alerts/subscribe.cfm
- Food Security in the U.S. United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service. https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/interactive-charts-and-highlights/. Updated September 6, 2017. Accessed November 22, 2017. ↵
- Choose MyPlate. US Department of Agriculture. http://www.choosemyplate.gov/. Accessed July 22, 2012. ↵

