Endocrine System
Learning Objectives
- Identify the anatomy of the endocrine system and describe the main functions of the endocrine system
- Analyze, translate, and define medical terms and common abbreviations of the endocrine system
- Practice the spelling and pronunciation of endocrine system terminology
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the endocrine system and explore common diseases, disorders, diagnostic tests and procedures
Key Word Components
Identify meanings of key word components of the endocrine system:
Prefixes
- eu- (good, normal)
- hypo- (below, under, deficient)
- hyper- (above, excessive)
- oxy- (rapid, sharp, acid)
- para- (around, beside, beyond, abnormal)
- pan- (all, total)
- poly- (many or much)
- syn- (joined, together)
- tetr- (four)
- tri- (three)
Combining Forms
- acr/o (extremities, height)
- aden/o (gland)
- adren/o (adrenal glands)
- adrenal/o (adrenal glands)
- calc/i (calcium)
- cortic/o (cortex, outer layer of a body organ)
- dips/o (thirst)
- glyc/o (sugar)
- endocrin/o (endocrine)
- home/o (sameness)
- kal/i (potassium)
- myx/o (mucus)
- natr/o (sodium)
- parathyroid/o (parathyroid gland)
- phys/o (growing)
- pituitar/o (pituitary gland)
- somat/o (body)
- thyr/o (thyroid gland)
- thyroid/o (thyroid gland)
Suffixes
- -drome (run, running together)
- -ectomy (excision, cut out)
- -emia (in the blood)
- -ia (conditon of, abnormal state, diseased state)
- -ism (state of)
- -itis (inflammation)
- -logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
- -logy (study of)
- -megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
- -oid (resembling)
- -oma (tumor)
- -pathy (disease)
- -plasia (condition of, formation, development, growth)
- -tomy (incision, cut into)
Endocrine System Words
Endocrine System Medical Terms (Text Version)
Practice the following endocrine system words by breaking into word parts and pronouncing.
- endocrinopathy
- endocrin/o/pathy
- disease of the endocrine system
- adrenalectomy
- adrenal/ectomy
- excision of the adrenal glands
- parathyroidectomy
- parathyroid/ectomy
- excision of the parathyroid glands
- adenitis
- aden/itis
- inflammation of the gland
- parathyroidoma
- parathyroid/oma
- tumour of the parathyroid glands
- thyroiditis
- thyroid/itis
- inflammation of the thyroid gland
- thyroidotomy
- thyroid/o/tomy
- incision into the thyroid gland
- hyperthyroidism
- hyper/thyroid/ism
- state of excessive thyroid gland activity
- acromegaly
- acr/o/megaly
- enlargement of the extremeties
- adrenomegaly
- adren/o/megaly
- enlargement of one or both adrenal glands
- glycemia
- glyc/emia
- sugar in the blood
- hypokalemia
- hypo/kal/emia
- deficient potassium in the blood
- hypopituitarism
- hypo/pituitar/ism
- state of deficient pituitary gland activity
- adenomegaly
- aden/o/megaly
- enlarged gland
- hypocalcemia
- hypo/calc/emia
- deficient calcium in the blood
- polydipsia
- poly/dips/ia
- condition of excessive thirst
- hypoglycemia
- hypo/glyc/emia
- deficient sugar in the blood
- hyperkalemia
- hyper/kal/emia
- excessive potassium in the blood
- endocrinopathy
- endocrin/o/pathy
- disease of the endocrine system
- hypercalcemia
- hyper/calc/emia
- excessive calcium in the blood
- panhypopituitarism
- pan/hypo/pituitar/ism *rebel does not follow the rules
- state of total deficient pituitary gland activity
- cortical
- cortic/al
- pertaining to the cortex
- thyroidectomy
- thyroid/ectomy
- excision of the thyroid gland
- syndrome
- syn/drome
- run together (signs and symptoms occur together characterizing of a specific disorder)
- thyroparathyroidectomy
- thyr/o/parathyroid/ectomy
- excision of the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands
- adrenalitis
- adrenal/itis
- inflammation of adrenal glands
- thyroidectomy
- thyroid/ectomy
- excision of the thyroid gland
- endocrinologist
- endocrin/o/logist
- specialist who studies and treats diseases of the endocrine system
- adrenopathy
- adren/o/pathy
- disease of the adrenal gland(s)
- corticoid
- cortic/oid
- resembling the cortex
- euthyroid
- eu/thyr/oid
- resembling a normal thyroid gland
- endocrinology
- endocrin/o/logy
- study of the endocrine system
- hyponatremia
- hypo/natr/emia
- deficient sodium in the blood
- adenectomy
- aden/ectomy
- excision of a gland
- euglycemia
- eu/glyc/emia
- normal (level) of blood sugar in the blood
- adenosis
- aden/osis
- abnormal condition of a gland
- adrenocorticohyperplasia
- adren/o/cortic/o/hyper/plasia
- excessive development of the adrenal cortex
Activity source: Endocrine System Medical Terms by Kimberlee Carter, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Pronouncing and Defining Commonly Abbreviated Endocrine System Terms
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated endocrine system terms:
- ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
- ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
- DI (diabetes insipidus)
- DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis)
- DM (diabetes mellitus)
- FBS (fasting blood sugar)
- FNA (fine needle aspiration)
- FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)
- GH (growth hormone)
- HbA1C (glycosylated hemoglobin)
- LH (luteinizing hormone)
- PRL (prolactin)
- RAIU (radioactive iodine uptake)
- Thyroid Profile (T4, T3, and TSH)
- T4 (thyroxine level)
- T3, (triiodothyronine level)
- TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
Sorting Terms
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories:
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Endocrine System Structures
Label the following endocrine system anatomy:
Endocrine System Anatomy labeling activity (Text Version)
Label the diagram with words listed below:
- Trachea
- Testes (male)
- Pancreas
- Thyroid cartilage of the larynx
- Pineal gland
- Thyroid gland
- Thalamus
- Adrenal glands
- Uterus
- Ovaries (female)
- Parathyroid glands (on posterior side of thyroid)
- Thymus
- Pituitary gland
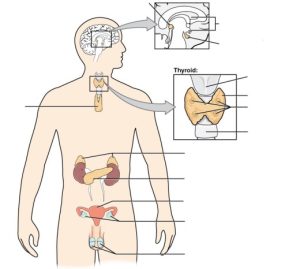
Endocrine System Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows the endocrine glands and cells that are located throughout the body. The endocrine system organs shown from top to bottom include the pea size structure known as the ______[Blank 1] as well as the primary glandular structure of the endocrine system found enclosed within the ______[Blank 2] known as the _______[Blank 3]. The pituitary is located on the anterior side of the thalamus while the pineal gland is located on the posterior side of the thalamus. The ______[Blank 4] is a shield shaped cartilage that forms part of the laryngeal skeleton. This is a butterfly-shaped gland that wraps around the _______[Blank 5] within the neck. Four small, disc-shaped ________[Blank 6] are embedded into the posterior side of the thyroid. The _______[Blank 7] are located on top of the kidneys. The ________[Blank 8] is located at the center of the abdomen. In females, the ______[Blank 9] connects the two ______[Blank 10] a by two long, curved, tubes in the pelvic region. In males, the two _______[Blank 11] are in the scrotum below the penis. One the left side of the diagram and located in the center of the chest is the _______[Blank 12], a glandular structure responsible for the secretion of a hormone called thymosin.
Check your answers [1]
Activity source: Endocrine System Anatomy by Gisele Tuzon, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
Endocrine System – Consultation Report (Text version)
Use the words below to fill in the consultation report:
- menstrual
- palpitations
- conjunctival
- antibodies
- side effects
- medications
- discontinue
- elevated
PATIENT NAME: Jane SMITH
AGE: 26
SEX: Female
DATE OF CONSULTATION: January 15, 2020
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Mary Johnstone, MD, Internal Medicine
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Hyperthyroidism; Graves disease.
PATIENT NAME: Jane SMITH
AGE: 26
SEX: Female
DATE OF CONSULTATION: January 15, 2020
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Mary Johnstone, MD, Internal Medicine
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Hyperthyroidism; Graves disease.
HISTORY: Around 2 months ago she started noticing ________[Blank 1] and peripheral tremor. She was feeling more anxious and edgy. She had a 10-pound weight loss despite eating well. She was having some heat intolerance and diarrhea, and her ________[Blank 2] cycles were irregular. She also noticed her eyes were different. She went to see her family doctor who did lab work and was found to have a TSH suppressed with a free T4 around 40 and free T3 around 10. She then had a 24-hour thyroid uptake and scan that was abnormal with a 24-hour of 70 and a diffuse pan with a homogeneous pattern percentage in keeping with Graves disease. Her TSI was _______[Blank 3] at around 30.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: On physical exam her blood pressure was 140/60, heart rate was 120 with regular rhythm. She had mild proptosis with no infection of the _________[Blank 4] area. Normal eye movement. No pretibial myxedema. She had a diffuse goiter of around 60 g with no murmur and no nodularity. No abnormal lymphadenopathies. There was a positional tremor. Her weight was 90 pounds.
SOCIAL HISTORY: Jane has no significant past medical history. She is finishing her fourth year in biological studies. She is also working on a part-time basis. She is not aware of a family history of thyroid disease. She is currently on no medications. She is a smoker, around 15 cigarettes a day. She rarely drinks alcohol. She denies marijuana use.
SUMMARY: Jane presents with Graves disease. She has hyperthyroidism positive __________[Blank 5] and an increased thyroid uptake and a thyroid scan in keeping with her condition.
We talked about different repair options. We discussed Tapazole versus radioactive iodine. We discussed the pros and cons of each treatment option. She preferred to start on Tapazole. We talked about the potential __________[Blank 6] of these medications including the risk of rash, increasing liver enzymes, and the rare risk of agranulocytosis. I explained to her that if she has a mild or high fever, she should have her CBC checked through the ER, and if there is evidence of a granulocytosis, she cannot resume Tapazole. Usually Tapazole is well tolerated.
PLAN: I have started her on Tapazole 30 mg, and she will repeat lab work in a month and see me at that point. I explained to her that usually 8-18 months of treatment are necessary. Response varies from patient to patient. Frequent levels are necessary to adjust the _________[Blank 7] according to response.
If she has side effects to Tapazole or there is no response, or she is experiencing regular flares, then she should ________[Blank 8] the use of the Tapazole. Other options such as radioactive viral can be considered. I would not favour radioactive iodine in her case as she is a smoker and that she has had a mild ophthalmopathy. Radioactive iodine can worsen ophthalmopathy, therefore it should be avoided in smokers.
We talked about the importance of discontinuing smoking as it can worsen the disease.
________________________________
Mary Johnstone, MD, Internal Medicine
Check your answers: [2]
Activity source: Endocrine System – Consultation Report by Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Medical Terms in Context
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below:
“Endocrine System – Consultation Report” (Text version)
Use the words below to fill in the consultation report:
- diabetes
- metabolic
- palpitations
- neuropathy
- congestive
- rhythm
- pulses
- diuretics
- sugars
- vascular disease
- edema
PATIENT NAME: Margaret JONES
SEX: Female
AGE: 56
DATE OF CONSULTATION: January 15, 2020
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Mary Johnstone, MD, Internal Medicine
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Type 2 diabetes.
HISTORY: I saw Margaret as a follow up today in regards to poorly controlled type 2 ________[Blank 1]. She is reluctant to make any changes in her current medications. She is very afraid of side effects of all her medications. She has not been testing her blood sugar but is planning to start doing it again.
Unfortunately, Mary did not do lab work prior to seeing me. I do not have an updated lab work for at least 2 years. It is very difficult to assess her __________[Blank 2] control without any information.
She continues to be sedentary, but she tells me she has no chest pain or shortness of breath when doing the chores around the house or going up or down the stairs. She denies of orthopnea, ankle swelling, _________[Blank 3], presyncope or syncope.
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY
- Type 2 diabetes diagnosed 2009. Advanced microvascular complications including non-proliferative retinopathy. Nephropathy with significant microalbuminuria. No ___________[Blank 4]. Positive coronary artery disease and peripheral vascular disease. Poor control for several years.
- Coronary artery disease. CABG 4 in 2019. LIMA to LAD SVG to OM and RCA. Grade 2 left ventricular function. Previous episodes of ____________[Blank 5] heart failure preserved ejection fraction with regular admissions due to volume overload.
- Hypertension.
- Hypercholesterolemia.
- Smoker.
- Alcohol, 5-8 beers a week.
- Obesity.
- Peripheral vascular disease, femoral popliteal bypass in 2017.
MEDICATIONS
Aspirin 81 g q.d..
Bisoprolol 5 mg q.d.
Ramipril 20 mg q.d.
Rosuvastatin 20 mg q.d.
Invokana 300 mg q.d.
Tresiba 20 units q.d.
Metformin 1 b.i.d.
Ozempic 1 mg q.wk.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: On physical exam her weight was 100 kg. Blood pressure 160/70, heart rate 88/min. Sa and S2 were heard in 4 areas with regular __________[Blank 6]. There is a 2/6 systolic murmur best heard in aortic area with no radiation. Strong carotid pulses and radial ____________[Blank 7]. JVP was 3 cm above sternal angle. Lungs were clear. There was bilateral leg _________[Blank 8] with venous changes in keeping with venous stasis dermatitis. Abdomen was soft, no evidence of ascites. No focal findings.
SUMMARY: Margaret has a history of poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and today is very difficult to assess her metabolic control as I do not have any information as she is not checking her blood ____________[Blank 9] and has not had lab work for several years. She tells me she is compliant with her plan.
She also has a history of coronary artery disease and currently has no exertional symptoms. There is no evidence of significant volume overload, but she has a history of recurrent admissions due to congestive heart failure preserved ejection fraction. She is currently not on ____________[Blank 10] and I do not think that needs to be restarted. She should continue on the combination of ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, antiplatelets, and high intensity setting therapy.
PLAN: I asked her to do lab work and come back to see me to reassess if her treatment plan is adequate. We talked about the importance of quitting smoking. Smoking is associated with increased risk of further coronary events and progression of her peripheral _____________[Blank 11].
________________________________
Mary Johnstone, MD, Internal Medicine
Check your answers: [3]
Activity source: Endocrine System – Consultation Report by Heather Scudder, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Test Your Knowledge
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below:
Endocrine System Reinforcement Activity (Text version)
- Endocrine glands ______[Blank 1].
- secrete chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream
- secrete hormones that travel through a duct to the target organs
- release neurotransmitters into the junction between two neurons (synaptic cleft)
- include sebaceous glands and sweat glands
- Chemical signaling that affects neighboring cells is called ________[Blank 2].
- autocrine
- paracrine
- endocrine
- neuron
- Graves disease is __________[Blank 3].
- a condition marked by a disorder of the pancreas, resulting in high levels of glucose in the blood.
- a condition marked by low levels of thyroid hormones that results in weight gain, cold sensitivity, and reduced mental activity.
- a condition marked by a disorder of the thyroid gland, resulting in hyperthyroidism.
- a condition marked by high levels of thyroid hormones that results in weight loss, profuse sweating, and increased heart rate.
- In the endocrine system ________[Blank 4].
- the distance travelled by hormones is always short
- hormones are secreted into the extracellular fluid
- the response time is always fast
- the glands release their secretions through ducts
Check your answers: [4]
Activity source: Endocrine System Reinforcement Activity by Tiffany Hunt, from Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Kimberlee Carter and Marie Rutherford, licensed under CC BY- 4.0. /Text version added.
Downloadable Worksheets
View or download & print the PDF or Word format worksheet below:
Design Your Own Worksheet [Word]
17. Endocrine System – Pronunciation Scenario [Word]
17. Endocrine System – Hormones Matching Activity [Word]
Attribution
Except where otherwise noted, this book is adapted from Medical Terminology by Grimm et al. (2022), Nicolet College, CC BY 4.0 International. / A derivative of Building a Medical Terminology Foundation by Carter & Rutherford (2020), and Anatomy and Physiology by Betts, et al., CC BY 4.0, which can be accessed for free at OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology.
-
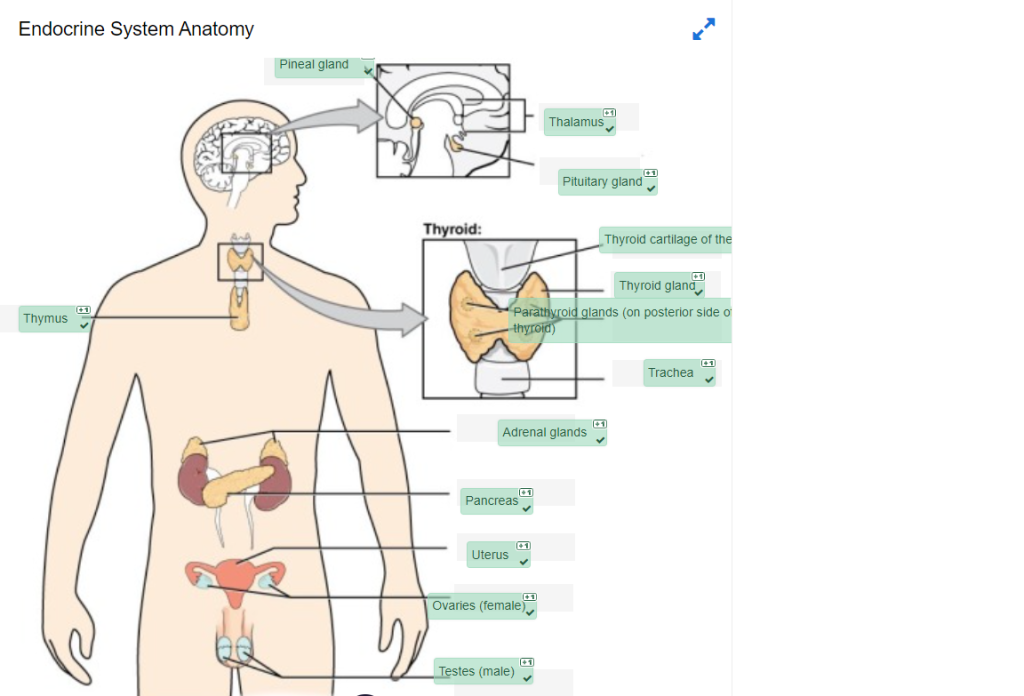
Check your answers: Endocrine System Diagram (Text Version)
This diagram shows the endocrine glands and cells that are located throughout the body. The endocrine system organs shown from top to bottom include the pea size structure known as the pineal gland as well as the primary glandular structure of the endocrine system found enclosed within the thalamus known as the pituitary gland. The pituitary is located on the anterior side of the thalamus while the pineal gland is located on the posterior side of the thalamus. The thyroid cartilage of the larynx is a shield shaped cartilage that forms part of the laryngeal skeleton. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland that wraps around the trachea within the neck. Four small, disc-shaped parathyroid glands are embedded into the posterior side of the thyroid. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The pancreas is located at the center of the abdomen. In females, the uterus connects the two ovaries a by two long, curved, tubes in the pelvic region. In males, the two testes are in the scrotum below the penis. One the left side of the diagram and located in the center of the chest is the thymus, a glandular structure responsible for the secretion of a hormone called thymosin. ↵ - 1.palpitations, 2.menstrual, 3.elevated, 4.conjunctival, 5.antibodies, 6.side effects, 7.medications, 8.discontinue ↵
- 1.diabetes, 2.metabolic, 3.palpitations, 4.neuropathy, 5.congestive, 6.rhythm, 7.pulses, 8.edema, 9.sugars, 10.diuretics, 11.vascular disease ↵
- 1. a) secrete chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream, 2. b) paracrine, 3. c) a condition marked by a disorder of the thyroid gland, resulting in hyperthyroidism, 4. b) hormones are secreted into the extracellular fluid, ↵

