Respiratory System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the respiratory system
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the respiratory system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of respiratory system terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the respiratory system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic testing and procedures related to the respiratory system
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the respiratory system:
Prefixes
- a- (absence of, without)
- an- (absence of, without)
- brady- (slow)
- dys- (difficult, painful, abnormal, labored)
- endo- (within, in)
- eu- (normal, good)
- hyper- (above, excessive)
- hypo- (below, incomplete)
- intra- (within, in)
- poly- (many, much)
- tachy- (fast, rapid)
Combining Forms
- adenoid/o (adenoids)
- alveol/o (alveolus)
- atel/o (imperfect, incomplete)
- bronch/o (bronchus)
- bronchi/o (bronchus)
- capn/o (carbon dioxide)
- diaphragmat/o (diaphragm)
- epiglott/o (epiglottis)
- hem/o (blood)
- hemat/o (blood)
- laryng/o (larynx)
- lob/o (lobe)
- muc/o (mucus)
- nas/o (nose)
- orth/o (straight)
- ox/i (oxygen)
- pharyng/o (pharynx)
- phon/o (sound, voice)
- phren/o (diaphragm)
- pleur/o (pleura)
- pneum/o (lung, air)
- pneumon/o (lung, air)
- pneumat/o (lung)
- pulmon/o (lung)
- py/o (pus)
- radi/o (x-rays, ionizing radiation)
- respir/o (breath, breathing)
- rhin/o (nose)
- sept/o (septum)
- sinus/o (sinus)
- somn/o (sleep)
- son/o (sound)
- spir/o (breathe, breathing)
- thorac/o (thorax, chest cavity)
- tom/o (to cut, section, slice)
- tonsill/o (tonsil)
- trache/o (trachea)
Suffixes
- -algia (pain)
- -ar (pertaining to)
- -ary (pertaining to)
- -cele (hernia, protrusion)
- -centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
- -eal (pertaining to)
- -ectasis (stretching out, dilation, expansion)
- -ectomy (excision, cut out)
- -emia (in the blood)
- -genic (producing, originating, causing)
- -gram (the record, radiographic image)
- -graph (instrument used to record)
- -graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
- -ia (condition, diseased state, abnormal state)
- -ic (pertaining to)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
- -logy (study of)
- -meter (instrument used to measure)
- -metry (measurement)
- -oid (resembling)
- -pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -pnea (breathing)
- -ptysis (spitting, coughing)
- -rrhagia (rapid flow of blood, excessive bleeding)
- -scope (instrument used for visual examination)
- -scopic (pertaining to visual examination)
- -scopy (process of visually examining, visual examination)
- -spasm (sudden involuntary muscle contraction, spasmodic contraction)
- -stenosis (constriction, narrowing)
- -stomy (creation of an artificial opening)
- -thorax (chest, chest cavity)
- -tome (instrument used to cut)
- -tomy (cut into, incision)
Respiratory System Words
Respiratory System Medical Terms (Text version)
- Adenoiditis
- adenoid/itis
- inflammation of the adenoids
- adenoidectomy
- adenoid/ectomy
- excision of the adenoids
- adenotome
- aden/o/tome
- instrument used to cut the adenoids
- alveolitis
- alveol/itis
- inflammation of the alveoli
- alveolar
- alveol/ar
- pertaining to the alveolus
- atelectasis
- atel/ectasis
- incomplete expansion
- bronchitis
- bronch/itis
- inflammation of the bronchus
- bronchogenic carcinoma
- bronch/o/genic carcin/oma
- cancerous tumour originating in a bronchus
(lung cancer)
- bronchopneumonia
- bronch/o/pneumon/ia
- diseased state of bronchi and lungs
- bronchoplasty
- bronch/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the bronchi
- bronchoscope
- bronch/o/scope
- instrument used for visual examination of the bronchi
- bronchoscopy
- bronch/o/scopy
- visual examination of the bronchi
- bronchoalveolar
- bronch/o/alveol/ar
- pertaining to the bronchi and alveoli
- bronchospasm
- bronch/o/spasm
- spasmodic contraction of the bronchi
- bronchiectasis
- bronchi/ectasis
- dilation of the bronchi
- capnometer
- capn/o/meter
- instrument used to measure carbon dioxide
- acapnia
- a/capn/ia
- condition of absence (less than normal level) of carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- hypercapnia
- hyper/capn/ia
- condition of excessive (greater than normal levels) carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- hypocapnia
- hypo/capn/ia
- condition of deficient (low levels) of carbon dioxide (in the blood)
- diaphragmatocele
- diaphragmat/o/cele
- hernia of the diaphragm
- diaphragmatic
- diaphragmat/ic
- pertaining to the diaphragm
- epiglottitis
- epiglott/itis
- inflammation of the epiglottis
- hemothorax
- hem/o/thorax
- blood in the thoracic cavity
- hematology
- hemat/o/logy
- study of blood
- hematologist
- hemat/o/logist
- specialist in blood and blood disorders
- laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB)
- laryng/o/trache/o/bronch/itis
- inflammation of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi
- laryngoplasty
- laryng/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the larynx
- laryngostomy
- laryng/o/stomy
- creation of an artificial opening into the larynx
- laryngotracheotomy
- laryng/o/trache/o/tomy
- incision into the larynx and trachea
- laryngoscope
- laryng/o/scope
- instrument used for visual examination of the larynx
- laryngoscopy
- laryng/o/scopy
- process of viewing the larynx
- laryngeal
- laryng/eal
- pertaining to the larynx
- laryngospasm
- laryng/o/spasm
- spasmodic contraction of the larynx
- laryngitis
- laryng/itis
- inflammation of the larynx
- lobar pneumonia
- lob/ar pneumon/ia
- disease state of the lung pertaining to the lobe(s)
- lobectomy
- lob/ectomy
- excision of the lobe(s)
- mucoid
- muc/oid
- resembling mucus
- mucous
- muc/ous
- pertaining to mucus
- nasopharyngitis
- nas/o/pharyng/itis
- inflammation of the nose and pharynx
- nasopharyngeal
- nas/o/pharyng/eal
- pertaining to the nose and pharynx
- orthopnea
- orth/o/pnea
- breathing is easier in a straight position
- anoxia
- an/ox/ia
- condition of absence (deficiency) of oxygen
- oximeter
- oxi/meter
- instrument used to measure oxygen
- hypoxemia
- hyp/ox/emia
- condition of deficient oxygen in the blood
- hypoxia
- hyp/ox/ia
- condition of deficient oxygen
- pharyngitis
- pharyng/itis
- inflammation of the pharynx
- aphonia
- a/phon/ia
- condition of absence of voice
- dysphonia
- dys/phon/ia
- condition of difficult speaking (voice)
- phrenalgia
- phren/algia
- pain in the diaphragm
- phrenospasm
- phren/o/spasm
- spasm of the diaphragm
- pleuritic
- pleurit/ic
- pertaining to the pleura
- pleuritis
- pleur/itis
- inflammation of the pleura
- pleuropexy
- pleur/o/pexy
- surgical fixation of the pleura
- interpleural
- inter/pleur/al
- pertaining to between the pleura (space between the pleural membranes)
- pneumoconiosis
- pneum/o/coni/osis
- abnormal condition of dust in the lungs
- pneumonia
- pneumon/ia
- diseased state of lung
- pneumonitis
- pneumon/itis
- inflammation of the lung
- pneumothorax
- pneum/o/thorax
- air in the thoracic cavity
- pneumonectomy
- pneumon/ectomy
- excision of the lung
- pneumatocele
- pneumat/o/cele
- hernia of the lung
- pulmonary
- pulmon/ary
- pertaining to the lung(s)
- pyothorax
- py/o/thorax
- pus in the thoracic cavity
- radiography
- radi/o/graphy
- process of recording x-rays
- radiologist
- radi/o/logist
- physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disease using medical imaging
- radiology
- radi/o/logy
- study of the use of radiant energy in diagnosing disease
- respirologist
- respir/o/logist
- specialist who studies and treats disease and disorders related to breathing
- respirology
- respir/o/logy
- the study of breathing disorders and disease
- rhinitis
- rhin/itis
- inflammation of the nose
- rhinomycosis
- rhin/o/myc/osis
- abnormal condition of fungus in the nose
- rhinorrhagia
- rhin/o/rrhagia
- rapid flow of blood from the nose
- rhinoplasty
- rhin/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the nose
- rhinorrhea
- rhin/o/rrhea
- discharge from the nose
- septoplasty
- sept/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the septum
- septotomy
- sept/o/tomy
- incision into the (nasal) septum
- sinusitis
- sinus/itis
- inflammation of a sinus
- polysomnography (PSG)
- poly/somn/o/graphy
- process of recording many (test) during sleep
- sonogram
- son/o/gram
- the record of sound
- sonography
- son/o/graphy
- process of recording sound
- spirometer
- spir/o/meter
- instrument used to measure breathing (lung volume)
- spirometry
- spir/o/metry
- measuring breathing (air flow)
- thoracalgia
- thorac/algia
- pain in the chest, thorax
- thoracocentesis
- thorac/o/centesis
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid (from the thoracic cavity)
- thoracentesis
- thora/centesis
- surgical puncture to aspirate fluid from thoracic cavity
- thoracotomy
- thorac/o/tomy
- incision into the thoracic cavity
- thoracoscopy
- thorac/o/scopy
- visual examination of the thoracic cavity
- thoracic
- thorac/ic
- pertaining to the chest, thorax
- thoracoscope
- thorac/o/scope
- instrument used to visualize the thoracic cavity
- tomography
- tom/o/graphy
- process of recording slices
- tonsillitis
- tonsill/itis
- inflammation of the tonsils
- tonsillectomy
- tonsill/ectomy
- excision of the tonsils
- tracheitis
- trache/itis
- inflammation of the trachea
- tracheoplasty
- trache/o/plasty
- surgical repair of the trachea
- tracheostomy
- trache/o/stomy
- creation of an artificial opening into the trachea
- tracheotomy
- trache/o/tomy
- incision into the trachea
- endotracheal
- endo/trach/eal
- pertaining to within the trachea
- tracheostenosis
- trache/o/stenosis
- narrowing of the trachea
- endoscope
- endo/scope
- instrument used to view within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- endoscopic
- endo/scopic
- pertaining to view within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- endoscopy
- endo/scopy
- visual examination within
(a hollow organ or cavity)
- apnea
- a/pnea
- absence of breathing
- dyspnea
- dys/pnea
- breathing that is difficult
- eupnea
- eu/pnea
- normal breathing
- hypopnea
- hypo/pnea
- deficient breathing
- tachypnea
- tachy/pnea
- rapid breathing
Activity Source: Respiratory System Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Respiratory System Medical Terms
Respiratory System Word Not Easily Broken Down (Text version)
- Epistaxis
- nosebleed (rhinorrhagia)
- influenza (flu)
- highly contagious viral infection effecting the respiratory tract
- pleural effusion
- fluid in the pleural space
(caused by disease or trauma)
- fluid in the pleural space
- pulmonary edema
- fluid accumulation in alveoli and bronchioles
(related to heart failure)
- fluid accumulation in alveoli and bronchioles
- pulmonary embolism (PE)
- blockage of pulmonary circulation to the lungs
- upper respiratory infection
- infection of the nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx and larynx
- stethoscope
- instrument used to hear internal body sounds
- asphyxia
- deprivation of oxygen to tissues, suffocation
- aspirate
- suction of fluid, inhalation of fluid
- mucus
- slimy liquid secreted by mucous membranes
- nebulizer
- device that creates a mist for giving respiratory treatment or medication
- nosocomial infection
- infection acquired in hospital
- sputum
- mucous secretion from lungs, bronchi, and trachea that is expelled through the mouth
- ventilator
- mechanical device that assist with breathing
Activity Source: Respiratory System Word Not Easily Broken Down by Kimberlee Carter, licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Respiratory System Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated respiratory system terms:
- ABGs (arterial blood gases)
- AFB (acid-fast bacilli)
- ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
- BiPAP (bilevel positive airway pressure)
- C&S (culture and sensitivity)
- CAP (community-acquired pneumonia)
- CF (cystic fibrosis)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure)
- CPT (chest physiotherapy)
- CT (computed tomography, computerized tomography)
- CXR (chest x-ray)
- DPI (dry powder inhaler)
- flu (influenza)
- IPPB (intermittent positive-pressure breathing)
- IPF (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis)
- LLL (left lower lobe)
- LTB (laryngotracheobronchitis)
- LUL (left lower lobe)
- MDI (metered-dose inhaler)
- NIPPV (non-invasive positive-pressure ventilator)
- O2 (oxygen)
- OSA (obstructive sleep apnea)
- PEP (positive expiratory pressure)
- PFM (peak flow meter)
- PFTs (pulmonary function tests)
- RLL (right lower lobe)
- RML (right middle lobe)
- RUL (right upper lobe)
- SOB (shortness of breath)
- SVN (small-volume nebulizer)
- TB (tuberculosis)
- URI (upper respiratory infection)
- VAP (ventilator-associated pneumonia)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Respiratory System Structures
Label the following respiratory system structures:
Labeling the Respiratory System (Text Version)
Label the diagram with correct words listed below:
- Left Bronchus
- Trachea
- Pharynx
- Diaphragm
- Right Bronchus
- Right Lung
- Left Lung
- Oral Cavity
- Nasal Cavity
- Larynx
- Nostril
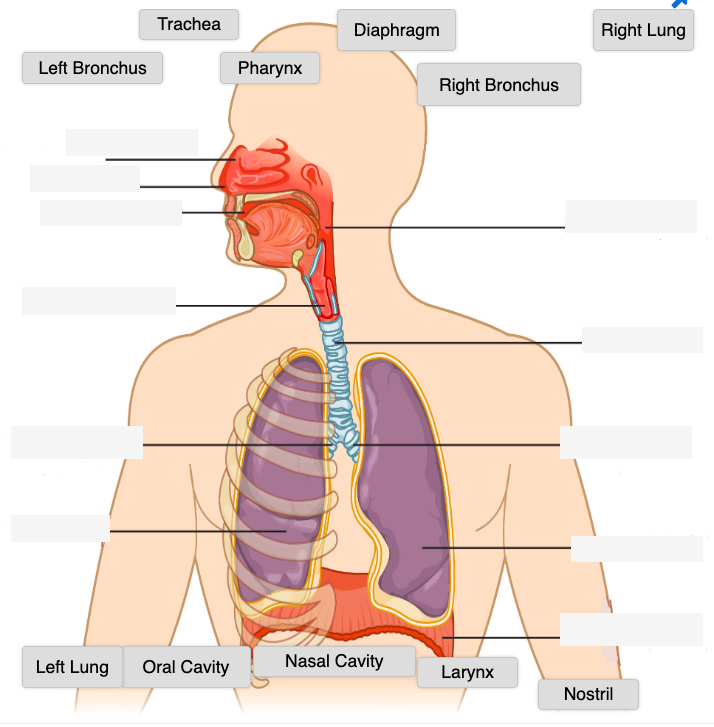
Labeling the Respiratory System Diagram (Text version)
This is an anatomical diagram of the major organs and structure of the human respiratory system. Identified starting from the top of the diagram is the organs and structures which serve as a passageway for air and include, _______[Blank 1] which warms and moistens the air, the ______[Blank 2] where air enters the respiratory system and travels to the _______[Blank 3] also know as the mouth, from the mouth the air moves to the _______[Blank 4], then to through the voice box correctly called the ________[Blank 5], and passes into the ________[Blank 6] often referred to as the windpipe. The trachea bifurcates meaning it separates into two anatomical branches each leading to each lung, on the right side is the __________[Blank 7], on the left side, the _________[Blank 8]. Air arrives at the lungs to allow for the exchange of gases arrives and enters on the right side into the _________[Blank 9] and on the left side the ______[Blank 10]. The muscular partition supporting the lungs known as the ___________[Blank 11]. This detailed illustration supports understanding of the respiratory system’s structure and function.
Check your answers: [1]
Activity source: Respiratory System Anatomy by Kimberlee Carter, illustration from Anatomy and Physiology (OpenStax), licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Respiratory System History and Physical (Text Version)
Fill in the consultation report with correct words listed below:
- Exert
- Edema
- diuretic
- membranes
- HEENT
- apnea
- heart failure
- lobes
- inspiration
- allergens
- breath
- erythema
- monitor
- asthma
- edema
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM – HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
PATIENT NAME: Randy BURNS
AGE: 56
DOB: July 2
SEX: Male
ATTENDING PHYSICIAN: Joyce Mathers, MD, Pulmonology
HISTORY: This 56-year-old male is presenting with a 2-week history of worsening dyspnea not associated with exertion. The patient states that he does not have to _____[Blank 1] himself for his breathing to get difficult. He feels that “he cannot get his breath” sometimes even with lying in bed. He does report developing a cold and runny nose over the last 10 days, but the worsened breathing seemed to have started a few days earlier than this. He reports that the shortness of _____[Blank 2] has progressively gotten worse in the past 2-3 days. Patient does not report any leg or foot _____[Blank 3].
PAST HISTORY: The patient has a life history of asthma triggered by environmental _____[Blank 4] – grass cutting, trees budding in the spring, street dust etc. He has used a puffer when he has symptoms since he was a child. He has a history of congestive _____[Blank 5] (CHF) and sleep _____[Blank 6] for which he uses a CPAP machine nightly.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: GENERAL APPEARANCE: The patient appears laboring in breathing. He is quite distressed. VITAL SIGNS: Temperature 97.1, pulse 88, blood pressure 121/86, weight 209 pounds, height 5 feet 8 inches. _____[Blank 7] : Eye exam PERRLA. Normocephalic, atraumatic. Moist mucous _____[Blank 8]. No oropharyngeal _____[Blank 9]. No signs of infection. Tongue is coated but tonsils are clear. NECK: Supple. No lymphadenopathy. No bruits. LUNGS: There is marked wheezing on _____[Blank 10] bilaterally. Some minimal evidence of consolidation in the lower _____[Blank 11] bilaterally. No rales or rubs. CARDIAC: Irregular rate and rhythm, variable S1 and S2. EXTREMITIES: Some pedal and ankle _____[Blank 12] noted in low extremities. No cyanosis or clubbing.
ASSESSMENT AND PLAN
- Acute shortness of breath with a history of allergic _____[Blank 13]. Rule out upper respiratory infection (URI). Will order chest x-ray stat.
- Atrial fibrillation. Patient has a controlled rate. Will administer one dose of Lovenox overnight.
- Mild symptoms of CHF due to lower extremity edema. Will administer Aldactone to bring this under control. Will _____[Blank 14] the patient’s diuretic volume.
- Plan to admit patient overnight for observation to await stat CXR result and to monitor the effects of _____[Blank 15] and anticoagulant therapies.
___________________________________
Joyce Mathers, MD, Pulmonology
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Respiratory System History and Physical by Sheila Bellefeuille and Heather Scudder, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Respiratory System Consultation Report (Text Version)
Fill in the consultation report with correct words listed below:
- Oxygen
- pleura
- basal
- hemoptysis
- dyspnea
- thoracostomy
- q. d.
- COPD
- antibiotics
- wheezing
- atelectasis
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Wayne SAUNDERS
AGE: 59
DOB: September 7
SEX: Male
DATE OF CONSULTATION: March 29
CONSULTANT: Joyce Mathers, MD, Pulmonology
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Sudden onset dyspnea and respiratory distress.
HISTORY: This garrulous 59-year-old was seen in the ER today with a complaint of sudden onset _____[Blank 1] and some respiratory distress. Denies any nausea, vomiting, chest pain, _____[Blank 2], cough, fever or chills.
PAST HISTORY: Is positive for asthma and _____[Blank 3] as patient is a lifelong smoker at 1+ packs per day.
ASSESSMENT: CHEST has good air entry bilaterally. No _____[Blank 4]. Bilateral _____[Blank 5] crackles are noted. Some dullness to percussion on the left. CT scan was ordered and shows a left _____ [Blank 6] effusion and acute pneumothorax due to infectious process. Probable comprehensive _____[Blank 7].
MEDICATIONS
- Adalat 30 mg _____[Blank 8].
- Atenolol 50 mg (half dose) q.d.
- Flonase 50 mcg one spray on each side q.d.
- Zoloft 100 mg once q.d.
PLAN
- Admit patient to the unit for treatment and possible left _____[Blank 9] if indicated by lack of improvement on standard therapy.
- Treat with a course of _____[Blank 10] for the URI.
- _____[Blank 11] therapy if indicated by 02 sats.
- Repeat CT scan in 48 hours.
__________________________________
Joyce Mathers, MD, Pulmonology
Note: Report samples (H5P and Pressbooks) are to encourage learners to identify correct medical terminology and do not represent the Association for Health Documentation Integrity (AHDI) formatting standards.
Check your answers: [3]
Activity source: Respiratory System Consultation Report by Sheila Bellefeuille and Heather Scudder, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Respiratory System Consultation Report (Text Version)
Fill in the consultation report with correct words listed below:
- Kidney
- respiratory
- childhood
- urinalysis
- shadowing
- mid-thoracic
- pulmonary
- hepatotoxic
- x-ray
- apex
- dyspnea
- flu shot
- myoplasmal
- rasping
- rhinorrhea
- expiration
- rales
- vaccine
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Mateo DIAZ
AGE: 22
DOB: June 25
SEX: Male
DATE OF CONSULTATION: April 16
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Joyce Mathers, MD Pulmonology
HISTORY: This 22-year-old Hispanic gentleman is referred to me for a 2-week history of new rasping cough associated with a dull right _____[Blank 1] intercostal discomfort. He has some associated _____[Blank 2] on exertion but is otherwise well with no presenting symptoms of a cold or _____[Blank 3] infection. No fever, sputum or _____[Blank 4].
PAST HISTORY: He has a history of _____[Blank 5] asthma that seemed to disappear after he hit his mid-20s. He has a history of extensive travel for work and leisure and most recently was on a work trip to Wuhan, China in late December. He receives a _____[Blank 6] annually and did have the most recent _____[Blank 7] in October 2019.
His physical exam is relatively unremarkable. Blood pressure is 120/83, respirations 12. Temperature normal at 37. Chest exam is CTA with no _____[Blank 8], rhonchi or wheezes. Even on a forced exhalation, we could not reproduce the ______[Blank 9] cough symptom.
ASSESSMENT: A PA and lateral chest _____[Blank 10] revealed a new infiltrate and _____[Blank 11] along the left mid-lung margin all the way to the _____[Blank 12]. Spirometry showed normal pressures on forced _____[Blank 13].
PLAN
- Rule out _____[Blank 14] pneumonia versus other lung infection or infiltrates such as granulomatosis, aspergillosis or sarcoidosis.
- CBC with differential, chem panel, ESR, ACE, and mycoplasma titres.
- Repeat full function tests (PFTs) in 2 weeks.
If required, will treat with Amphotericin B, Tosufloxacin, Macrolide or similar. If any of these treatments are indicated, weekly LFTs and _____[Blank 15] function testing will be required as these classes of drugs is notoriously _____[Blank 16] and nephrotoxic.
I will see the patient again in approximately 4 days to review the results and decide on a course of action – more testing or appropriate treatments as indicated above.
____________________________
Joyce Mathers, MD Pulmonology
Note: Report samples (H5P and Pressbooks) are to encourage learners to identify correct medical terminology and do not represent the Association for Health Documentation Integrity (AHDI) formatting standards.
Check your answers: [4]
Activity source: Respiratory System Consultation Report by Sheila Bellefeuille and Heather Scudder, licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Respiratory System Glossary Reinforcement Activity (Text Version)
- A small bulbous, teardrop-shaped structure located at the apex of the soft palate is called the ____[Blank 1].
- Lymphocytes
- Posterior
- Uvula
- Located at the anterior region of the nasal cavity and is composed of bone is the _____[Blank 2].
- Glottis
- Fauces
- Hard Palate
- A ridge of cartilage that separates the two main bronchi is called the ______[Blank 3].
- Carina
- Eupnea
- Alveolar Duct
- ____[Blank 4] serves as an airway and is continuous with the nasal cavity.
- Conducting zone
- Nasopharynx
- Hilum
- ______[Blank 5] consists of the surface and skeletal structure that result in the outward appearance of the nose and contribute to its numerous functions.
- Pharynx
- Inferior
- External nose
Check your answers: [5]
Activity source: Respiratory System Glossary Reinforcement Activity by Gisele Tuzon, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheets below:
Worksheet – Respiratory System – Chapter 4 [Word]
4. Respiratory – Words Not Easily Broken [Word]
4. Respiratory – Abbreviations [Word]
4. Respiratory – Definitions Using Word Parts [Word]
4. Respiratory – Scenario [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
↵
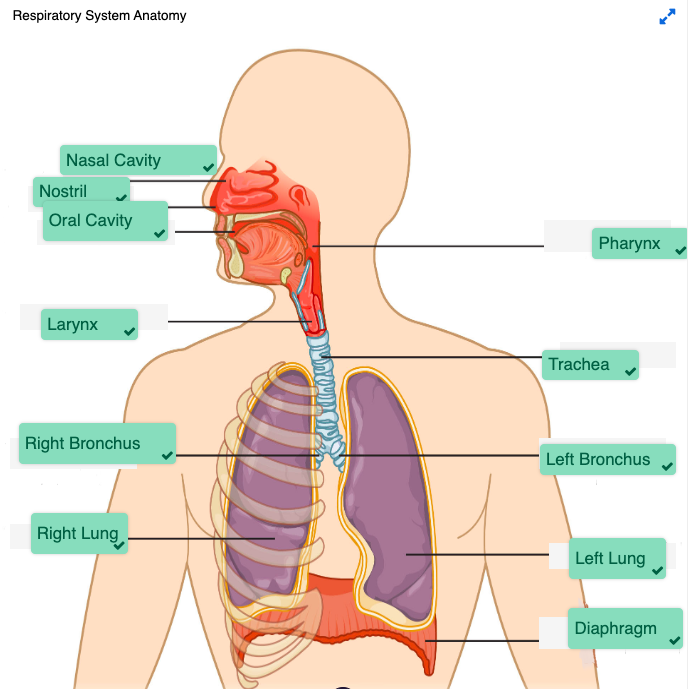
Check your answers: Labeling the Respiratory System Diagram
This is an anatomical diagram of the major organs and structure of the human respiratory system. Identified starting from the top of the diagram is the organs and structures which serve as a passageway for air and include, nasal cavity which warms and moistens the air, the nostril where air enters the respiratory system and travels to the oral cavity also know as the mouth, from the mouth the air moves to the pharynx, then to through the voice box correctly called the larynx, and passes into the trachea often referred to as the windpipe. The trachea bifurcates meaning it separates into two anatomical branches each leading to each lung, on the right side is the right main bronchus branch, on the left side, the left main bronchus. Air arrives at the lungs to allow for the exchange of gases arrives and enters on the right side into the right lung and on the left side the left lung. The muscular partition supporting the lungs known as the diaphragm. This detailed illustration supports understanding of the respiratory system's structure and function. - 1. Exert, 2. Breath, 3. Edema, 4. Allergens, 5. Heart failure, 6. Apnea, 7. HEENT, 8. Membranes, 9. Erythema, 10. Inspiration, 11. Lobes, 12. Edema, 13. Asthma, 14. Monitor, 15. Diuretic ↵
- 1. Dyspnea, 2. Hemoptysis, 3. COPD, 4. Wheezing, 5. Basal, 6. Pleural, 7. atelectasis , 8. q. d., 9. Thoracostomy, 10. Antibiotics, 11. Oxygen ↵
- 1.Mid-thoracic, 2. Dyspnea, 3. Respiratory, 4. Rhinorrhea, 5. Childhood, 6. Flu-shot, 7. Vaccine, 8. Rales, 9. Rasping, 10. X-ray, 11. Shadowing, 12. Apex, 13. Expiration, 14. Myoplasmal, 15. Urinalysis, 16. Pulmonary, 17. Kidney, 18. Hepatotoxic. ↵
- 1. Uvula, 2. Hard Palate, 3. Carina, 4. Nasopharynx, 5. External nose ↵

