Male Reproductive System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy and describe the main functions of the male reproductive system
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the male reproductive system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of male reproductive system medical terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the male reproductive system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic tests and procedures
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the male reproductive system:
Prefixes
- a- (absence of, without)
- an- (absence of, without)
- crypt- (hidden)
- dys- (painful, difficult)
- en- (in)
- epi- (above)
- hyper- (above, excessive)
- hypo- (below)
- par- (near)
- trans- (through, across, beyond)
Combining Forms
- andr/o (male)
- balan/o (glans penis)
- epididym/o (epididymis)
- gonad/o (gonad)
- orch/o (testis, testicle)
- orchi/o (testis, testicle)
- orchid/o (testis, testicle)
- pen/o (penis)
- pen/i (penis)
- phall/o (penis)
- preputi/o (prepuce, foreskin)
- posth/o (prepuce, foreskin)
- prostat/o (prostate gland)
- scrot/o (scrotum)
- semin/i (semen)
- sperm/o (sperm, spermatozoon)
- spermat/o (sperm, spermatozoon)
- test/o (testis, testicle)
- testicular/o (testis, testicle)
- vas/o (vas deferens, vessel, duct)
- vesicul/o (seminal vesicle)
- urethr/o (urethra)
Suffixes
- -al (pertaining to)
- -algia (pain)
- -ar (pertaining to)
- -atic (pertaining to)
- -cision (processing of cutting)
- -ectomy (excision or surgical removal)
- -ferous (pertaining to)
- -genesis ((beginning, development, or production))
- -gram (record)
- -graphy (process of recording)
- -ia (diseased state, abnormal state, condition of, condition)
- -ic (pertaining to)
- -ile (pertaining to)
- -ism (state of, condition)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -logy (study of)
- -lysis (loosening, dissolution, separating)
- -oma (tumor, mass)
- -ous (pertaining to)
- -pathy (disease)
- -pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
- -plasia (development, growth)
- -plasty (surgical repair)
- -rrhea (flow, discharge)
- -sis (condition)
- -stomy (creation of new opening, process of new opening)
- -tion (process of)
- -tomy (cut into, incision)
Male Reproductive System Words
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following male reproductive system words.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
- andropathy (ăn-DROP-ă-thē)
- anorchism (ă-NOR-kĭzm)
- aspermia (ā-SPĔR-mē-ă)
- balanitis (bal-ă-NĪT-ĭs)
- balanorrhea (BAL-ă-nō-RĒ-ă)
- balanoplasty (BAL-ă-nō-plăs-tē)
- benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (bē-NĪN prŏs-TĂT-ĭk hī-pĕr-PLĀ-zhē-ă)
- cryptorchidism (krip-TOR-kĭd-izm)
- epididymectomy (ĕp-ĭ-dĭd-ĭ-MĔK-tō-mē)
- epididymitis (ep-ĭ-did-ĭ-MĪT-ĭs)
- oligospermia (ŏl-ĭ-gō-SPĔR-mē-ă)
- orchialgia (or-kē-ĂL-jē-ă)
- orchiditis (or-kĭ-DĪ-tĭs)
- orchiectomy (or-kē-EK-tŏ-mē)
- orchiepididymitis (or-kē-ĕp-ĭ-dĭd-ĭ-MĪ-tĭs)
- orchiopexy (or-kē-ō-PĔK-sē)
- orchioplasty (OR-kē-ō-plăs-tē)
- orchiotomy (or-kē-ŎT-ō-mē)
- orchitis (or-KĪ-tĭs)
- prostatitis (pros-tă-TĪT-ĭs)
- prostatocystitis (pros-tă-tō-sĭs-TĪ-tĭs)
- prostatolith (prŏs-TĂT-ō-lĭth)
- prostatolithotomy (prŏs-tăt-ō-lĭ-THŎT-ō-mē)
- prostatorrhea (pros-tă-tō-RĒ-ă)
- prostatovesiculitis (pros-tă-tō-vē-sĭk-ū-LĪ-tĭs)
- spermatolysis (spĕr-mă-TŎL-ĭ-sĭs)
- transurethral (trans-ū-RĒ-thrăl)
- vasectomy (vă-SEK-tŏ-mē)
- vesiculectomy (vĕ-sik-yŭ-LEK-tŏ-mē)
- vasovasostomy (vā-zō-vā-ZOS-tŏ-mē)
Pronouncing and Defining Male Reproductive System Medical Terms
Male Reproductive System terms not easily broken down into word parts (Text version)
- ablation
- a-BLĀ-shŏn (Original Term)
- destruction of abnormal or excessive tissue by eroding, vaporizing or melting
- acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
- ă-KWĪRD im-yū-nō-dĕ-FISH-ĕn-sē SĬN-drōm
- advanced, chronic immune system suppression caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
- artificial insemination
- art-ĭ-FISH-ăl in-sem-ĭ-NĀ-shŏn
- the medical procedure of injecting concentrated sperm into the vagina or uterus.
- azoospermia
- ā-zō-ŏ-SPĔR-mē-ă
- absence of viable sperm in the semen.
- chlamydia
- klă-MID-ē-ă
- sexually transmitted disease caused by a very small parasitic bacterium (also known as the silent STD).
- circumcision
- sĭr-kŭm-SIZH-ŏn (Original Term)
- surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin)
- coitus
- KŌ-ĭ-tŭs (Original Term)
- sexual intercourse
- condom
- KON-dŏm (Original Term)
- sheath (cover) for penis, worn during coitus to prevent conception and spread of sexually transmitted infection
- ejaculation
- i-jak-yŭ-LĀ-shŏn
- the action of ejecting semen from the body.
- enucleation
- ē-nū-klē-Ā-shŭn (Original Term)
- excision of a whole organ or mass without cutting into it
- erectile dysfunction (ED)
- ĕ-RĔK-tīl dis-FŬNGK-shŏn
- the inability of a male to attain or maintain an erection sufficient to perform sexual intercourse
- genital herpes
- JEN-ĭt-ăl HĔRP-ēz
- a sexually transmitted disease characterized by blisters in the genital area, caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2.
- gonorrhea
- gon-ŏ-RĒ-ă
- a sexually transmitted disease involving inflammatory discharge from the urethra or vagina.
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- hu-man im-yŭ-nō-dĕ-FISH-ĕn-sē VĪ-rŭs
- a retrovirus that attacks the T-helper cells of the immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
- human papillomavirus (HPV)
- hu-man PAP-ĭ-LŌ-mă-VĪ-rŭs
- a sexually transmitted disease with over 40 subtypes that cause diseases in humans ranging from common warts to cervical cancer.
- hydrocele
- HĪ-drŏ-sēl (Original Term)
- fluid-filled sac around the testicle
- hydrocelectomy
- hī-drō-sē-LĔK-tō-mē (Original Term)
- surgical removal of a fluid-filled sac around the testicle causing scrotal swelling (hydrocele)
- infertility
- in-fĕr-TIL-ĭt-ē (Original Term)
- inability to achieve pregnancy
- metastasis
- mĕ-TAS-tă-sĭs
- cancer spreading from one part of the body into another.
- morcellation
- mor-sĕ-LĀ-shŏn
- cutting or grinding solid tissue into smaller pieces for removal
- MRI ultrasound fusion biopsy
- FŪ-zhŏn BĪ-op-sē
- combination of magnetic resonance imaging with transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) to obtain a tissue from a prostate lesion. The combined MRI-TRUS image is used to direct the biopsy needle into the area of the prostate that looked suspicious on MRI.
- orgasm
- OR-gazm
- a climax of sexual stimulation
- phimosis
- fī-MŌ-sĭs
- a tightness of the prepuce (foreskin of the penis) that prevents its retraction over the glans penis. It may be congenital or the result of balanitis. Circumcision is the usual treatment.
- priapism
- PRĪ-ă-pizm
- persistant, abnormal erection of the penis accompanied by pain and tenderness
- prostate cancer
- PROS-tāt KAN-sĕr
- cancer of the prostate gland
- puberty
- PŪ-bĕrt-ē
- the period during which adolescents develop secondary sex characteristics and become capable of reproduction.
- robotic surgery
- rō-BŎ- tĭk SŬRJ-ĕ-rē
- use of small surgical instruments attached to a computer and operated by the surgeon from a console several feet from the operating table
- sexually transmitted disease (STD)
- SEKS-ū-ă-lē trăns-MĬT-ed diz-ĒZ
- infection spread through sexual contact; also known as sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- spermatocele
- spĕr-MĂT-ō-sēl
- distention of the epididymis containing an abnormal cyst-like collection of fluid and sperm cells
- sterility
- stĕ-RIL-ĭt-ē (Original Term)
- a condition of being unable to conceive or reproduce the species
- sterilization
- ster-ĭ-lĭ-ZĀ-shŏn
- procedure that prevents pregnancy, either a female’s ability to conceive or a male’s ability to induce conception
- syphilis
- SIF-ĭ-lĭs
- a chronic bacterial disease spread primarily through sexual intercourse, but also congenitally by infection of a developing fetus. Rapidly spreads through the body and if left untreated becomes systemic.
- testicular cancer
- tĕs-TĬK-ū-lăr KAN-sĕr
- cancer of the testicle
- testicular torsion
- tĕs-TĬK-ū-lăr TOR-shŏn
- twisting of the spermatic cord causing decreased blood flow to the testis. Considered a surgical emergency and accompanied by sudden onset of severe scrotal pain.
- transurethral
- trans-ū-RĒ-thrăl
- pertaining to through the urethra
- transurethral incision of the prostate gland (TUIP)
- surgical procedure that widens the urethra by making a few small incisions in the bladder neck and the prostate gland.
- transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP)
- surgical removal of pieces of the prostate gland tissue by using an instrument inserted through the urethra.
- transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT)
- treatment that eliminates excess tissue present in benign prostatic hyperplasia by using heat generated by microwave.
- trichomoniasis
- trĭk-ō-mō-NĪ-ă-sĭs
- sexually transmitted disease caused by the one-cell organism Trichomonas. Chiefly affects the urinary tract, vagina, or digestive system.
- varicocele
- VAR-ĭō-sēl (Original Term)
- enlarged veins of the spermatic cord, which may cause scrotal swelling
Activity Source: Male Reproductive System terms not easily broken down into word parts from Medical Terminology. by Grimm et al., licensed under CC BY 4.0. / Some H5P audio re-recorded by Tania Deane and David McCuaig and text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Male Reproductive System Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated male reproductive system terms:
Male Reproductive System Abbreviations
- AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
- BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia, benign prostatic hypertrophy)
- Bx (biopsy)
- DRE (digital rectal examination)
- ED (erectile dysfunction)
- GU (genitourinary)
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
- HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate gland)
- HPV (human papillomavirus)
- HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus 2)
- LUTS (lower urinary tract symptoms)
- PSA (prostate-specific antigen)
- PVP (photoselective vapourization of the prostate gland)
- RP (radical prostatectomy)
- STD (sexually transmitted disease)
- STI (sexually transmitted infection)
- TRUS (transrectal ultrasound)
- TSE (testicular self-examination)
- TUIP (transurethral incision of the prostate gland)
- TUMT (transurethral microwave thermotherapy)
- TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate gland)
- VD (venereal disease)
Reproductive Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Abbreviations
- AB (Antibiotic)
- CT (Chlamydia)
- GC (Gonorrhea)
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
- HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus)
- PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
- STD (Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
- STI (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Male Reproductive System Anatomy
Label the following male reproductive system anatomy:
Anatomy Labeling Activity (Text Version)
Label the following diagram correctly with words:
- Ureter
- Seminal Vesicle
- Pubic Bone
- Anus
- Prostate Gland
- Urethra
- Urinary Bladder
- Penis
- Testis
- Epididymis
- Vas Deferens
- Rectum
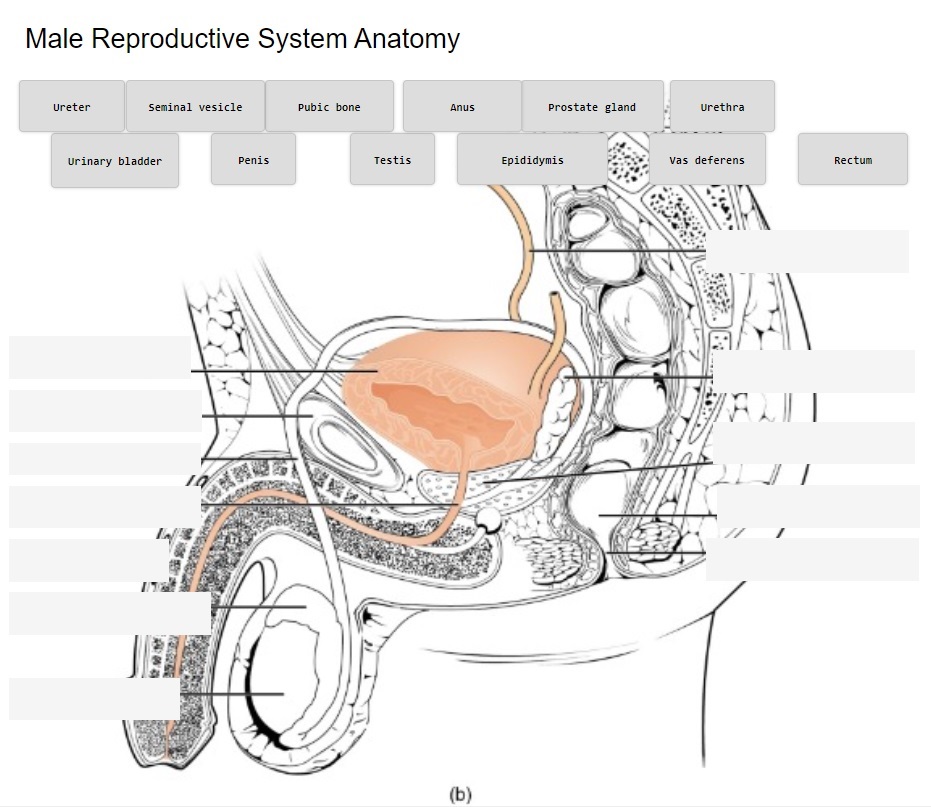
Anatomy Labeling Activity Diagram (Text Version)
Detailed anatomical diagram of the male reproductive system from a lateral viewpoint. The diagram highlights the location of key components from top of the diagram is the _______[Blank 1]. Then from right to left is the _________[Blank 2] followed by the ________[Blank 3] which are a pair of glands that secrete fluid making up a substantial portion of seminal fluid. The _______[Blank 4] is one of the three bones making up the pelvis. The _______[Blank 5] is a carrying vessel that transports sperm from the testes to the urethra. Located at the base of the bladder is ________[Blank 6], this gland secretes nourishing fluid for sperm and becomes a component of semen. The ______[Blank 7] extends from the urinary bladder and carries the semen towards the penis. The _______[Blank 8], the external male sex organ used to inseminate a female during reproduction. The ______[Blank 9] is the straight portion of the lower large intestines, and the _______[Blank 10] expels fecal matter. Located under the penis is the ______[Blank 11] and extending from the testes is a cordlike structure known as the ________[Blank 12].
Check your answers: [1]
Activity source: Male Reproductive System Anatomy by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY 4.0./ Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Male Reproductive System Medical Report (Text Version)
Fill in the consultation report with correct words listed below:
- Urethral
- Prostatitis
- Complete
- by mouth
- circumcised
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM – MEDICAL REPORT
PATIENT NAME: George SMITH
AGE: 57
SEX: Male
HISTORY (Hx): George Smith is a 57-year-old male who was referred to the urologist for a vasectomy.
FAMILY HISTORY: Has three living children. Occasional condom use for birth control.
PAST HISTORY
- Herpes Simples Virus-2 (HSV-2) diagnosis (Dx) in 2002 and treated sexually transmitted infection (STI) in 2014.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) in 2019.
- Current prostate specific antigen (PSA) is 15.6, with a previous result of 4.2.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION/ASSESSMENT: Upon examination, normal male anatomy with _____[Blank 1] penis, normal foreskin and one testicle is descended. Leukorrhea is evident from the tip of the urethral os.
Complains of (c/o) urinary retention, nocturia and dysuria. He has had unprotected sexual intercourse four days ago. Digital rectal exam (DRE) indicated _____[Blank 2] with proctalgia.
DIAGNOSIS (Dx)
- Urethral swab for gonorrhea/chlamydia (GC/CT).
- Serology: PSA, _____[Blank 3] blood count (CBC).
- Urine: Urinalysis, GC/CT, culture, and sensitivity (C&S).
- Sonography for the undescended testicle.
MEDICATIONS (Rx)
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscular immediately (IM STAT)
- Azithromycin 1 g _____[Blank 4] immediately (po STAT)
PRELIMINARY CONCERNS
- Rising PSA.
- _____[Blank 5] discharge.
- Undescended.
FOLLOW UP: Call office in 5 days for test results and follow up appointment in 2 weeks to discuss further booking of vasectomy and potential Bx (biopsy) of prostate.
_______________________
Steve Fosters, MD, Urology
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Male Reproduction – Medical Report by Connie Stevens and Heather Scudder, licensed under CC BY 4.0./Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Male Reproductive System Glossary Reinforcement Activity (Text Version)
- The reproductive organs (testes in men and ovaries in women) that produce gametes and reproductive hormones is called the ______[Blank 1].
- Penis
- Semen
- Gonads
- The transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa during spermatogenesis is called ______[Blank 2].
- Spermatogenesis
- Prepuce
- Ductus deferens
- Glands that secrete a lubricating mucus that cleans and lubricates the urethra prior to and during ejaculation are called _______[Blank 3].
- Testes
- Bulbourethral glands
- Scrotum
- A doughnut-shaped gland at the base of the bladder surrounding the urethra and contributing fluid to semen during ejaculation is called the _____[Blank 4].
- Seminal vesicle
- Epididymis
- Prostate gland
- Opening in the abdominal wall that connects the testes to the abdominal cavity is called the _____[Blank 5].
- Inguinal canal
- Sertoli cells
- Gamete
Check your answers: [3]
Activity source: Male Reproductive System Glossary Reinforcement Activity by Gisele Tuzon, licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheets below:
Worksheet – Male Reproductive System – Chapter 6 [Word]
6. Male Reproductive System – Pronunciation Scenario [Word]
6. Male Reproductive System – Abbreviations [Word]
6. Male Reproductive System – Definitions Using Word Parts [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
↵
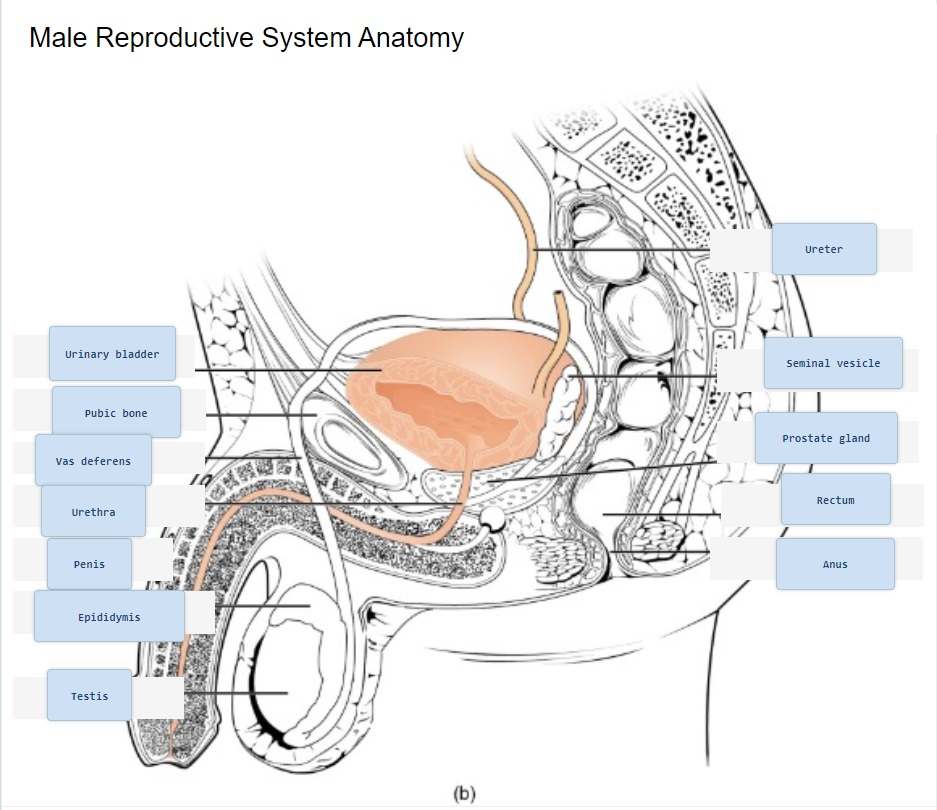
Check your answer: Anatomy Labeling Activity Diagram (Text Version)
Detailed anatomical diagram of the male reproductive system from a lateral viewpoint. The diagram highlights the location of key components from top of the diagram is the ureter. Then from right to left is the urinary bladder followed by the seminal vesicles which are a pair of glands that secrete fluid making up a substantial portion of seminal fluid. The pubic bone is one of the three bones making up the pelvis. The vas deferens is a carrying vessel that transports sperm from the testes to the urethra. Located at the base of the bladder is prostate gland, this gland secretes nourishing fluid for sperm and becomes a component of semen. The urethra extends from the urinary bladder and carries the semen towards the penis. The penis, the external male sex organ used to inseminate a female during reproduction. The rectum is the straight portion of the lower large intestines, and the anus expels fecal matter. Located under the penis is the testes and extending from the testes is a cordlike structure known as the epididymis. - 1. Circumcised, 2. Prostatitis, 3. Complete, 4. By mouth, 5. Urethral ↵
- 1. Gonads, 2. Spermatogenesis, 3. Bulbourethral glands, 4. Prostate gland, 5. Inguinal Canal ↵

