Using Captions to Identify Tables
Why are Table Captions important?
- Standardize the way tables are displayed across your OER
- Help screenreaders to find tables in a document and let the user decide if they want to read them
Video Demonstration
Watch Table Captions on Screencast-o-Matic (5 mins)
Video source: “Table Captions” by Jen Booth, is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 , except where otherwise noted.
Process for Adding/Correcting Captions
| Step |
Description | Time stamp |
Editor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Preview your page and determine if captions on tables are displaying in a consistent way. | 0:36 | Browser |
| 2 | Navigate to a table in Pressbooks editor. If the table does not have a caption (appears at top of the table surrounded by a dotted box/line), continue to #3 | 2:17 | Visual |
| 3 | Select the table & access Table Properties from the menu | 2:22 | Visual Table Properties |
| 4 | Click the checkbox for Caption & select OK | 2:32 | Table Properties |
| 5 | Add any existing caption / Table heading into the dotted box | 2:49 | Visual |
| 6 | If needed, remove table heading or extra cells once caption is in the caption field | 3:11 | Visual |
| 7 | Repeat for any further tables | 3:25 | Visual |
| 8 | If needed, check the HTML code to ensure caption is properly placed inside the table tag. | 3:40 | Text |
| 8 | Save & Preview. If captions appear at the bottom of the table rather than the top, notify your project team – we will change this via CSS. | 4:02 | Browser |
The Finished Product
| Element | Stem | Charge | Modern Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iron | ferr- | 2+ | iron(II) ion | ferrous ion |
| 3+ | iron(III) ion | ferric ion | ||
| copper | cupr- | 1+ | copper(I) ion | cuprous ion |
| 2+ | copper(II) ion | cupric ion | ||
| tin | stann- | 2+ | tin(II) ion | stannous ion |
| 4+ | tin(IV) ion | stannic ion | ||
| lead | plumb- | 2+ | lead(II) ion | plumbous ion |
| 4+ | lead(IV) ion | plumbic ion | ||
| chromium | chrom- | 2+ | chromium(II) ion | chromous ion |
| 3+ | chromium(III) ion | chromic ion | ||
| gold | aur- | 1+ | gold(I) ion | aurous ion |
| 3+ | gold(III) ion | auric ion |
Source: “3.4 Ionic Nomenclature” In The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry by Saylor Academy, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Table Summaries
Table Summaries are used in some older OER, and may or may not improve accessibility. In some cases, table summaries end up being a full list of every cell and it’s related data. This is likely not that useful to a screenreader.
View a sample of a table summary in HTML code
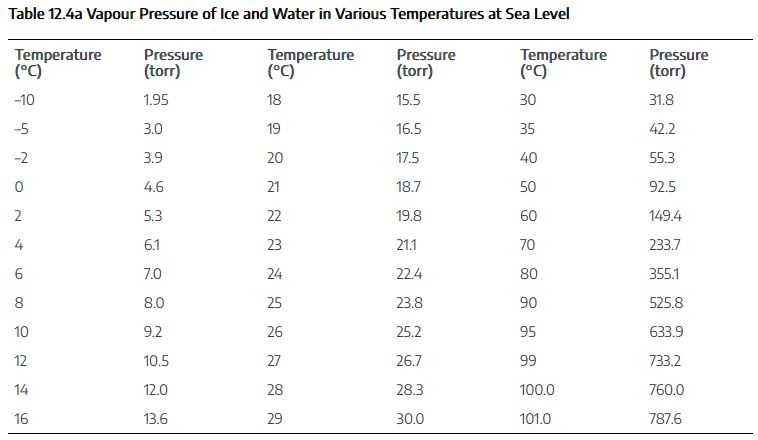
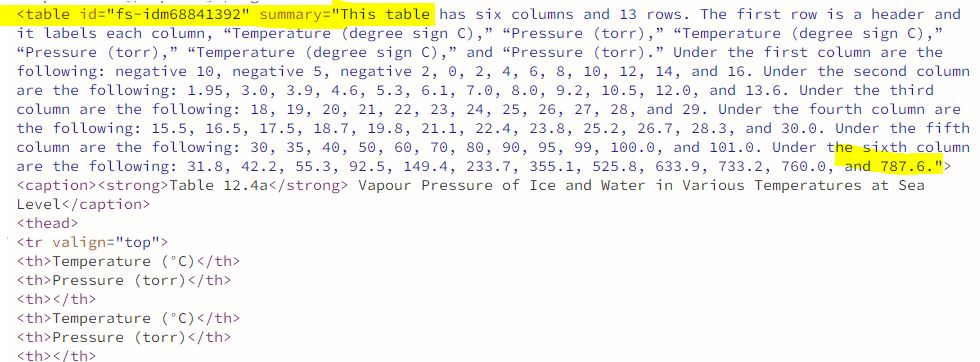
In this case, the summary repeats every data point from the table. This could be revised to just include information about the organization of the table, if necessary.
- Check the HTML/Text version of your page to determine if a Table summary has been included.
- Read the summary. An ideal summary should only list any pertinent details about the detail/layout of the table and/or why it’s included (context)
- Table summary tags are deprecated in HTML 5, so:
- It’s unclear if screenreaders actually access them and they may stop doing so
- If they do, a lengthy table summary is not going to be helpful.
- Recommendation is to put info in the Table caption, rather than a summary as it may not be supported
- It’s unclear if screenreaders actually access them and they may stop doing so
Resources
- WebAIM: Creating Accessible Tables – Data Tables
- H73: Using the summary attribute of the table element to give an overview of data tables
Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, “Using Captions to Identify Tables” by Jen Booth is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.
Media Attributions
- Summarized table © Paul Flowers, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley, & William R. Robinson adapted by Jen Booth is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Table Summary Code © Paul Flowers, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley, & William R. Robinson adapted by Jen Booth is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license

